目录
- 简介
- 思路
- 1、日志表结构
- 2、注解
- 3、AOP切面
- 4、RabbitMQ消息队列
- 5、应用
- 6、总结
简介
无论在什么系统中,日志管理模块都属于十分重要的部分,接下来会通过注解+AOP+MQ的方式实现一个简易的日志管理系统
思路
- 注解:标记需要记录日志的方法
- AOP:通过AOP增强代码,利用后置/异常通知的方式获取相关日志信息,最后使用MQ将日志信息发送到专门处理日志的系统
- RabbitMQ:利用解耦、异步的特性,协调完成各个微服务系统之间的通信
1、日志表结构
表结构(sys_log):
CREATE TABLE `sys_log` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '唯一ID', `opt_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作用户id', `opt_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作用户名', `log_type` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '日志类型', `log_message` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '日志信息(具体方法名)', `create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=17 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='系统日志表';
实体类(SysLog):
@Data
public class SysLog {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* 唯一ID
*/
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
/**
* 操作用户id
*/
private Integer optId;
/**
* 操作用户名
*/
private String optName;
/**
* 日志类型
*/
private String logType;
/**
* 日志信息(具体方法名)
*/
private String logMessage;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
private Date createTime;
}
2、注解
注解(SystemLog):
仅作为标记的作用,目的让JVM可以识别,然后可以从中获取相关信息
@Target:定义注解作用的范围,这里是方法@Retention:定义注解生命周期,这里是运行时
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SystemLog {
SystemLogEnum type();
}
枚举(SystemLogEnum):
限定日志类型范围
public enum SystemLogEn编程客栈um {
SAVE_LOG("保存"),
DELETE_LOG("删除"),
REGISTER_LOG("注册"),
LOGIN_LOG("登录"),
LAUD_LOG("点赞"),
COLLECT_LOG("收藏"),
THROW_LOG("异常"),
;
private String type;
SystemLogEnum(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
}
3、AOP切面
AOP(SysLogASPect):
实现代码的增强,主要通过动态代理方式实现的代码增强。
拦截注解,并获取拦截到的相关信息,封装成日志对象发送到MQ队列(生产端)
Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class SysLogAspectandroid {
@Autowired
MqStream stream;
//切点
@Pointcut("@annotation(cn.zdxh.commons.utils.SystemLog)")
public void logPointcut(){}
//后置通知
@After("logPointcut()")
public void afterLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//一般日志
SysLog sysLog = wrapSysLog(joinPoint);
log.info("Log值:"+sysLog);
//发送mq消息
stream.logOutput().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(sysLog).build());
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "logPoiVfpUONntcut()", throwing = "e")
public void throwingLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e) {
//异常日志
SysLog sysLog = wrapSysLog(joinPoint);
sysLog.setLogType(SystemLogEnum.THROW_LOG.getType());
sysLog.setLogMessage(sysLog.getLogMessage()+"==="+e);
log.info("异常Log值:"+sysLog);
//发送mq消息
stream.logOutput().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(sysLog).build());
}
/**
* 封装SysLog对象
http://www.devze.com* @param joinPoint
* @return
*/
public SysLog wrapSysLog(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//获取请求响应对象
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
SysLog sysLog = new SysLog();
//获取方法全路径
String methodName = signature.getDeclaringTypeName()+"."+signature.getName();
//获取注解参数值
SystemLog systemLog = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(SystemLog.class);
//从header取出token
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) {
//操作人信息
Integer userId = JwtUtils.getUserId(token);
String username = JwtUtils.getUsername(token);
sysLog.setOptId(userId);
android sysLog.setOptName(username);
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(systemLog.type())){
sysLog.setLogType(systemLog.type().getType());
}
sysLog.setLogMessage(methodName);
sysLog.setCreateTime(new Date());
return sysLog;
}
}
4、RabbitMQ消息队列
MQ:
这里主要是通过Spring Cloud Stream集成的RabbitMQ
Spring Cloud Stream:
作为MQ的抽象层,已屏蔽各种MQ的各自名词,统称为开发者_C学习input、output两大块。可以更方便灵活地切换各种MQ,如 kafka、RocketMQ等
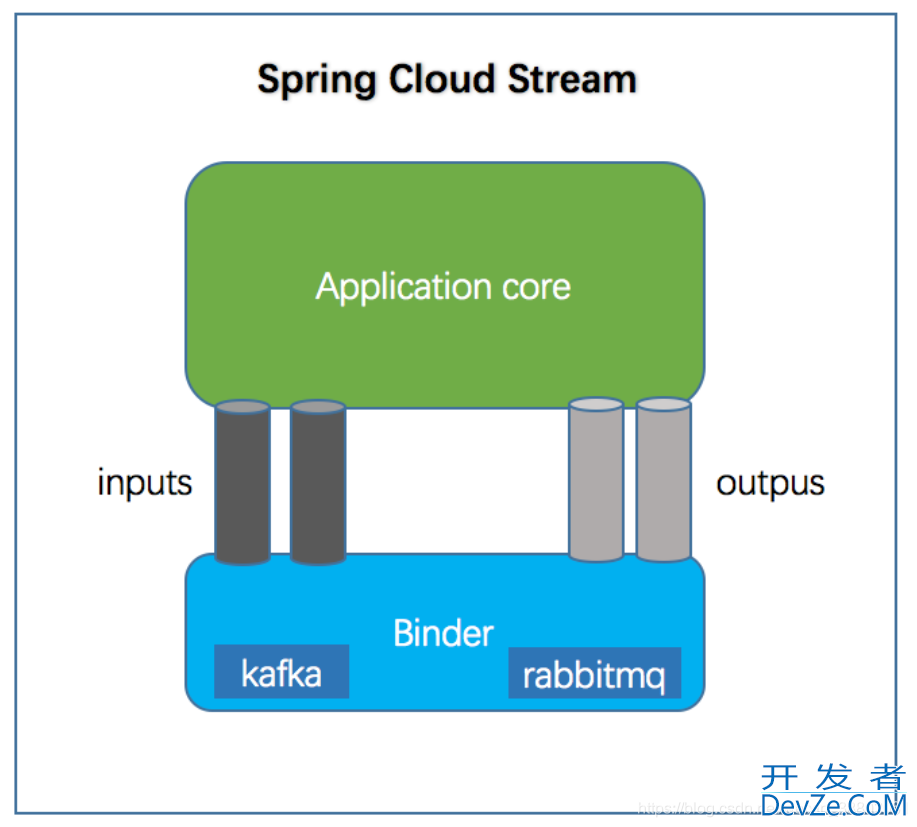
(1)定义Input/Ouput接口(MqStream)
@Component
public interface MqStream {
String LOG_INPUT = "log_input";
String LOG_OUTPUT = "log_output";
@Input(LOG_INPUT)
SubscribableChannel logInput();
@Output(LOG_OUTPUT)
MessageChannel logOutput();
}
(2)MQ生产者
注:这里使用到AOP切面的微服务,都属于MQ生产者服务
引入依赖:
这里没有版本号的原因是spring cloud已经帮我们管理好各个版本号,已无需手动定义版本号
<!--Spring Cloud Stream-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
在程序入口开启MQ的Input/Output绑定:
@EnableBinding(MqStream.class)
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"cn.zdxh.user","cn.zdxh.commons"})
@EnableEurekaClient
@MapperScan("cn.zdxh.user.mapper")
@EnableBinding(MqStream.class) //开启绑定
@EnableFeignClients
public class YouquServiceProviderUserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(YouquServiceProviderUserApplication.class, args);
}
}
yml配置:
在生产者端设置output
destination:相当于rabbitmq的exchangegroup:相当于rabbitmq的queue,不过是和destination一起组合成的queue名binder:需要绑定的MQ
#Spring Cloud Stream相关配置
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings: # exchange与queue绑定
log_output: # 日志生产者设置output
destination: log.exchange
content-type: application/json
group: log.queue
binder: youqu_rabbit #自定义名称
binders:
youqu_rabbit: #自定义名称
type: rabbit
environment:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: 25802580
注:完成以上操作,即完成MQ生产端的所有工作
(3)MQ消费者
引入依赖、开启Input/Output绑定:均和生产者的设置一致
yml配置:
在生产者端设置input
spring:
cloud: # Spring Cloud Stream 相关配置
stream:
bindings: # exchange与queue绑定
log_input: # 日志消费者设置input
destination: log.exchange
content-type: application/json
group: log.queue
binder: youqu_rabbit
binders:
youqu_rabbit:
type: rabbit
environment:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: 25802580
消费者监听(LogMqListener):
监听生产者发过来的日志信息,将信息添加到数据库即可
@Service
@Slf4j
public class LogMqListener {
@Autowired
SysLogService sysLogService;
@StreamListener(MqStream.LOG_INPUT)
public void input(SysLog sysLog) {
log.info("开始记录日志========================");
sysLogService.save(sysLog);
log.info("结束记录日志========================");
}
}
注:完成以上操作,即完成MQ消费端的所有工作
5、应用
简述:
只需将@SystemLog(type = SystemLogEnum.REGISTER_LOG),标记在需要记录的方法上,当有客户端访问该方法时,就可以自动完成日志的记录
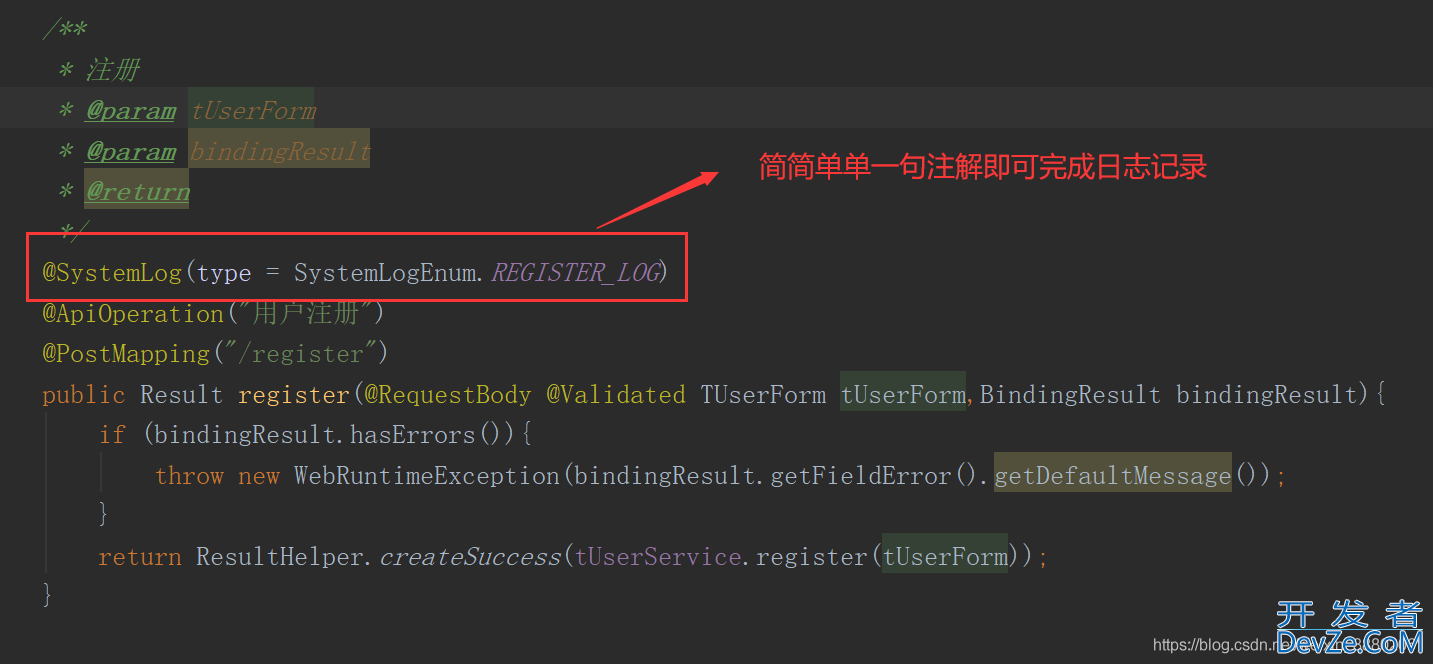
6、总结
流程:
注解标记--->AOP拦截--->日志发送到MQ--->专门处理日志的系统监听MQ消息 --->日志插入到数据库
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论