目录
- Arrays.sort实现降序排序
- 1.Collections的reverseorder
- 2.利用Comparator接口复写compare
- Arrays.sort底层原理
- 概述
- 案例
- 总结
Arrays.sort实现降序排序
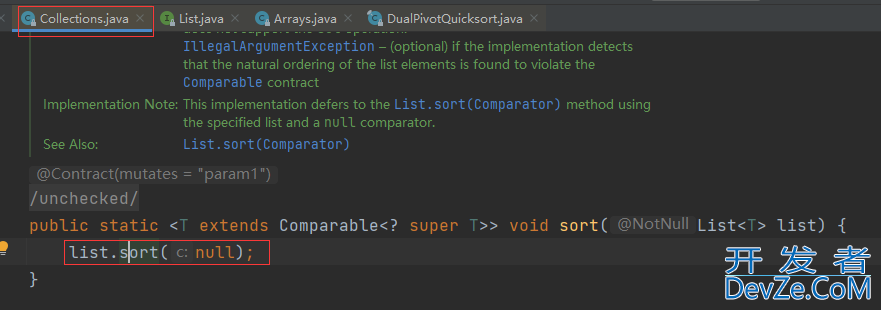
在调用Arrays.sort()对数组进行排序时,默认是升序排序的,如果想让数组降序排序,有下面两种方法:
1.Collections的reverseOrder
import Java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 注意这里是Integer,不是int
Integer[] arr={9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
Arrays.sort(arr,Collections.reverseOrder());
for(int i:arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
2.利用Comparator接口复写compare
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr={9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
Comparator cmp=new CMP();
Arrays.sort(arr,cmp);
for(int i:arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
class CMP implements Comparator<Integer>{
@Override //可以去掉。作用是检查下面的方法名是不是父类中所有的
public int compare(Integer a,Integer b){
// 两种都可以,升序排序的话反过来就行
// return a-b<0?1:-1;
return b-a;
}
}
注意:如果需要改变默认的排列方式,不能使用基本类型(int,char等)定义变量,而应该用对应的类
Arrays.sort底层原理
概述
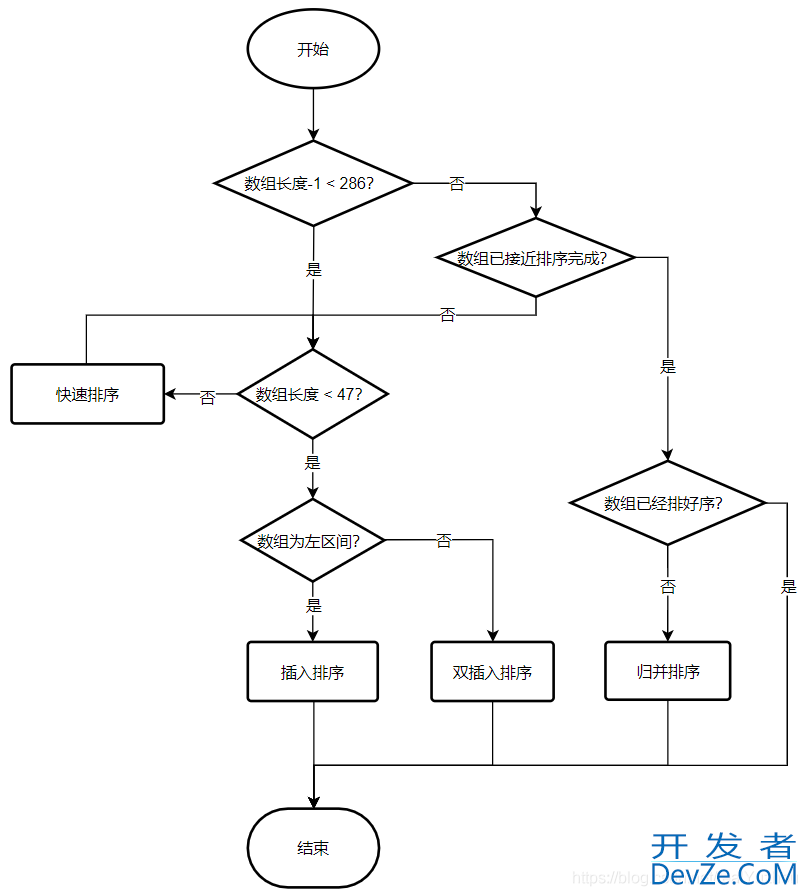
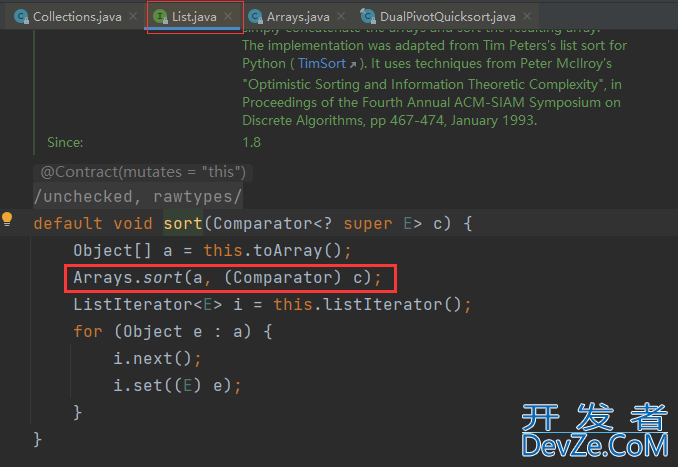
Collections.sort()方法底层调用的也是Arrays.sort()方法,下面我们通过测试用例debug,探究一下其源码,首先说一下结果,使用到了插入排序,双轴快排,归并排序
双轴快排(DualPivotQuicksort): 顾名思义有两个轴元素pivot1,pivot2,且pivot ≤
pivot2,将序列分成三段:x < pivot1、pivot1 ≤ x ≤ pivot2、x >pivot2,然后分别对三段进行递归。这个算法通常会比传统的快排效率更高,也因此被作为Arrays.java中给基本类型的数据排序的具体实现。大致流程:
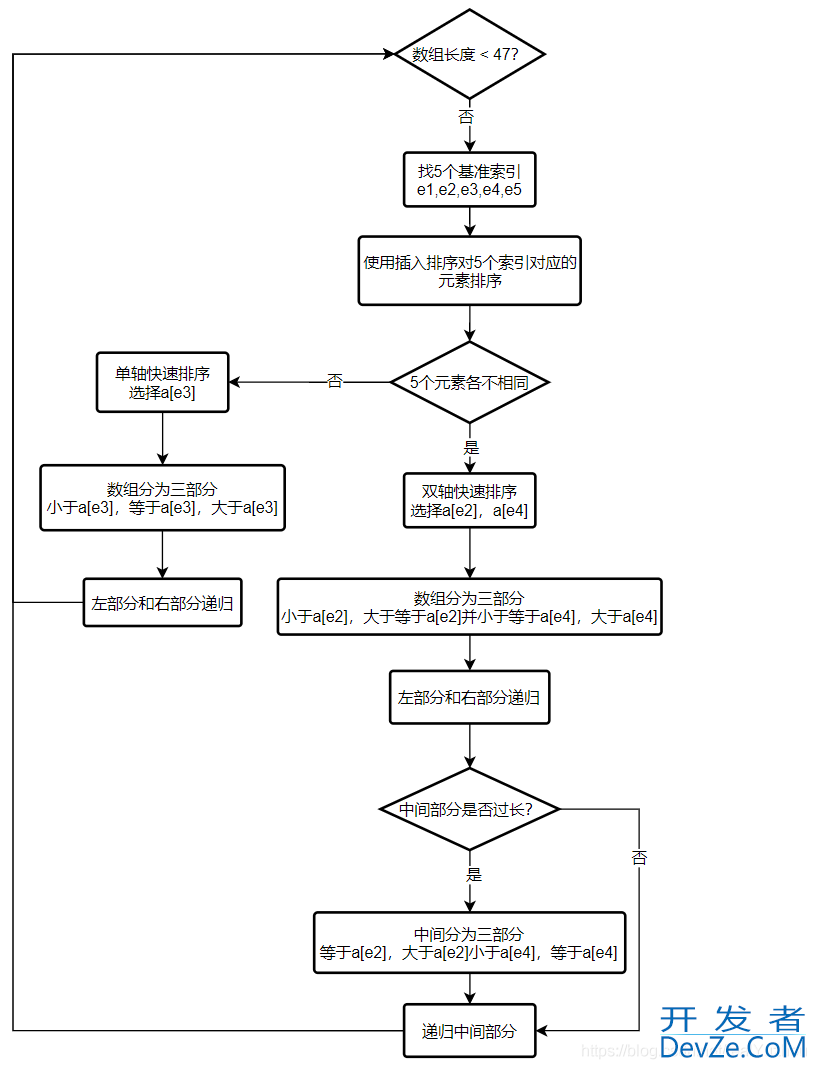
快速排序部分展开
案例
public static void main(String[] args) {
js int[] nums = new int[]{6,5,4,3,2,1};
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1);
Arrays.sort(nums);
Collections.sort(list);
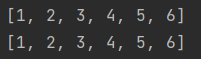
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
System.out.println(list);
}
运行结果
1 进入Arrays.sort()方法
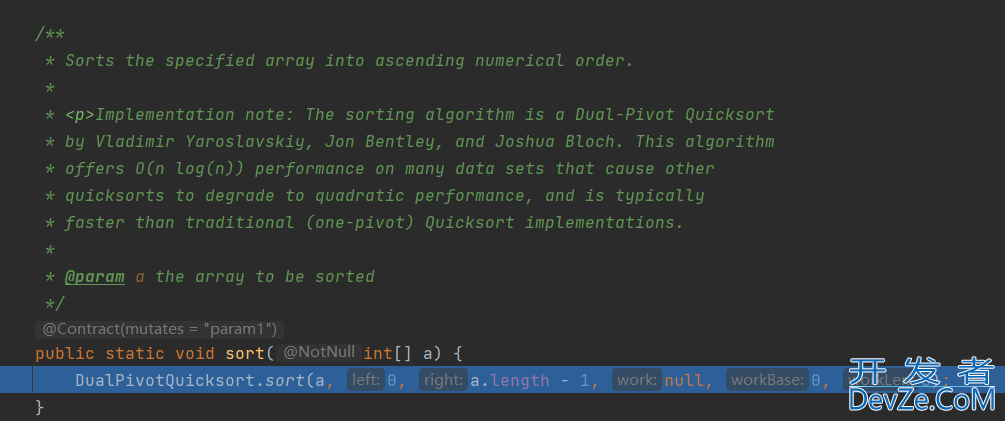
/**
* Sorts the specified array into ascending numerical order.
*
* <p>Implementation note: The sorting algorithm is a Dual-Pivot Quicksort
* by Vladimir Yaroslavskiy, Jon Bentley, and Joshua Bloch. This algorithm
* offers O(n log(n)) performance on many data sets that cause other
* quicksorts to degrade to quadratic performance, and is typically
* faster than traditional (one-pivot) Quicksort implementations.
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
方法上的注释

2 进入DualPivotQuicksort类内部的静态方法sort
方法上的注释

3 走sort的流程
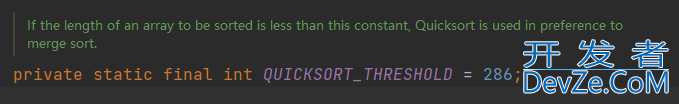

1. 排序范围小于286的数组使用快速排序
// Use Quicksort on small arrays
if (right - left < QUICKSORT_THRESHOLD) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
// Merge sort
......
2. 进入sort方法,判断数组长度是否小于47,小于则直接采用插入排序,否则执行3。

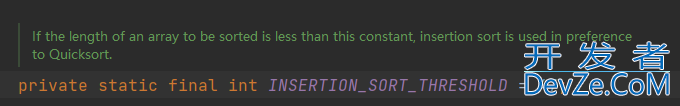
// Use insertion sort on tiny arrays
if (length < INSERTION_SORT_THRESHOLD) {
// Insertion sort
......
}
3. 用公式length/8+length/64+1近似计算出数组长度的1/7。
// Inexpensive approximation of length / 7 int seventh = (length >> 3) + (length >> 6) + 1;
4. 取5个根据经验得出的等距点。

/*
* Sort five evenly spaced elements around (and including) the
* center element in the range. These elements will be used for
* pivot selection as described below. The choice for spacing
* these elements was empirically determined to work well on
* a wide variety of inputs.
*/
int e3 = (left + right) >>> 1; // The midpoint
int e2 = e3 - seventh;
int e1 = e2 - seventh;
int e4 = e3 + seventh;
int e5 = e4 + seventh;
5.将这5个元素进行插入排序
// Sort these elements using insertion sort
if (a[e2] < a[e1]) { long t = a[e2]; a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
if (a[e3] < a[e2]) { long t = a[e3]; a[e3] = a[e2]; a[e2] = t;
if (t < a[e1]) { a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
}
if (a[e4] < a[e3]) { long t = a[e4]; a[e4] = a[e3]; a[e3] = t;
if (t < a[e2]) { a[e3] = a[e2]; a[e2] = t;
开发者_Go开发 if (t < a[e1]) { a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
}
}
if (a[e5] < a[e4]) { long t = a[e5]; a[e5] = a[e4]; a[e4] = t;
if (t < a[e3]) { a[e4] = a[e3]; a[e3] = t;
if (t < a[e2]) { a[e3] = a[e2]; a[e2] = t;
if (t < a[e1]) { a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
}
}
}
6. 选取a[e2],a[e4]分别作为pivot1,pivot2。由于步骤5进行了排序,所以必有pivot1 <=pivot2。定义两个指针less和great,less从最左边开始向右遍历,一直找到第一个不小于pivot1的元素,great从右边开始向左遍历,一直找到第一个不大于pivot2的元素。
/*
* Use the second and fourth of the five sorted elements as pivots.
* These values are inexpensive approximations of the first and
* second terciles of the array. Note that pivot1 <= pivot2.
*/
int pivot1 = a[e2];
int pivot2 = a[e4];
/*
* The first and the last elements to be sorted are moved to the
* locations formerly occupied by the pivots. When partitioning
* is complete, the pivots are swapped back into their final
* positions, and excluded from subsequent sorting.
*/
a[e2] = a[left];
a[e4] = a[right];
/*
* Skip elements, which are less or greater than pivot values.
*/
while (a[++less] < pivot1);
while (a[--great] > pivot2);
7. 接着定义指针k从less-1开始向右遍历至great,把小于pivot1的元素移动到less左边,大于pivot2的元素移动到great右边。这里要注意,我们已知great处的元素小于pivot2,但是它于pivot1的大小关系,还需要进行判断,如果比pivot1还小,需要移动到到less左边,否则只需要交换到k处。
/*
* Partitioning:
*
* left part center part right part
* +--------------------------------------------------------------+
* | < pivot1 | pivot1 <= && <= pivot2 | ? | > pivot2 |
* +--------------------------------------------------------------+
* ^ ^ ^
* | | |
* less k great
*
* Invariants:
*
* all in (left, less) < pivot1
* pivot1 <= all in [less, k) <= pivot2
* python all in (great, right) > pivot2
*
* Pointer k is the first index of ?-part.
*/
outer:
for (int k = less - 1; ++k <= great; ) {
short ak = a[k];
if (ak < pivot1) { // Move a[k] to left part
a[k] = a[less];
/*
* Here and below we use "a[i] = b; i++;" instead
* of "a[i++] = b;" due to performance issue.
*/
a[less] = ak;
++less;
} else if (ak > pivot2) { // Move a[k] to right part
while (a[great] > pivot2) {
if (great-- == k) {
break outer;
}
}
if (a[great] < pivot1) { // a[great] <= pivot2
a[k] = a[less];
a[less] = a[great];
++less;
} else { // pivot1 <= a[great] <= pivot2
a[k] = a[great];
}
/*
* Here and below we use "a[i] = b; i--;" instead
* of "a[i--] android= b;" due to performance issue.
*/
a[great] = ak;
--great;
}
}
8. 将枢轴交换到它们的最终位置
// Swap pivots into their final positions
a[left] = a[less - 1]; a[less - 1] = pivot1;
a[right] = a[great + 1]; a[great + 1] = pivot2;
9. 递归排序左右部分,不包括已知的枢轴
// Sort left and right parts recursively, excluding known pivots
sort(a, left, less - 2, leftmost);
sort(a, great + 2, right, false);
10. 对于中间的部分,如果大于4/7的数组长度,递归中间部分
/*
* If center part is too large (comprises > 4/7 of the array),
* swap internal pivot values to ends.
*/
if (less < e1 && e5 < great) {
/*
* Skip elements, which are equal to pivot values.
*/
while (a[less] == pivot1) {
++less;
}
while (a[great] == pivot2) {
--great;
}
/*
* Partitioning:
*
* left part center part right part
* +----------------------------------------------------------+
* | == pivot1 | pivot1 < && < pivot2 | ? | == pivot2 |
* +----------------------------------------------------------+
* ^ ^ ^
* | | |
* less k great
*
* Invariants:
*
* all in (*, less) == pivot1
* pivot1 < all in [less, k) < pivot2
* all in (gjsreat, *) == pivot2
*
* Pointer k is the first index of ?-part.
*/
outer:
for (int k = less - 1; ++k <= great; ) {
short ak = a[k];
if (ak == pivot1) { // Move a[k] to left part
a[k] = a[less];
a[less] = ak;
++less;
} else if (ak == pivot2) { // Move a[k] to right part
while (a[great] == pivot2) {
if (great-- == k) {
break outer;
}
}
if (a[great] == pivot1) { // a[great] < pivot2
a[k] = a[less];
/*
* Even though a[great] equals to pivot1, the
* assignment a[less] = pivot1 may be incorrect,
* if a[great] and pivot1 are floating-point zeros
* of different signs. Therefore in float and
* double sorting methods we have to use more
* accurate assignment a[less] = a[great].
*/
a[less] = pivot1;
++less;
} else { // pivot1 < a[great] < pivot2
a[k] = a[great];
}
a[great] = jsak;
--great;
}
}
}
// Sort center part recursively
sort(a, less, great, false);
4 小结
Arrays.sort对升序数组、降序数组和重复数组的排序效率有了很大的提升,这里面有几个重大的优化。
- 对于小数组来说,插入排序效率更高,每次递归到小于47的大小时,用插入排序代替快排,明显提升了性能。
- 双轴快排使用两个pivot,每轮把数组分成3段,在没有明显增加比较次数的情况下巧妙地减少了递归次数。
- pivot的选择上增加了随机性,却没有带来随机数的开销。
- 对重复数据进行了优化处理,避免了不必要交换和递归。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论