目录
- 引言
- 1. 架构设计
- 2. 启动流程源码分析
- 2.1 主方法:NamesrvStartup#main
- 2.2 创建controller:NamesrvStartup#createNamesrvController
- 2.2.1 处理配置
- 2.2.2 创建NamesrvController实例
- 2.3 启动nameServer:NamesrvStartup#start
- 2.3.2 启动:NamesrvController#start
- 3. 总结
引言
本文我们来分析NameServer相关代码,在正式分析源码前,我们先来回忆下NameServer的功能:
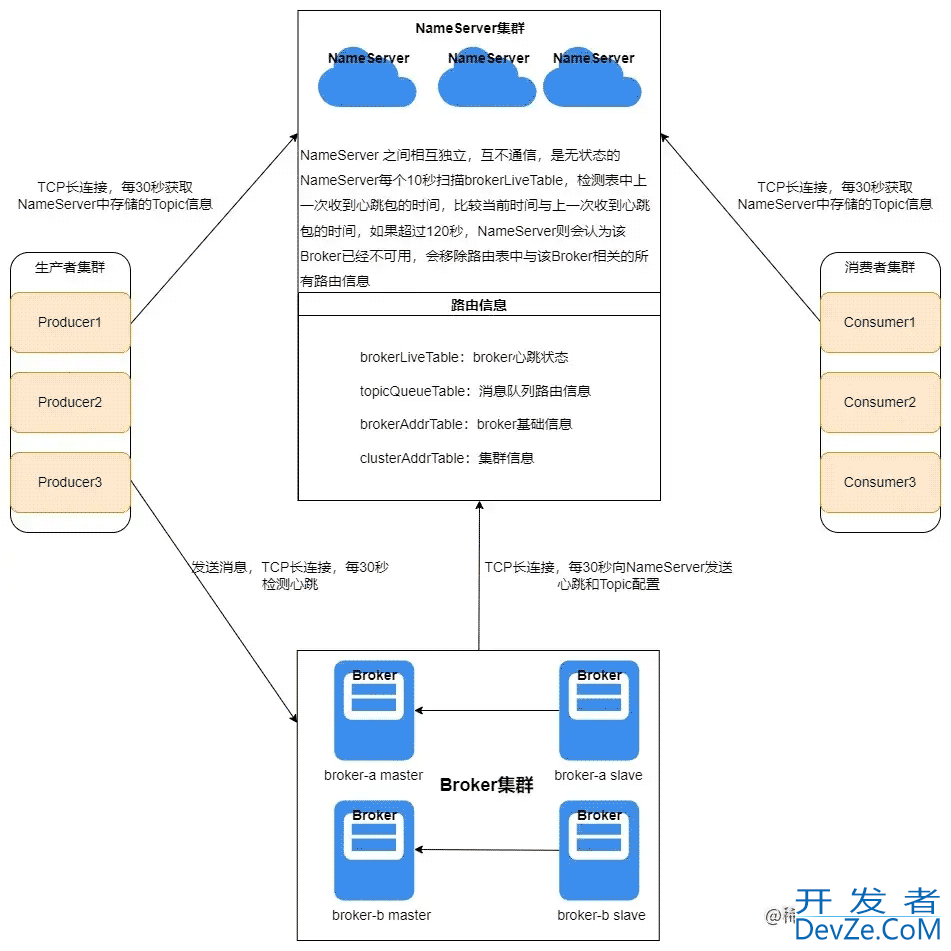
NameServer是一个非常简单的Topic路由注册中心,其角色类似Dubbo中的zookeeper,支持Broker的动态注册与发现。主要包括两个功能:
Broker管理,NameServer接受Broker集群的注册信息并且保存下来作为路由信息的基本数据。然后提供心跳检测机制,检查Broker是否还存活;- 路由信息管理,每个
NameServer将保存关于Broker集群的整个路由信息和用于客户端查询的队列信息。然后Producer和Conumser通过NameServer就可以知道整个Broker集群的路由信息,从而进行消息的投递和消费。
1. 架构设计
Broker启动的时候会向所有的NameServer注册,生产者在发送消息时会先从NameServer中获取Broker消息服务器的地址列表,根据负载均衡算法选取一台Broker消息服务器发送消息。NameServer与每台Broker之间保持着长连接,并且每隔10秒会检查Broker是否存活,如果检测到Broker超过120秒未发送心跳,则从路由注册表中将该Broker移除。
但是路由的变化不会马上通知消息生产者,这是为了降低NameServe的复杂性,所以在RocketMQ中需要消息的发送端提供容错机制来保证消息发送的高可用性,这在后续关于RocketMQ消息发送的章节会介绍。
2. 启动流程源码分析
2.1 主方法:NamesrvStartup#main
NameServer位于RocketMq项目的namesrv模块下,主类是org.apache.rocketmq.namesrv.NamesrvStartup,代码如下:
public class NamesrvStartup {
...
public static void main(String[] args) {
main0(args);
}
public static NamesrvController main0(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建 controller
NamesrvController controller = createNamesrvController(args);
// 启动
start(controller);
String tip = "The Name Server boot success. serializeType="
+ RemotingCommand.getSerializeTypeConfigInThisServer();
log.info(tip);
System.out.printf("%s%n", tip);
return controller;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(-1);
}
return null;
}
...
}
可以看到,main()方法里的代码还是相当简单的,主要包含了两个方法:
createNamesrvController(...):创建controllerstart(...):启动nameServer
接下来我们就来分析这两个方法了。
2.2 创建controller:NamesrvStartup#createNamesrvController
public static NamesrvController createNamesrvController(String[] args)
throws IOException, JoranException {
// 省略解析命令行代码
...
// nameServer的相关配置
final NamesrvConfig namesrvConfig = new NamesrvConfig();
// nettyServer的相关配置
final NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig = new NettyServerConfig();
// 端口写死了。。。
nettyServerConfig.setListenPort(9876);
if (commandLine.hasOption('c')) {
// 处理配置文件
String file = commandLine.getOptionValue('c');
if (file != null) {
// 读取配置文件,并将其加载到 properties 中
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
// 将 properties 里的属性赋值到 namesrvConfig 与 nettyServerConfig
MixAll.properties2Object(properties, namesrvConfig);
MixAll.properties2Object(properties, nettyServerConfig);
namesrvConfig.setConfigStorePath(file);
System.out.printf("load config properties file OK, %s%n", file);
in.close();
}
}
// 处理 -p 参数,该参数用于打印nameServer、nettyServer配置,省略
...
// 将 commandLine 的所有配置设置到 namesrvConfig 中
MixAll.properties2Object(ServerUtil.commandLine2Properties(commandLine), namesrvConfig);
// 检查环境变量:ROCKETMQ_HOME
if (null == namesrvConfig.getRocketmqHome()) {
// 如果不设置 ROCKETMQ_HOME,就会在这里报错
System.out.printf("Please set the %s variable in your environment to match
the location of the RocketMQ installation%n", MixAll.ROCKETMQ_HOME_ENV);
System.exit(-2);
}
// 省略日志配置
...
// 创建一个controller
final NamesrvController controller =
new NamesrvController(namesrvConfig, nettyServerConfig);
// 将当前 properties 合并到项目的配置中,并且当前 properties 会覆盖项目中的配置
controller.getConfiguration().registerConfig(properties);
return controller;
}
这个方法有点长,不过所做的事就两件:
- 处理配置
- 创建
NamesrvController实例
2.2.1 处理配置
咱们先简单地看下配置的处理。在我们启动项目中,可以使用-c /xxx/xxx.conf指定配置文件的位置,然后在createNamesrvController(...)方法中,通过如下代码
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); properties = new Properties(); properties.load(in);
将配置文件的内容加载到properties对象中,然后调用MixAll.properties2Object(properties, namesrvConfig)方法将properties的属性赋值给namesrvConfig,``MixAll.properties2Object(...)`代码如下:
public static void properties2Object(final Properties p, final Object object) {
Method[] methods = object.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
String mn = method.getName();
if (mn.startsWith("set")) {
try {
String tmp = mn.substring(4);
String first = mn.substring(3, 4);
// 首字母小写
String key = first.toLowerCase() + tmp;
// 从Properties中获取对应的值
String property = p.getProperty(key);
if (property != null) {
// 获取值,并进行相应的类型转换
Class<?>[] pt = method.getParameterTypes();
if (pt != null && pt.length > 0) {
String cn = pt[0].getSimpleName();
Object arg = null;
// 转换成int
if (cn.equals("int") || cn.equals("Integer")) {
arg = Integer.parseInt(property);
// 其他类型如long,double,float,boolean都是这样转换的,这里就省略了
} else if (...) {
...
} else {
continue;
}
// 反射调用
method.invoke(object, arg);
}
}
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
}
}
}
}
这个方法非常简单:
- 先获取到
object中的所有setXxx(...)方法 - 得编程客栈到
setXxx(...)中的Xxx - 首字母小写得到
xxx - 从
properties获取xxx属性对应的值,并根据setXxx(...)方法的参数类型进行转换 - 反射调用
setXxx(...)方法进行赋值
这里之后,namesrvConfig与nettyServerConfig就赋值成功了。
2.2.2 创建NamesrvController实例
我们再来看看createNamesrvController(...)方法的第二个重要功能:创建NamesrvController实例.
创建NamesrvController实例的代码如下:
final NamesrvController controller = new NamesrvController(namesrvConfig, nettyServerConfig);
我们直接进入NamesrvController的构造方法:
/**
* 构造方法,一系列的赋值操作
*/
public NamesrvController(NamesrvConfig namesrvConfig, NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig) {
this.namesrvConfig = namesrvConfig;
this.nettyServerConfig = nettyServerConfig;
this.kvConfigManager = new KVConfigManager(this);
this.routeInfoManager = new RouteInfoManager();
this.brokerHousekeepingService = new BrokerHousekeepingService(this);
this.configuration = new Configuration(log, this.namesrvConfig, this.nettyServerConfig);
thphpis.configuration.setStorePathFromConfig(this.namesrvConfig, "configStorePath");
}
构造方法里只是一系列的赋值操作,没做什么实质性的工作,就先不管了。
2.3 启动nameServer:NamesrvStartup#start
让我们回到一开始的NamesrvStartup#main0方法,
public static NamesrvController main0(String[] args) {
try {
NamesrvController controller = createNamesrvController(args);
start(controller);
...
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(-1);
}
return null;
}
接下来我们来看看start(controller)方法中做了什么,进入NamesrvStartup#start方法:
public static NamesrvController start(final NamesrvController controller) throws Exception {
if (null == controller) {
throw new androidIllegalArgumentException("NamesrvController is null");
}
// 初始化
boolean initResult = controller.initialize();
if (!initResult) {
controller.shutdown();
System.exit(-3);
}
// 关闭钩子,可以在关闭前进行一些操作
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new ShutdownHookThread(log, new Callable<Void>() {
@Override
public Void call() throws Exception {
controller.shutdown();
return null;
}
}));
// 启动
controller.start();
return controller;
}
start(...)方法的逻辑也十分简洁,主要包含3个操作:
- 初始化,想必是做一些启动前的操作
- 添加关闭钩子,所谓的关闭钩子,可以理解为一个线程,可以用来监听jvm的关闭事件,在jvm真正关闭前,可以进行一些处理操作,这里的关闭前的处理操作就是
controller.shutdown()方法所做的事了,所做的事也很容易想到,无非就是关闭线程池、关闭已经打开的资源等,这里我们就不深究了 - 启动操作,这应该就是真正启动
nameServer服务了
接下来我们主要来探索初始化与启动操作流程。
2.3.1 初始化:NamesrvController#initialize
初始化的处理方法是NamesrvController#initialize,代码如下:
public boolean initialize() {
// 加载 kv 配置
this.kvConfigManager.load();
// 创建 netty 远程服务
this.remotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(this.nettyServerConfig,
this.broke编程客栈rHousekeepingService);
// netty 远程服务线程
this.remotingExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
nettyServerConfig.getServerWorkerThreads(),
new ThreadFactoryImpl("RemotingExecutorThread_"));
// 注册,就是把 remotingExecutor 注册到 remotingServer
this.registerProcessor();
// 开启定时任务,每隔10s扫描一次broker,移除不活跃的broker
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
NamesrvController.this.routeInfoManager.scanNotActiveBroker();
}
}, 5, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 省略打印kv配置的定时任务
...
// Tls安全传输,我们不关注
if (TlsSystemConfig.tlsMode != TlsMode.DISABLED) {
...
}
return true;
}
这个方法所做的事很明了,代码中都已经注释了,代码看着多,实际干的就两件事:
- 处理netty相关:创建远程服务与工作线程
- 开启定时任务:移除不活跃的broker
什么是NettyRemotingServer呢?在本文开篇介绍NamerServer的功能时,提到NameServer是一个简单的注册中心,这个NettyRemotingServer就是对外开放的入口,用来接收broker的注册消息的,当然还会处理一些其他消息,我们后面会分析到。
- 1. 创建NettyRemotingServer
我们先来看看NettyRemotingServer的创建过程:
public NettyRemotingServer(final NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig,
final ChannelEventListener channelEventListener) {
super(nettyServerConfig.getServerOnewaySemaphoreValue(),
nettyServerConfig.getServerAsyncSemaphoreValue());
this.serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
this.nettyServerConfig = nettyServerConfig;
this.channelEventListener = channelEventListener;
int publicThreadNums = nettyServerConfig.getServerCallbackExecutorThreads();
if (publicThreadNums <= 0) {
publicThreadNums = 4;
}
// 创建 publicExecutor
this.publicExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(publicThreadNums, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyServerPublicExecutor_"
+ this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
// 判断是否使用 epoll
if (useEpoll()) {
// boss
this.eventLoopGroupBoss = new EpollEventLoopGroup(1, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyEPOLLBoss_%d",
this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
// worker
this.eventLoopGroupSelector = new EpollEventLoopGroup(
nettyServerConfig.getServerSelectorThreads(), new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
p开发者_Go学习rivate int threadTotal = nettyServerConfig.getServerSelectorThreads();
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, String.format("NettyServerEPOLLSelector_%d_%d",
threadTotal, this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet()));
}
});
} else {
// 这里也是创建了两个线程
...
}
// 加载ssl上下文
loadSslContext();
}
整个方法下来,其实就是做了一些赋值操作,我们挑重点讲:
serverBootstrap:熟悉netty的小伙伴应该对这个很熟悉了,这个就是netty服务端的启动类publicExecutor:这里创建了一个名为publicExecutor线程池,暂时并不知道这个线程有啥作用,先混个脸熟吧eventLoopGroupBoss与eventLoopGroupSelector线程组:熟悉netty的小伙伴应该对这两个线程很熟悉了,这就是netty用来处理连接事件与读写事件的线程了,eventLoopGroupBoss对应的是netty的boss线程组,eventLoopGroupSelector对应的是worker线程组
到这里,netty服务的准备工作本完成了。
- 2. 创建netty服务线程池
让我们再回到NamesrvController#initialize方法,NettyRemotingServer创建完成后,接着就是netty远程服务线程池了:
this.remotingExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
nettyServerConfig.getServerWorkerThreads(),
new ThreadFactoryImpl("RemotingExecutorThread_"));
创建完成线程池后,接着就是注册了,也就是registerProcessor方法所做的工作:
this.registerProcessor();
在registerProcessor()中 ,会把当前的 NamesrvController 注册到 remotingServer中:
private void registerProcessor() {
if (namesrvConfig.isClusterTest()) {
this.remotingServer.registerDefaultProcessor(
new ClusterTestRequestProcessor(this, namesrvConfig.getProductEnvName()),
this.remotingExecutor);
} else {
// 注册操作
this.remotingServer.registerDefaultProcessor(
new DefaultRequestProcessor(this), this.remotingExecutor);
}
}
最终注册到为NettyRemotingServer的defaultRequestProcessor属性:
@Override
public void registerDefaultProcessor(NettyRequestProcessor processor, ExecutorService executor) {
this.defaultRequestProcessor
= new Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService>(processor, executor);
}
好了,到这里NettyRemotingServer相关的配置就准备完成了,这个过程中一共准备了4个线程池:
publicExecutor:暂时不知道做啥的,后面遇到了再分析
eventLoopGroupBoss:处理netty连接事件的线程组
eventLoopGroupSelector:处理netty读写事件的线程池
remotingExecutor:暂时不知道做啥的,后面遇到了再分析
- 3. 创建定时任务
准备完netty相关配置后,接着代码中启动了一个定时任务:
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
NamesrvController.this.routeInfoManager.scanNotActiveBroker();
}
}, 5, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
这个定时任务位于NamesrvController#initialize方法中,每10s执行一次,任务内容由RouteInfoManager#scanNotActiveBroker提供,它所做的主要工作是监听broker的上报信息,及时移除不活跃的broker,关于源码的具体分析,我们后面再详细分析。
2.3.2 启动:NamesrvController#start
分析完NamesrvController的初始化流程后,让我们回到NamesrvStartup#start方法:
public static NamesrvController start(final NamesrvController controller) throws Exception {
...
// 启动
controller.start();
return controller;
}
接下来,我们来看看NamesrvController的启动流程:
public void start() throws Exception {
// 启动nettyServer
this.remotingServer.start();
// 监听tls配置文件的变化,不关注
if (this.fileWatchService != null) {
this.fileWatchService.start();
}
}
这个方法主要调用了NettyRemotingServer#start,我们跟进去:
public void start() {
...
ServerBootstrap childHandler =
// 在 NettyRemotingServer#init 中准备的两个线程组
this.serverBootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupBoss, this.eventLoopGroupSelector)
.channel(useEpoll() ? EpollServerSocketChannel.class : NIOServerSocketChannel.class)
// 省略 option(...)与childOption(...)方法的配置
...
// 绑定ip与端口
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(this.nettyServerConfig.getListenPort()))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
HANDSHAKE_HANDLER_NAME, handshakeHandler)
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
encoder,
new NettyDecoder(),
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0,
nettyServerConfig.getServerChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
connectionManageHandler,
serverHandler
);
}
});
if (nettyServerConfig.isServerPooledByteBufAllocatorEnable()) {
childHandler.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
}
try {
ChannelFuture sync = this.serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
InetSocketAddress addr = (InetSocketAddress) sync.channel().localAddress();
this.port = addr.getPort();
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
throw new RuntimeException("this.serverBootstrap.bind().sync() InterruptedException", e1);
}
...
}
这个方法中,主要处理了NettyRemotingServer的启动,关于其他一些操作并非我们关注的重点,就先忽略了。
可以看到,这个方法里就是处理了一个netty的启动流程,关于netty的相关操作,非本文重点,这里就不多作说明了。这里需要指出的是,在netty中,如果Channel是出现了连接/读/写等事件,这些事件会经过Pipeline上的ChannelHandler上进行流转,NettyRemotingServer添加的ChannelHandler如下:
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
HANDSHAKE_HANDLER_NAME, handshakeHandler)
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
encoder,
new NettyDecoder(),
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0,
nettyServerConfig.getServerChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
connectionManageHandler,
serverHandler
);
这些ChannelHandler只要分为几类:
handshakeHandler:处理握手操作,用来判断tls的开启状态encoder/NettyDecoder:处理报文的编解码操作IdleStateHandler:处理心跳connectionManageHandler:处理连接请求serverHandler:处理读写请求
这里我们重点关注的是serverHandler,这个ChannelHandler就是用来处理broker注册消息、producer/consumer获取topic消息的,这也是我们接下来要分析的重点。
执行完NamesrvController#start,NameServer就可以对外提供连接服务了。
3. 总结
本文主要分析了NameServer的启动流程,整个启动流程分为3步:
- 创建
controller:这一步主要是解析nameServer的配置并完成赋值操作 - 初始化
controller:主要创建了NettyRemotingServer对象、netty服务线程池、定时任务 - 启动
controller:就是启动nettjavascripty服务
好了,本文的分析就到这里了,下篇文章我们继续分析NameServer。
以上就是RocketMQ NameServer架构设计启动流程的详细内容,更多关于RocketMQ NameServer架构的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!




 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论