目录
- 总述
- 一、节点类
- 二、迭代器类
- 成员变量
- 构造函数
- *重载
- ->重载
- “++”
- “==“和”!=”
- 三、反向迭代器类
- 成员变量
- *重载
- ->重载
- “++”
- “- -”
- " == " 和"!="
- 四、list类
- 成员变量
- 构造相关
- 迭代器
- 反向迭代器
- 容量操作
- 元素访问
- 打印链表
- 元素修改
- 头插与头删
- 附:完整list类,含测试用例
- 总结
总述
list模拟实现主要包括四个类:节点类、迭代器类、反向迭代器类、list类。
list底层结构:
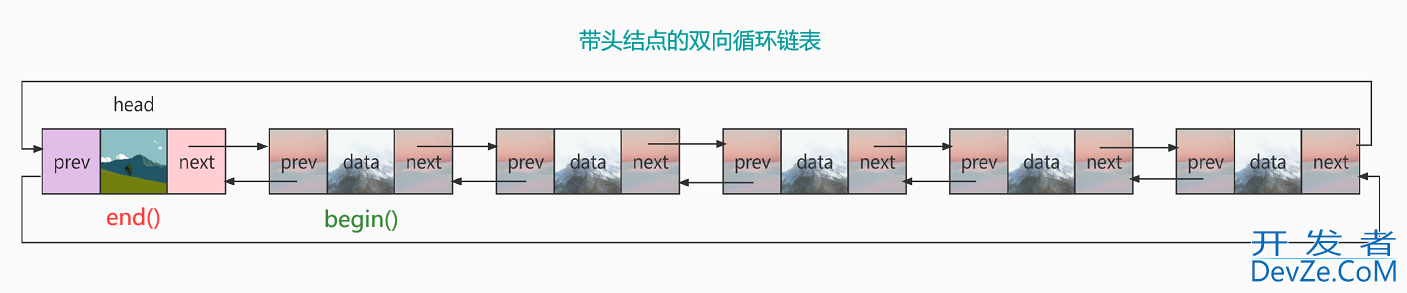
因为list的底层空间不连续,所以迭代器不能使用原生态的指针,将节点类型的指针封装成类,重载解引用及自增等常用操作。list可以保存多种数据类型,所以这些类都写成类模板
一、节点类
list底层是带头结点的双向循环链表,先实现节点类,给成类模板的形式,便于插入不同类型的数据。
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* prev;
ListNode<T>* next;
T data;//要在链表中保存的数据类型
ListNode(const T& value = T())
:prev(nullptr)
, next(nullptr)
, data(value)
{ }
};
定义新节点的方法:
ListNode<变量类型>*变量名=new ListNode(value);
二、迭代器类
迭代器类模板有三个参数
- T:迭代器指向的元素类型
- Ref:返回的引用类型
- Ptr:返回的指针类型
Ref和Ptr一般不写成T&和T*。

成员变量
迭代器类的成员变量就是节点类型的指针
Node* _pNode;//成员变量,节点类型指针
构造函数
编译器默认的构造函数是无参的,构造函数需要给出
ListIterator(Node* pNode = nullptr)
:_pNode(pNode)
{}
*重载
返回节点中保存的数据
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->data;
}
->重载
返回节点中保存的数据的地址
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pNode->data;
}
->的重载只对内置类型有意义:
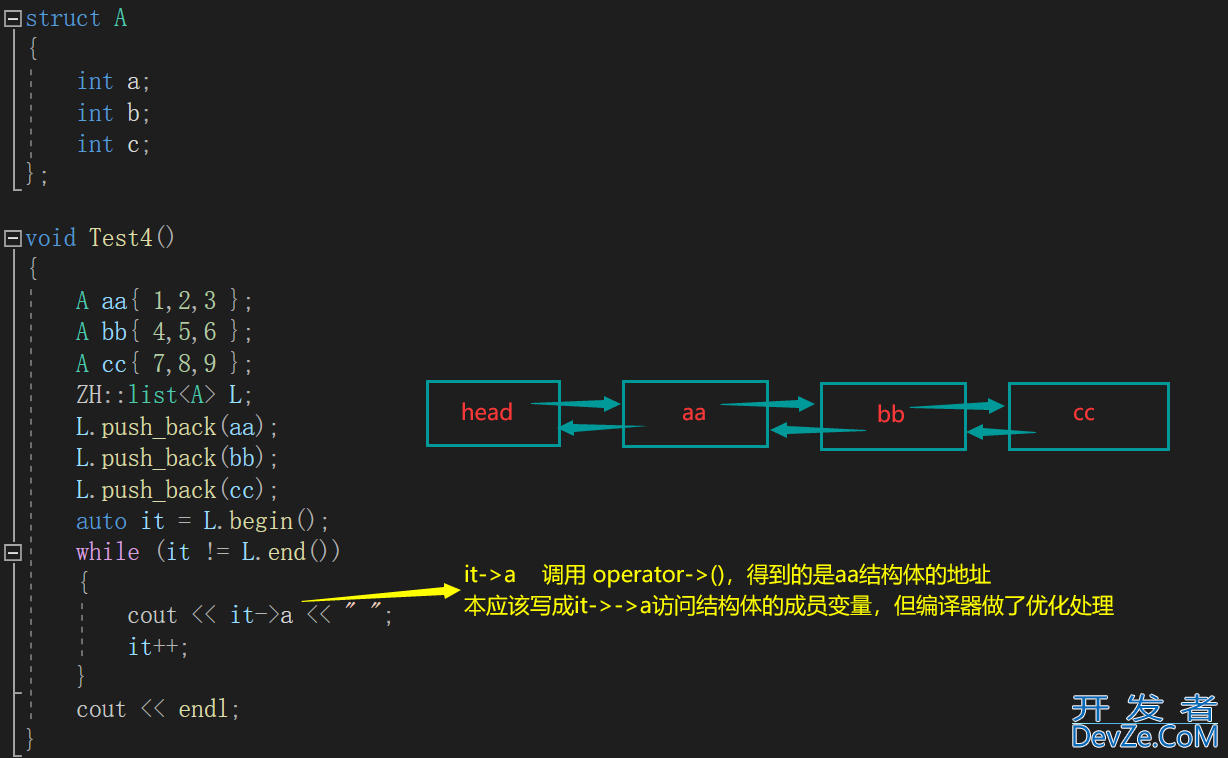
“++”
前置++
返回值是迭代器自身类型的引用,前面已经将ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr>重命名位Self,表示迭代器自身的类型。
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->next;
return *this;
}
后置++
定义临时变量,返回自增前的值
Self operator++(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
_pNode = _pNode->next;
return temp;
}
“–”
与++原理相同
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->prev;
return (*this);
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
_pNode = _pNode->prev;
return temp;
}
“==“和”!=”
比较两个迭代器中封装的指针
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _pNode != it._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _pNode == it._pNode;
}
三、反向迭代器类
反向迭代器可以对迭代器类进行复用
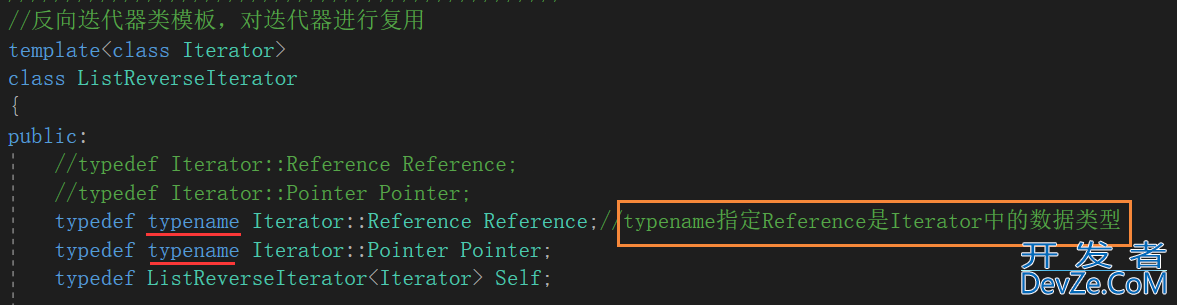
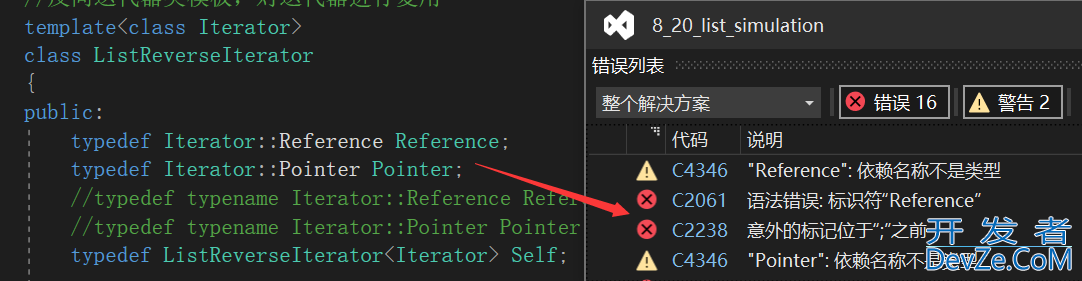
因为类外访问静态成员变量时也会使用类名::变量名的方式,所以对迭代器类中的Reference和Pointer进行重命名时要加上typename,明确告诉编译器要重命名的是一个数据类型。否则编译器会报错:
成员变量
反向迭代器对迭代器类进行复用
private: Iterator _it;//正向迭代器
*重载
反向迭代器的解引用要做特殊处理,返回的是对迭代器–的值
Reference operator*()
{
//*做特殊处理,先--,再解引用返回
auto temp = _it;
--temp;
return *temp;
}
->重载
复用*的重载,返回value的地址
Pointer operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
“++”
反向迭代器的++即为正向迭代器的–
Self operator++()
{
--_it;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
--_it;
return *this;
}
“- -”
反向迭代器的–用正向迭代器的++替代
Self operator--()
{
++_it;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
++_it;
return temp;
}
" == " 和"!="
比较反向迭代器类中保存的正向迭代器,复用正向迭代器中的比较方法
bool operator==(const Self& rit)
{
return _it == rit;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& rit)
{
return _it == rit._it;
}
四、list类

成员变量
list的成员变量只有一个head指针,指向链表的第一个节点
private: Node* head;
构造相关
空对象
list()
{
CreatHead();
}
创造头节点的方法:
//提供一个创造头结点的方法
void CreatHead()
{
//调用节点类的构造方法
head = new Node();
head->next = head;
head->prev = head;
}
0000000
new申请空间,令head指向这段空间,head的next和prev都指向自己。
n个T类型元素
调用push_back方法,创造头节点后,不断进行尾插直到元素个数等于n
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
CreatHead();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_b编程客栈ack(value);
}
}
拷贝构造
复用push_back
list(const list<T>& l)
{
CreatHead();
auto it = l.cbegin();
while (it != l.cend())
{
push_back(*it);
it++;
}
}
迭代器构造
将迭代器构造方法写成函数模板,可以传入不同类型的迭代器来构造list对象
template<class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
CreatHead();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
赋值运算符重载
与拷贝构造写法相同
list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& l)
{
if (this != &l)
{
clear();//先清空当前对象中的节点
auto it = l.cbegin();
while (it != l.cend())
{
push_back(*it);
it++;
}
}
return *this;
}
析构
清空当前对象,释放头节点空间,将头节点置空
~list()
{
clear();
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
迭代器
正向迭代器
begin
此处的iterator是对ListIterator<T, T&, T*>的重命名,这里会返回一个ListIterator<T, T&, T*>类对象
iterator begin()
{
//iterator it(head->next);
//return it;
//head->next是传递给迭代器类对象构造函数的参数,调用iterator的构造函数
return iterator(head->next);//构造匿名对象返回
}
end
iterator end()
{
return iterator(head);
}
const类型迭代器
iterator和const_iterator 是两个不同的类:
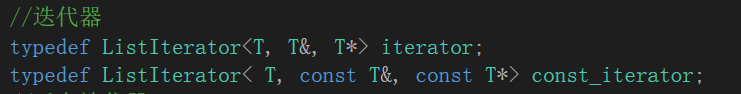
两者使用的是相同的类模板,但是传递的参数不同,最终实例化的也是不同的类。
cbegin&cend
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return const_iterator(head->next);
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(head);
}
反向迭代器
rbegin&rend
返回正向迭代器的end和begin
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(end());
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(begin());
}
crbegin&crend
复用正向迭代器的cend和cbegin
const_reverse_iteraotr crbegin()const
{
return const_reverse_iteraotr(cend());
}
const_reverse_iteraotr crend()const
{
return const_reverse_iteraotr(cbegin());
}
容量操作
size
遍历链表,统计节点个数
size_t size()
{
auto it = cbegin();
size_t count = 0;
while (it != cend())
{
++count;
++it;
}
return count;
}
empty
如果head->next是head本身则表明链表为空
bool empty()
{
return head->next == head;
}
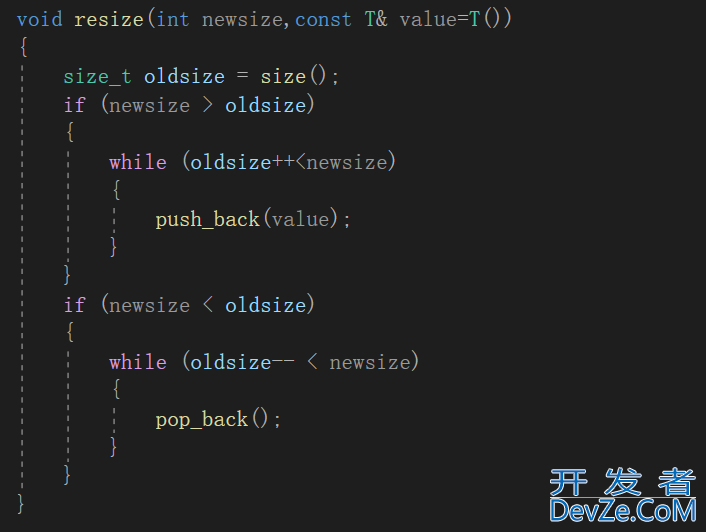
resize
改变节点个数,若新的节点个数大于旧的,则调用push_back填充元素;若新的节点个数小于原来的调用pop_back尾删
元素访问
front
复用迭代器解引用的方法,返回begin()位置元素
T& front()
{
return *begin();
}
const T& front()const
{
return *cbegin();
}
back
back表示最后一个元素,但是end()指向的是最后一个元素的下一个位置,需要定义临时变量,不能直接对end()进行- -。
T& back()
{
auto it = end();
//re开发者_JS教程turn --end()//错误写法
it--;
return *it;
}
const T& back()const
{
auto it = end();
it--;
return *it;
}
打印链表
定义一个打印链表的函数模板,检验方法。通过迭代器遍历链表,打印每一个节点的数据。
template<class T>
void PrintList(const list<T>& l)
{
auto it = l.cbegin();
while (it != l.cend())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
元素修改
尾插与尾删
push_back
复用insert方法在end位置插入
void push_back(const T& value)
{
insert(end(), value);
}
pop_back
先判断链表是否为空,复用erase方法在end的前一个位置进行插入
void pop_back()
{
if (empty())
{
return;
}
auto it = end();
it--;
erase(it);
}
头插与头删
复用insert与erase方法,在begin()位置进行插入或删除
void push_front(const T& value = T())
{
insert(begin(), value);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
⭐insert
任意位置的插入:申请新节点,连接新节点与链表,断开旧的连接。
这里传入的参数是一个迭代器类对象,不能直接进行操作,要对对象中封装的_pNode指针进行操作。
返回值是新插入的节点的迭代器,所以要用申请的新节点的指针newnode构造一个迭代器类对象返回,不能直接返回newnode
iterator insert(iterator Insertpos, const T& value)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(value);
Node* pos = Insertpos._pNode;//_pNode是节点类型的指针
newnode->next = pos;
newnode->prev = pos->prev;
newnode->prev->next = newnode;
pos->prev = newnode;
//return newnode;
//⭐迭代器是封装的Node*指针,此时不能再返回newnode
return iterator(newnode);//构造匿名对象返回
}
⭐erase
任意位置的删除:分别改变前后两个节点的next和prev指针的指向即可
iterator erase(iterator Erasepos)
{
Node* pos = Erasepos._pNode;
Node* ret = pos->next;
pos->prev->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
delete pos;
return iterator(ret);
}
区间删除:复用单个节点删除的方法,遍历要删除的区间。
要用接收erase的返回值,防止迭代器失效
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last)
{
auto it = first;
while (it != last)
{
//it=erase(it);
//后置++会构造临时对象返回,不会导致迭代器失效
erase(it++);
}
return it;
}
clear&swap
- clear复用erase区间删除的方法,从begin删除到end位置;
- swap方法调用标准库中的swap,交换两个链表的头节点。
void clear()
{
erase(begin(), end());
}
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(head, l.head);
}
附:完整list类,含测试用例
#include<IOStream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
namespace ZH
{
/
//节点类模板,
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* prev;
ListNode<T>* next;
T data;
ListNode(const T& value = T())
:prev(nullptr)
, next(nullptr)
, data(value)
{ }
};
/
//迭代器类模板
//list的迭代器不能使用原生态的指针,要进行封装
//T:迭代器指向的元素类型
//Ref:给operator*使用,返回引用类型,不要写成T&
//Ptr:返回值使用,不要写成T*
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
class ListIterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;//化简节点类的名字
typedef Ref Reference;//在反向迭代器类中使用
typedef Ptr Pointer;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//简化迭代器类的名字
//构造函数
ListIterator(Node* pNode=nullptr)
:_pNode(pNode)
{}
//重载部分需要使用的运算符即可:*、->、++、--、==
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->data;
}
//T为自定义类型时有意义,
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pNode->data;
}
//前置++,返回值是迭代器自身类型的引用
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->next;
return *this;
}
//后置
Self operator++(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
_pNode = _pNode->next;
return temp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->prev;
return (*this);
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
_pNode = _pNode ->prev;
return temp;
}
//迭代器能进行比较
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _pNode != it._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _pNode == it._pNode;
}
Node* _pNode;//成员变量,节点类型指针
};
//反向迭代器类模板,对迭代器进行复用
template<class Iterator>
class ListReverseIterator
{
public:
//typedef Iterator::Reference Reference;
//typedef Iterator::Pointer Pointer;
typedef typename Iterator::Reference Reference;//typename指定Reference是Iterator中的数据类型
typedef typename Iterator::Pointer Pointer;
typedef ListReverseIterator<Iterator> Self;
ListReverseIterator(Iterator it)
: _it(it)
{ }
Reference operator*()
{
//*做特殊处理,先--,再解引用返回
auto temp = _it;
--temp;
return *temp;
}
Pointer operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
Self operator++()
{
--_it;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
--_it;
return *this;
}
Self operator--()
{
++_it;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
++_it;
return temp;
}
bool operator==(const Self& rit)
{
return _it == rit;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& rit)
{
return _it == rit._it;
}
private:
Iterator _it;//正向迭代器
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
//typedef Node* iterator;//不能使用Node*作迭代器
//迭代器
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator< T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef ListReverseIterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
typedef ListReverseIterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iteraotr;
public:
///
//构造
list()
{
CreatHead();
}
list(int n, const T& value=T())
{
CreatHead();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{
CreatHead();
auto it = l.cbegin();
while (it != l.cend())
{
push_back(*it);
it++;
}
}
//迭代器区间构造
template<class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
CreatHead();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
//赋值运算符重载
list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& l)
{
if (this != &l)
{
clear();//先清空当前对象中的节点
auto it = l.cbegin();
while (it != l.cend())
{
push_back(*it);
it++;
}
}
return *this;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
public:
//迭代器
iterator begin()
{
//iterator it(head->next);
//return it;
//iterator是对ListIterator<T, T&, T*>的重命名
//这里会返回一个ListIterator<T, T&, T*>类对象
//head->next是传递给迭代器类对象构造函数的参数,调用iterator的构造函数
return iterator(head->next);//构造匿名对象返回
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(head);
}
//const类型迭代器
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return const_iterator(head->next);
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(head);
}
//反向迭代器
//反向迭代器的成员变量是一个迭代器类对象
//end()即为传递给反向迭代器类构造函数的参数
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(end());
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(begin());
}
//反向const类型迭代器
const_reverse_iteraotr crbegin()const
{
return const_reverse_iteraotr(cend());
}
const_reverse_iteraotr crend()const
{
return const_reverse_iteraotr(cbegin());
}
/
//容量
size_t size()
{
auto it = cbegin();
size_t count = 0;
while (it != cend())
{
++count;
++it;
}
return count;
}
bool empty()
{
return head->next == head;
}
void resize(int newsize,const T& value=T())
{
size_t oldsize = size();
if (newsize > oldsize)
{
while (oldsize++<newsize)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
if (newsize < oldsize)
{
while (oldsize-- < newsize)
{
pop_back();
}
}
}
///
//元素访问
T& front()
{
return *begin();
}
const T& front()const
{
return *cbegin();
}
T& back()
{
auto it = end();
it--;
return *it;
}
const T& back()const
{
auto it = end();
it--;
return *it;
}
/
//元素修改
void push_back(const T& value)
{
insert(end(), value);
}
void pop_back()
{
if (empty())
{
retphpurn;
}
auto it = end();
it--;
erase(it);
}
void push_front(const T& value = T())
{
//Node* pos = head->next;
/*Node* newnode = new Node(value);
newnode->next = head->next;
newnode->prev = head;
head->next->prev = newnode;
head->next = newnode;*/
//复用insert
insert(begin(), value);
}
void pop_front()
{
python erase(begin());
}
//⭐insert
// iterator是ListIterator<T, T&, T*>
iterator insert(iterator Insertpos, const T& value)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(value);
Node* pos = Insertpos._pNode;//_pNode是节点类型的指针
newnode->next = pos;
newnode->prev = pos->prev;
newnode->prev->next = newnode;
pos->prev = newnode;
//return newnode;
//⭐迭代器是封装的Node*指针,此时不能再返回newnode
return iterator(pythonnewnode);//构造匿名对象返回
}
//⭐erase
iterator erase(iterator Erasepos)
{
Node* pos = Erasepos._pNode;
Node* ret = pos->next;
pos->prev->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
delete pos;
return iterator(ret);
}
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last)
{
auto it = first;
while (it != last)
{
//it=erase(it);
erase(it++);
}
return it;
}
void clear()
{
erase(begin(), end());
}
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(head, l.head);
}
private:
//提供一个创造头结点的方法
void CreatHead()
{
//调用节点类的构造方法
head = new Node();
head->next = head;
head->prev = head;
}
private:
Node* head;
};
template<class T>
void PrintList(const list<T>& l)
{
auto it = l.cbegin();
while (it != l.cend())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void Test1()
{
ZH::list<int> l1;
ZH::list<int> l2(3, 1);
PrintList(l2);
ZH::list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end());
PrintList(l3);
vector<int> v{ 0,1,2,3,4 };
ZH::list<int> l4(v.begin(), v.end());
PrintList(l4);
}
void Test2()
{
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4 };
ZH::list<int> L1(v.begin(), v.end());
L1.push_back(5);
L1.push_back(6);
L1.push_front(0);
PrintList(L1);
L1.pop_back();
L1.pop_front();
PrintList(L1);
L1.erase(--L1.end());
PrintList(L1);
}
void Test3()
{
ZH::list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(2);
L1.push_back(3);
javascriptL1.push_front(0);
PrintList(L1);
L1.resize(6, 5);
PrintList(L1);
}
struct A
{
int a;
int b;
int c;
};
void Test4()
{
A aa{ 1,2,3 };
A bb{ 4,5,6 };
A cc{ 7,8,9 };
ZH::list<A> L;
L.push_back(aa);
L.push_back(bb);
L.push_back(cc);
auto it = L.begin();
while (it != L.end())
{
//⭐it->得到的是节点的地址
//本应是it->->a,编译器做了特殊处理
cout << it->a << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Test5()
{
ZH::list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(0);
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(2);
L1.push_back(3);
PrintList(L1);
cout << L1.back() << endl;
cout << L1.front() << endl;
cout << L1.size() << endl;
L1.clear();
cout << L1.size() << endl;
}
void Test6()
{
ZH::list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(0);
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(2);
L1.push_back(3);
PrintList(L1);
//区间删除
/*L1.erase(L1.begin(), L1.end());
PrintList(L1);*/
ZH::list<int> L2;
L2.push_back(1);
L2.push_back(2);
L2.push_back(3);
L2.push_back(4);
L2.push_back(5);
PrintList(L2);
L1.swap(L2);
PrintList(L1);
PrintList(L2);
}
int main()
{
Test6();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论