目录
- 一 开发环境
- 二 题目
- 三 具体实现
- 3.1 获取数据
- 3.2 数据展示
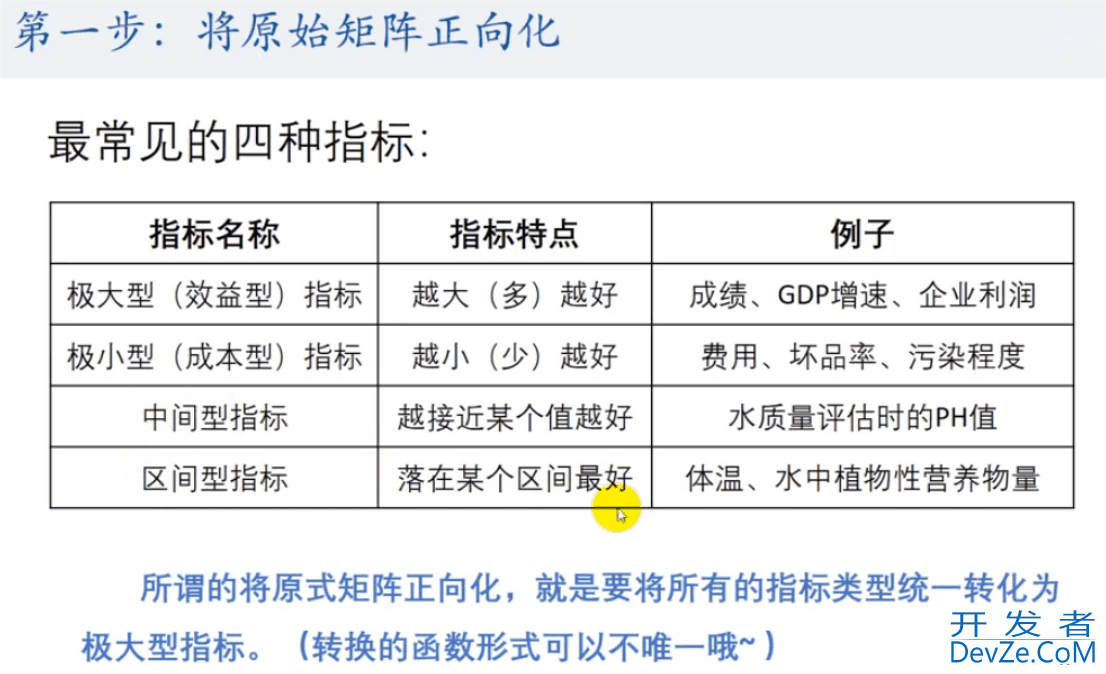
- 3.3 对矩阵进行正向化
- 3.4 对正向化后的数据进行标准化
- 3.5 计算与最大值的距离和最小值的距离,并算出得分
- 四 将最后结果可视化
一 开发环境
集成开发工具:jupyter notebook 6.2.5
集成开发环境:python 3.10.6
第三方库:numpy、matplotlib.pyplot
二 题目
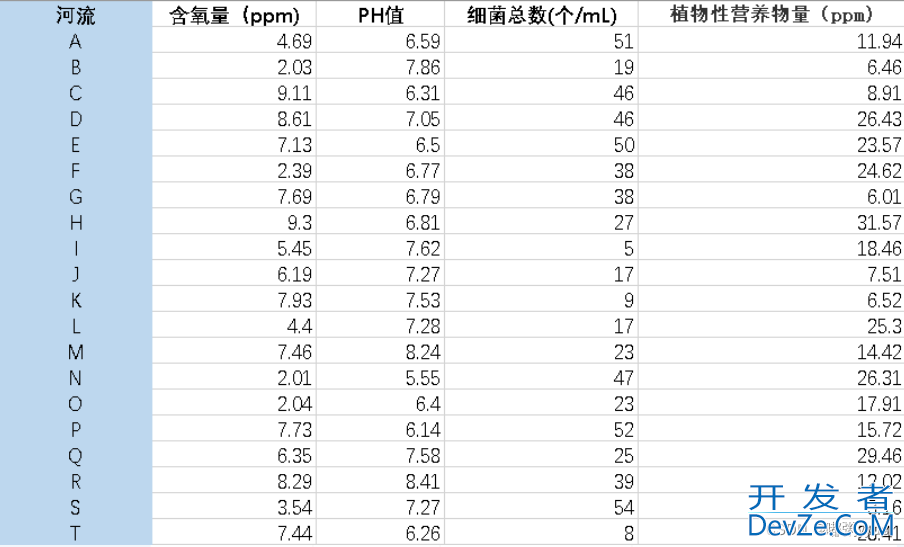
题目:评价下表中20条河流的水质情况。
注:含氧量越高越好(极大型指标),PH值越接近7越好(中间型指标),细菌总数越少越好(极小型指标),植物性营养物量介于10~20之间最佳,超过20或低于10均不好(范围型指标)。
三 具体实现
3.1 获取数据
因为数据量不大,所以本文选择直接创建20x4的数据矩阵
# 含氧量 PH值 细菌总数 植物性营养物量
def get_matrix() -> np.array:
return np.array([
[4.69, 6.59, 51, 11.94],
[2.03, 7.86, 19, 6.46],
[9.11, 6.31, 46, 8.91],
[8.61, 7.05, 46, 26.43],
[7.13, 6.5, 50, 23.57],
[2.39, 6.77, 38, 24.62],
[7.69, 6.79, 38, 6.01],
[9.3, 6.81, 27, 31.57],
[5.45, 7.62, 5, 18.46],
[6.19, 7.27, 17, 7.51],
[7.93, 7.53, 9, 6.52],
[4.4, 7.28, 17, 25.3],
[7.46, 8.24, 23, 14.42],
[2.01, 5.55, 47, 26.31],
[2.04, 6.4, 23, 17.91],
[7.73, 6.14, 52, 15.72],
[6.35, 7.58, 25, 29.46],
[8.29, 8.41, 39, 12.02],
[3.54, 7.27, 54, 3.16],
[7.44, 6.26, 8, 28.41]
])
3.2 数据展示
matrix = get_matrix()
print(f"数据矩阵为:\n{matrix}")
array([[ 4.69, 6.59, 51. , 11.94],
[ 2.03, 7.86, 19. , 6.46],
[ 9.11, 6.31, 46. , 8.91],
[ 8.61, 7.05, 46. , 26.43www.devze.com],
[ 7.13, 6.5 , 50. , 23.57],
[ 2.39, 6.77, 38. , 24.62],
[ 7.69, 6.79, 38. , 6.01],
[ 9.3 , 6.81, 27. , 31.57],
[ 5.45, 7.62, 5. , 18.46],
[ 6.19, 7.27, 17. , 7.51],
[ 7.93, 7.53, 9. , 6.52],
[ 4.4 , 7.28, 17. , 25.3 ],
[ 7.46, 8.24, 23. , 14.42],
[ 2.01, 5.55, 47. , 26.31],
[ 2.04, 6.4 , 23. , 17.91],
[ 7.73, 6.14, 52. , 15.72],
[ 6.35, 7.58, 25. , 29.46],
[ 8.29, 8.41, 39. , 12.02],
[ 3.54, 7.27, 54. , 3.16],
[ 7.44, 6.26, 8. , 28.41]])
3.3 对矩阵进行正向化
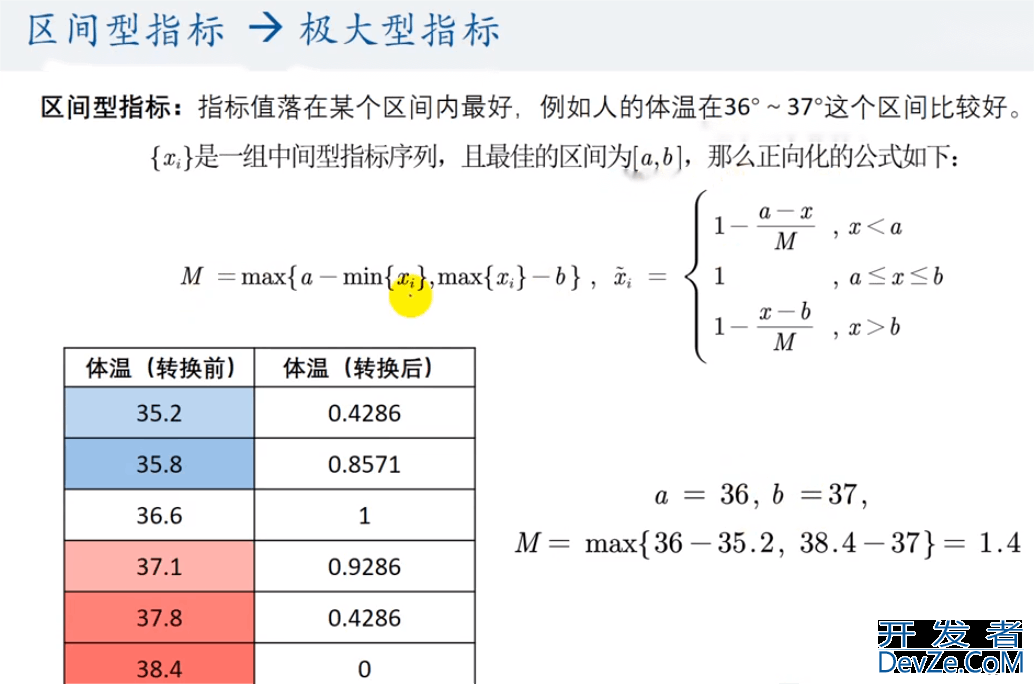
# 定义position接收需要进行正向化处理的列 position = np.array([1, 2, 3]) # 定义处理类型:1 - > 极小型 2 - > 中间型 3 - > 区间型 Type = np.array([2, 1, 3])
# 定义正向化函数
def positivization(x: np.array, pos: int, type: int) -> np.array:
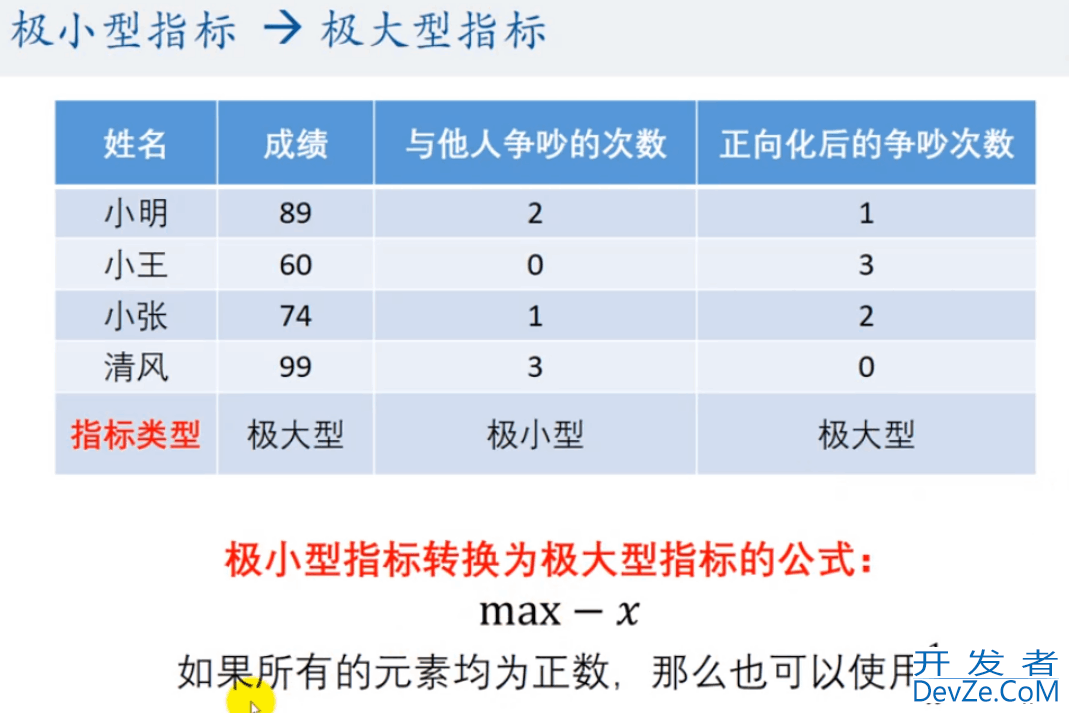
if type == 1:
print(f"第{pos}列是极小型,正在正向化")
x = x.max() - x
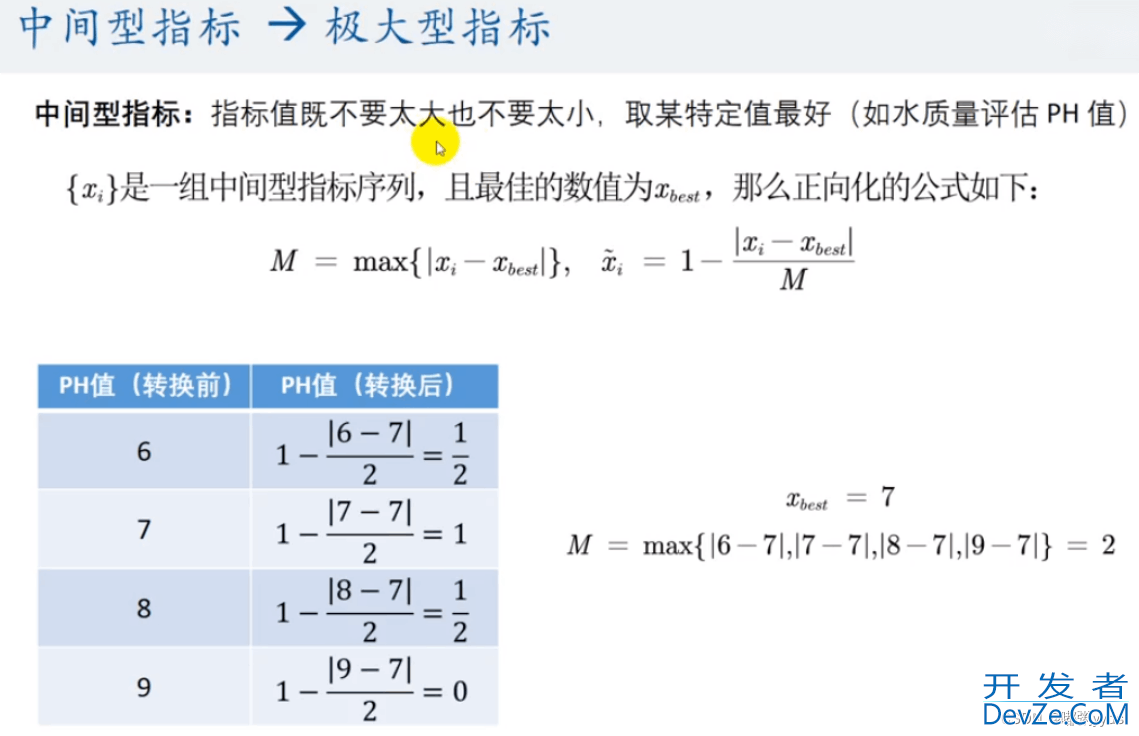
elif type == 2:
print(f"第{pos}列是中间型,正在正向化")
best = 7 # 最佳值
abs_max = np.max(np.abs(x - best))
x = 1 - np.abs(x - best) / abs_max
else:
print(f"第{pos}列是区间型,正在正向化")
left, rig编程ht = 10, 20 # 区间的上界和下界
max_tem = max(left - x.min(), x.max() - right)
x = np.where(x < left, 1 - (left - x) / max_tem, x)
x = np.where(x > right, 1 - (x - right) / max_tem, x)
x = np.where(x > 1, 1, x)
print(f"处理后的数据为:\n{x}")
return x
for i in range(len(position)):
print(f"当前处理的列为:\n{matrix[:, position[i]]}")
matrix[:, position[i]] = positivization(matrix[:, position[i]], position[i], Type[i])
print(f"正向化后的矩阵为:\n{matrix}")
array([[ 4.69 , 0.71724138, 3. , 1. ],
[ 2.03 , 0.40689655, 35. , 0.6940363 ],
[ 9.11 , 0.52413793, 8. , 0.90579084],
[ 8.61 , 0.96551724, 8. , 0.44425238],
[ 7.13 , 0.65517241, 4. , 0.69144339],
[ 2.39 , 0.84137931, 16. , 0.60069144],
[ 7.69 , 0.85517241, 16. , 0.65514261],
[ 9.3 , 0.86896552, 27. , 0. ],
[ 5.45 , 0.57241379, 49. , 1. ],
[ 6.19 , 0.8137931 , 37. , 0.78478825],
[ 7.93 , 0.www.devze.com63448276, 45. , 0.69922213],
[ 4.4 , 0.80689655, 37. , 0.54191876],
[ 7.46 , 0.14482759, 31. , 1. ],
[ 2.01 , 0. , 7. 编程客栈 , 0.45462403],
[ 2.04 , 0.5862069 , 31. , 1. ],
[ 7.73 , 0.40689655, 2. , 1. ],
[ 6.35 , 0.6 , 29. , 0.18236819],
[ 8.29 , 0.02758621, 15. , 1. ],
[ 3.54 , 0.8137931 , 0. , 0.4088159 ],
[ 7.44 , 0.48965517, 46. , 0.27312014]])
3.4 对正向化后的数据进行标准化

Z = matrix / np.sum(matrix * matrix, axis=0) ** 0.5
print(f"标准化后的矩阵为:\n{Z}")
array([[0.16218592, 0.24825528, 0.02454403, 0.30645756],
[0.07019987, 0.14083713, 0.28634707, 0.21269267],
[0.3150349 , 0.18141732, 0.06545076, 0.27758645],
[0.29774429, 0.3341898 , 0.06545076, 0.1361445 ],
[0.24656409, 0.22677165, 0.03272538, 0.21189806],
[0.08264911, 0.29122254, 0.13090152, 0.18408644],
[0.26592957, 0.29599668, 0.13090152, 0.20077341],
[0.32160534, 0.30077082, 0.22089631, 0. ],
[0.18846764, 0.19812681, 0.4008859 , 0.30645756],
[0.21405774, 0.28167426, 0.30270976, 0.24050429],
[0.27422907, 0.21961044, 0.36816052, 0.21428191],
[0.15215736, 0.27928719, 0.30270976, 0.1660751 ],
[0.25797589, 0.05012847, 0.25362169, 0.30645756],
开发者_C培训[0.06950825, 0. , 0.05726941, 0.13932297],
[0.07054569, 0.20290095, 0.25362169, 0.30645756],
[0.26731282, 0.14083713, 0.01636269, 0.30645756],
[0.21959074, 0.20767509, 0.237259 , 0.05588811],
[0.2866783 , 0.00954828, 0.12272017, 0.30645756],
[0.12241751, 0.28167426, 0. , 0.12528473],
[0.25728427, 0.16948197, 0.37634187, 0.08369973]])
3.5 计算与最大值的距离和最小值的距离,并算出得分
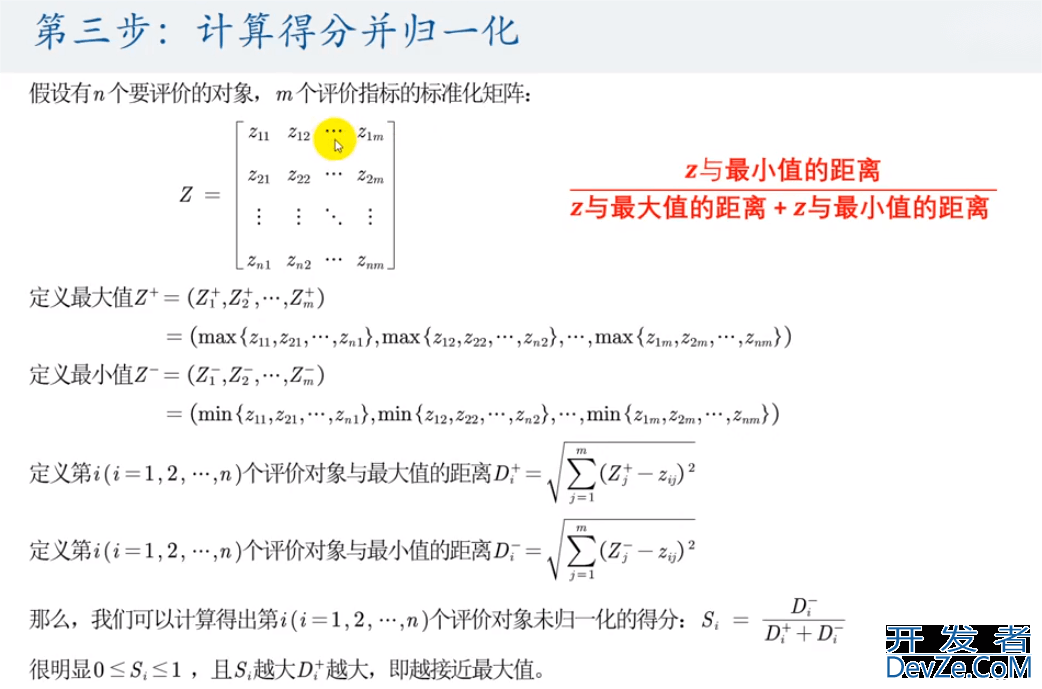
max_score = np.max(Z, axis=0) min_score = np.min(Z, axis=0) max_dist = np.sum((max_score - Z) * (max_score - Z), axis=1) ** 0.5 min_dist = np.sum((min_score - Z) * (min_score - Z), axis=1) ** 0.5 final_score = (min_dist / (max_dist + min_dist)) final_score /= np.sum(final_score) final_score = np.around(final_score, decimals=3) # 保留精度为3
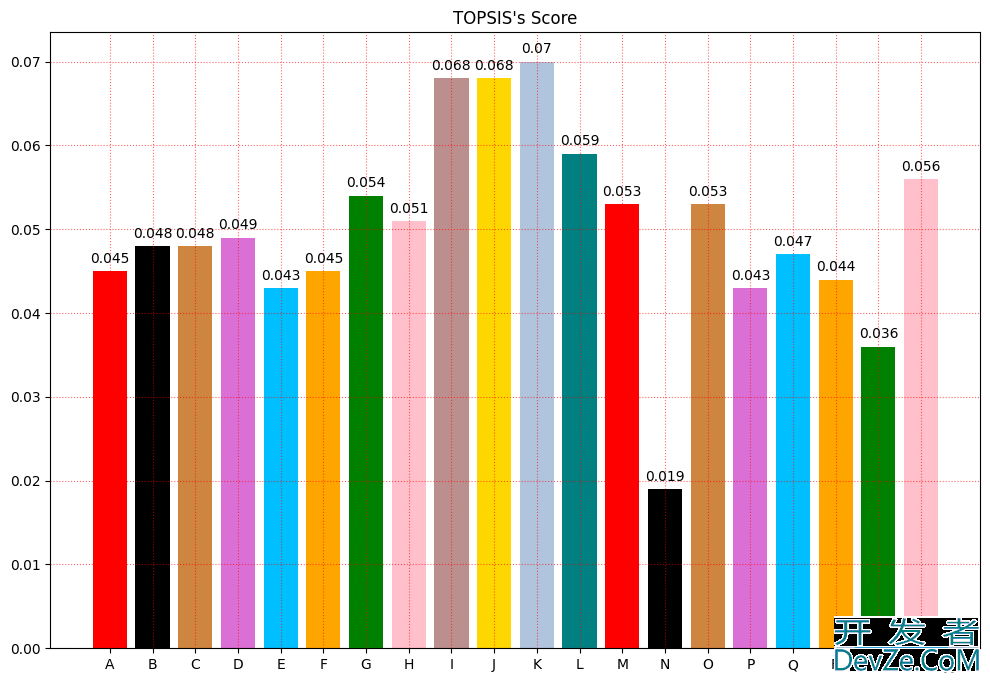
四 将最后结果可视化
x = np.arange(20) # 确定柱状图数量,可以认为是x方向刻度
color=['red','black','peru','orchid','deepskyblue', 'orange', 'green', 'pink', 'rosybrown', 'gold', 'lightsteelblue', 'teal']
x_label = [chr(i) for i in range(65,85)]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.xticks(x, x_label) # javascript绘制x刻度标签
plt.bar(x, final_score,color=color) # 绘制y刻度标签
#设置网格刻度
plt.grid(True,linestyle=':',color='r',alpha=0.6)
plt.title("TOPSIS's Score")
for xx, yy in zip(x, final_score):
plt.text(xx, yy + 0.001, str(yy), ha='center')
plt.show()
以上就是Python实现TOPSIS分析法的示例代码的详细内容,更多关于Python TOPSIS分析法的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!



 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论