目录
- QT与MATLAB混合编程
- 一、环境
- 二、将matlab程序写成函数形式
- 三、将函数的.m文件转换成动态链接库形式
- 四、QT调用
- 1.添加外部库
- 2.Matlab其他依赖库和头文件搜索路径的加入
- 3.工程中的头文件中添加.h文件
- 4.系统环境变量的设置
- 5 编写使用DLL内函数的代码
- 6 mwArray类的使用
- 四、编译和运行
- 总结
QT与MATLAB混合编程
本文就介绍使用 Qt 和 Matlab 进行混合编程的基本流程,主要包括:
- 如何在Matlab中将m文件编译为C++语言的DLL文件
- 如何在Qt项目中加入自定义DLL相关的LIB文件,以及MATLAB相关的LIB文件和H文件搜索路径
- MATLAB运行时DLL文件所在路径,及系统相关的环境变量设置
- 如何在Qt中调用自定义DLL中的函数,如何通过mwArray类传递输入输出参数
一、环境
- Win10
- Qt 5.14.2 (MSVC 2017, 32 bit)
- matlab R2016b
- vs2017
二、将matlab程序写成函数形式
在MATLAB中编写一个画有向图的函数Matlab_Digraph.m为例,其代码如下:
function Matlab_Digraph(fullLineS,fullLineT,v,dottedLineS,dottedLineT,taskNum,jobId,oper,iCriticalPathS,iCriticalPathT,select)
close all;
figure('NumberTitle', 'off','Name', '有向图');
nodenames=cell(1,taskNum+2);
for i=1:taskNum+2
if i==1
nodenames{1,i}='开始';
elseif i==taskNum+2
nodenames{1,i}='结束';
else
txt = sprintf('J%d.%d(%d)',jobId(i-1),oper(i-1),v(i-1));
nodenames{1,i}=txt;
end
end
G= digraph(fullLineS,fullLineT,[],nodenames);
p=plot(G,'Layout','force');
p.ArrowSize=15; %箭头大小
p.LineWidth=编程2; %线宽
p.EdgeColor ='black'; %线颜色
p.Marker = 'o'; %节点标记符号
p.MarkerSize=10; %节点大小
p.NodeColor = 'cyan'; %节点颜色
set( gca,'XTick' ,[] ,'YTick',[]);
highlight(p,dottedLineS,dottedLineT,'LineStyle','--') ;
if select==1
highlight(p,iCriticalPathS,iCriticalPathT,'EdgeColor','r','LineWidth',5) ;
end
end
在matlab中运行一下,如:
% 函数digraph(s,t,v):可在 s 和 t 中的对应节点之间创建边,并生成一个图 % s 和 t 都必须具有相同的元素数;这些节点必须都是从1开始的正整数,或都是字符串元胞数组。 >> fullLineS=[1 1 5 1 3 8 7 2 6 9 4 10 2 3 5 6 8 9http://www.devze.com]; >> fullLineT= [2 3 4 5 6 7 11 8 9 11 10 11 3 4 6 7 9 10 ]; >> v=[3 2 4 3 3 3 3 5 3]; >> dottedLineS=[1 2 3]; %虚线 >> dottedLineT=[2 3 4]; >> taskNum=9; >> jobId=[ 2 1 3 3 1 2 2 1 3 ]; >> oper=[ 1 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 3 ]; >> iCriticalPathS=[5 8]; %关键路径 >> iCriticalPathT=[6 9]; >> select=1;
同时绘图如下:
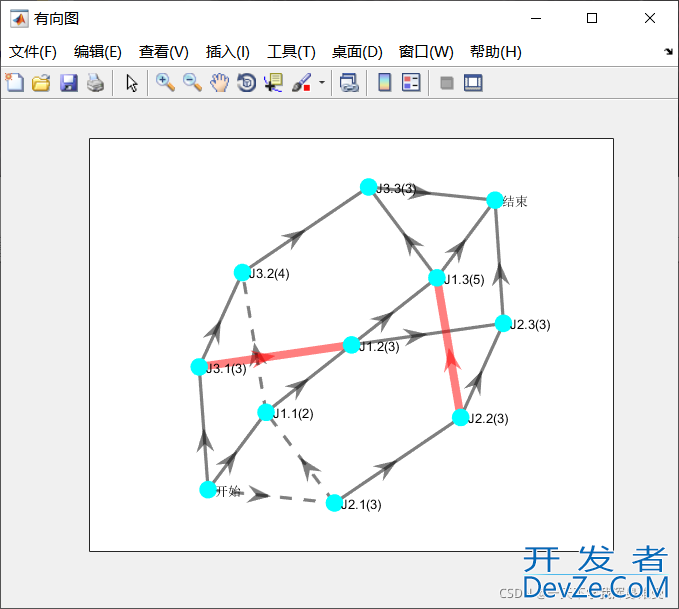
三、将函数的.m文件转换成动态链接库形式
首先,检查一下自己的mcc编译器是否可用
命令行输入指令
>> !mcc
正常的结果应该如下:
mcc Compile MATLAB functions for deployment outside MATLAB.
mcc [-options] fun [fun2...] OPTIONS: a <filename> Add <filename> to the deployable archive. If the specified file is an m, mex or p file, this function will not be exported in the resulting target. C Generate a separate deployable archive. d <directory> Output directory. e Suppress MS-DOS Command Window. Use in place of -m. g Include debugging symbol information. I <path> Add <path> to the list of paths to search for files. m Generate a standalone application. N Clear the compilation search path of all directories except the following core directories: <matlabroot>/toolbox/matlab <matlabroot>/toolbox/local <matlabroot>/toolbox/compiler o <outputfilename> Output name. p <directory> Add <directory> to the compilation search path. This option can only be used in conjunction with the -N option. R <option> Specify the run-time options for the MATLAB Runtime. v Verbose. Y <license.dat file> Override the default license.dat file. EXAMPLES: Make a standalone executable for myfun.m: mcc -m myfun Make standalone executable for myfun.m. Look for myfun.m in the directory /files/source, and put the resulting C files and executable in the directorpythony /files/target: mcc -m -I /files/source -d /files/target myfun Make a standalone executable from myfun1.m and myfun2.m: mcc -m myfun1 myfun2 For more details, execute "doc mcc" from MATLAB.
如果出现error,那么就是Matlab的编译器不能用,原因是Matlab并未完全破解。
解决了编译器问题之后,之后输入mbuild -setup>> mbuild -setup MBUILD 配置为使用 'Microsoft Visual C++ 2017 (C)' 以进行 C 语言编译。 要选择不同的语言,请从以下选项中选择一种命令: mex -setup C++ -client MBUILD mex -setup FORTRAN -client MBUILD
要使用C++编译器,所以要点击上面的mex -setup C++ -client MBUILD
之后,在命令行输入
>> mex -setup
>> mex -setup MEX 配置为使用 'Microsoft Visual C++ 2017 (C)' 以进行 C 语言编译。 警告: MATLAB C 和 Fortran API 已更改,现可支持 包含 2^32-1 个以上元素的 MATLAB 变量。不久以后, 您需要更新代码以利用 新的 API。您可以在以下网址找到相关详细信息: http://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_external/upgrading-mex-files-to-use-64-bit-api.html。 要选择不同的语言,请从以下选项中选择一种命令: mex -setup C++ mex -setup FORTRAN
然后选择:mex -setup C++
需要注意的是,matlab每次重启后,都要重新按以上步骤进行mbuild -setup/mex -setup的配置。
选择Liberty Complier
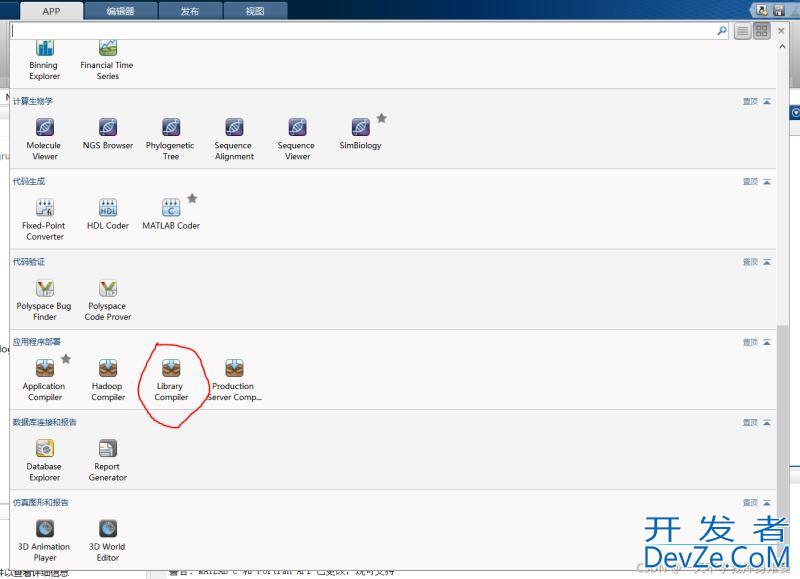
“TYPE”部分选择C++ shared Library,“EXPORTED FUNCTIONS”是需要导出的m文件,点击右侧的“Add”按钮选择编写的文件Matlab_Digraph.m。右侧是MATLAB运行时库的安装打包方式,在本机上测试可选择“Runtime downloaded from web”。
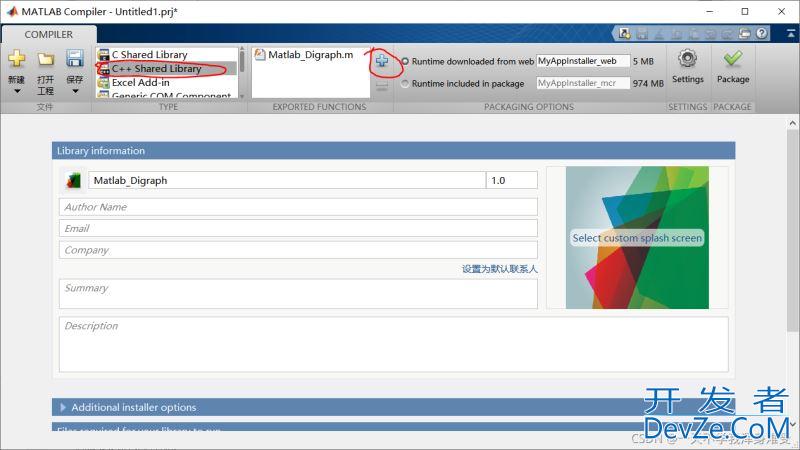
打包完成后,在项目文件Matlab_Digraph.prj的目录下生成与项目同名的子目录,即\Matlab_Digraph,该目录下有3个文件夹。
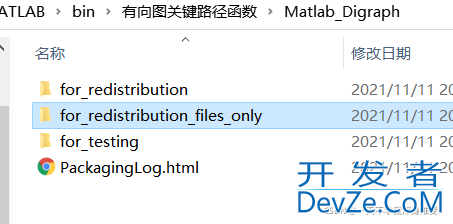
Matlab_Digraph\for_Redistribution_files_only目录下是编译生成的.dll 、.lib和.h文件,其中.lib和.h文件是在Qt项目编译时需要用到的,.dll文件是程序运行时需要用到的。
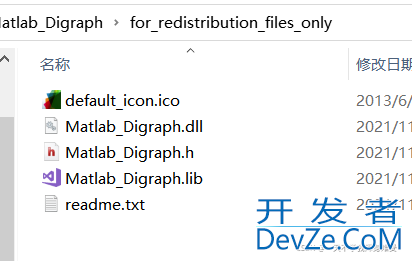
将生成的.h.lib.dll文件三个一起拷到代码所在的文件夹。
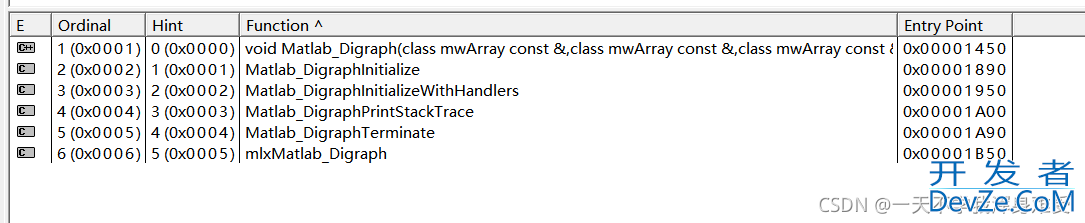
可以使用Dependency Walker来查看.dll文件中的一些内容
四、QT调用
1.添加外部库

点击下一步,之后按如下配置,点击浏览选择库,之后勾掉linux和MAC,且勾掉为debug版本添加’d’作为后缀。
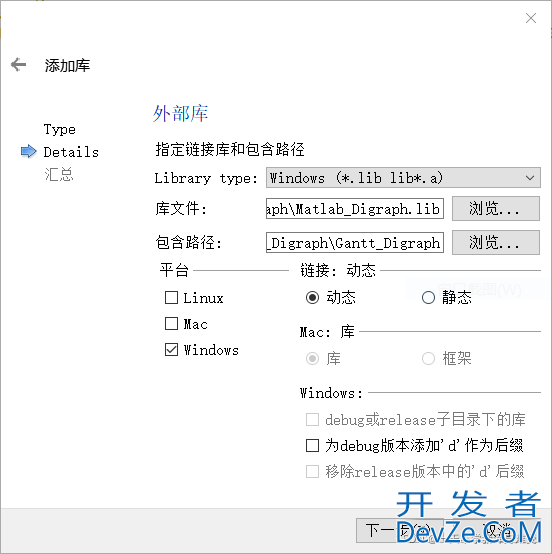
点击下一步,你就会发现你的.pro文件中多了几行:
win32: LIBS += -L$$PWD/./ -lMatlab_Digraph INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD/. DEPENDPATH += $$PWD/.
2.Matlab其他依赖库和头文件搜索路径的加入
重点是Qt 的pro文件的配置,我们需要在pro文件中加入以下内容:
DEFINES += __MW_STDINT_H__ INCLUDEPATH += D:/MATLAB/extern/include INCLUDEPATH += D:/MATLAB/extern/include/win64 LIBS += -LD:/MATLAB/extern/lib/win64/microsoft -llibmx LIBS += -LD:/MATLAB/extern/lib/win64/microsoft -llibmat LIBS += -LD:/MATLAB/extern/lib/win64/microsoft -lmclmcr LIBS += -LD:/MATLAB/extern/lib/win64/microsoft -lmclmcrrt LIBS += -LD:/MATLAB/extern/lib/win64/microsoft -llibeng
(这个要根据自己的Matlab具体的安装位置来修改。)
3.工程中的头文件中添加.h文件
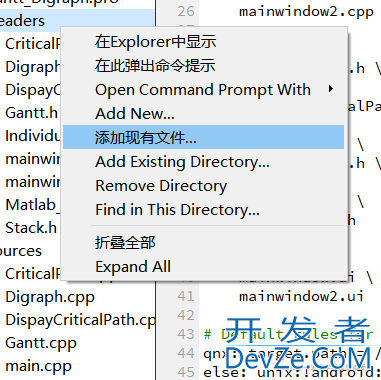
#include "Matlab_Digraph.h"
4.系统环境变量的设置
额外加入的一些库实际上对应于MATLAB运行时的一些DLL文件,这些运行时文件主要在以下几个目录下,所以要保证这些目录添加到了Windows的环境变量PATH里。
D:\MATLAB\runtime\win64; D:\MATLAB\\bin\win64;
若是程序发布到没有安装MATLAB的电脑上,需要用Matlab Compiler编译生成的安装包。
5 编写使用DLL内函数的代码
(1)DLL的初始化
Matlab_DigraphInitialize();
在使用Matl编程客栈ab_Digraph.dll里的函数之前,必须先初始化。Matlab_DigraphInitialize()是库初始化函数。
(2)函数的输入输出参数
mwArray是MATLAB的数组类,MATLAB编译生成的DLL的接口函数的参数都是采用mwArray类型,例如Matlab_Digraph.h文件中的函数Matlab_Digraph()的函数原型为:
extern LIB_Matlab_Digraph_CPP_API void MW_CALL_CONV Matlab_Digraph(const mwArray& fullLineS, const mwArray& fullLineT, const mwArray& v, const mwArray& dottedLineS, const mwArray& dottedLineT, const mwArray& taskNum, const mwArray& jobId, const mwArray& oper, const mwArray& iCriticalPathS, const mwArray& iCriticalPathT, const mwArray& s编程elect);
6 mwArray类的使用
四、编译和运行
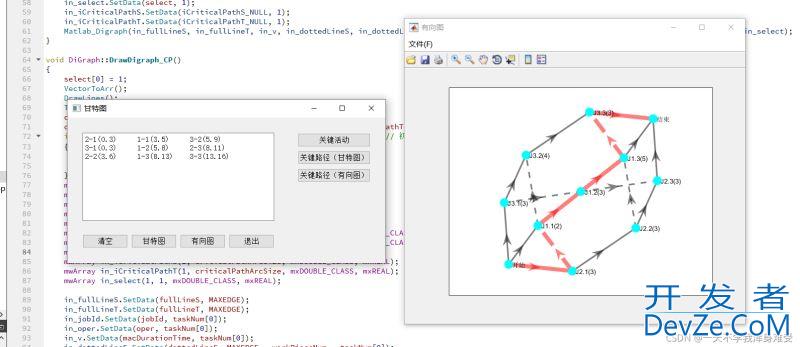
void DiGraph::DrawDigraph_CP()
{
select[0] = 1;
VectorToArr();
DrawLines();
TransFormat();
c.ImportData_Digraph(in_degree, in_out_weight, MAXVEX, MAXEDGE);
criticalPathArcSize = c.TransferResults_CP(&iCriticalPathS, &iCriticalPathT);
if (!Matlab_DigraphInitialize()) // 初始化,必须要使用
{
qDebug() << "add init failed.";
return;
}
mwArray in_fullLineS(1, MAXEDGE, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_fullLineT(1, MAXEDGE, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_jobId(1, taskNum[0], mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_oper(1, taskNum[0], mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_v(1, taskNum[0], mxDOUBLE_CLA开发者_开发学习SS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_dottedLineS(1, MAXEDGE - workPieceNum - taskNum[0], mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_dottedLineT(1, MAXEDGE - workPieceNum - taskNum[0], mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_taskNum(1, 1, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_iCriticalPathS(1, criticalPathArcSize, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_iCriticalPathT(1, criticalPathArcSize, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
mwArray in_select(1, 1, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
in_fullLineS.SetData(fullLineS, MAXEDGE);
in_fullLineT.SetData(fullLineT, MAXEDGE);
in_jobId.SetData(jobId, taskNum[0]);
in_oper.SetData(oper, taskNum[0]);
in_v.SetData(macDurationTime, taskNum[0]);
in_dottedLineS.SetData(dottedLineS, MAXEDGE - workPieceNum - taskNum[0]);
in_dottedLineT.SetData(dottedLineT, MAXEDGE - workPieceNum - taskNum[0]);
in_taskNum.SetData(taskNum, 1);
in_iCriticalPathS.SetData(iCriticalPathS, criticalPathArcSize);
in_iCriticalPathT.SetData(iCriticalPathT, criticalPathArcSize);
in_select.SetData(select, 1);
Matlab_Digraph(in_fullLineS, in_fullLineT, in_v, in_dottedLineS, in_dottedLineT, in_taskNum, in_jobId, in_oper, in_iCriticalPathS, in_iCriticalPathT, in_select);
}
然后构建项目运行,弹出plot绘图,与预期相符
总结
到此这篇关于QT与MATLAB混合编程的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关QT与MATLAB混合编程内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论