目录
- Sequential模型和Functional模型区别
- Sequential模型
- Functional模型
- 总结
Sequential模型和Functional模型区别
Sequential模型
只有一个输入和输出,而且网络是层的线性堆叠
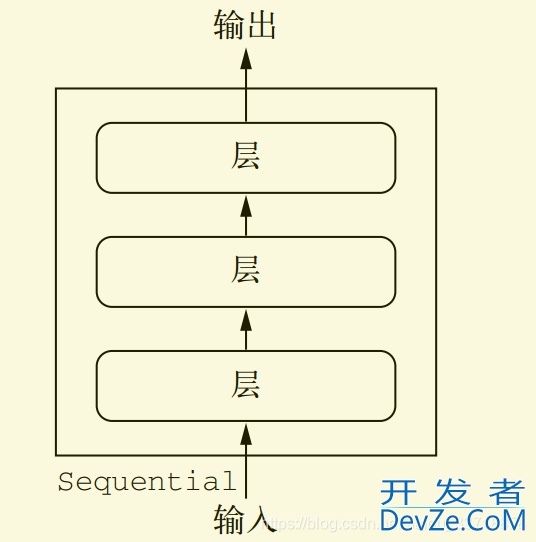
可以通过向Sequential模型传递一个layer的list来构造该模型:
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Activation
#Sequential的第一层需要接受一个关于输入数据shape的参数,后面的各个层则可以自动的推导出中间数据的shape
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, input_shape=(784,)))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.compile(optim开发者_JAVAizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # Generate dummy data import numpy as np data = np.random.random((1000, 100)) labels = np.random.randint(2, size=(1000, 1)) # Train the model, iterating on the data in BATches of 32 samples model.fit(data, labels, epochs=10, batch_size=32) # For a single-input model with 10 classes (categorical classification): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu', input_dim=100)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # Generate dummy data import numpy as np data = np.random.random((1000, 100)) labels = np.random.randint(10, size=(1000, 1)) # Convert labels to categorical one-hot encoding one_hot_labels = keras.utils.to_categorical(labels, num_classes=10) # Train the model, iterating on the data in batches of 32 samples model.fit(data, one_hot_labels, epochs=10, batch_size=32)
Functional模型
区别:
1.层对象接受张量为参数,返回一个张量。
2.输入是张量,输出也是张量的一个框架就是一个模型,通过Model定义。
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras import layers
from keras import Input
"""
# Sequential模型实现
seq_model = Sequential()
seq_model.add(layers.Dense(32, activation='relu', input_shape=(64,)))
seq_model.add(layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'))
seq_model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
"""
# 对应的函数式模型实现
input_tensor = Input编程客栈(shape=(64,))
x = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')(input_tensor)
x = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')(x)
output_tensor = layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x)
model = Model(input_tensor, output_tensor)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(data, labels) # starts training
model.summary() # 查看模型
3.所有的模型都是可调用的,就像层一样
这种方式可以允许你快速的创建能处理序列信号的模型,你可以很快将一个图像分类的模型变为一个对视频分类的模型,只需要一行代码:
from keras.layers import TimeDistributed # Input tensor for sequences of 20 timesteps, # each containing a 784-dimensional vector input_sequences = Input(shape=(20, 784)) # This applies our previous model to every timestep in the input sequences. # the output of the previous model was a 10-way softmax, # so the output of the layer below will be a sequence of 20 vectors of size 10. processed_sequences = TimeDistributed(jsmodel)(input_sequences)
4.构建具有多个输入的模型或多个输出的模型
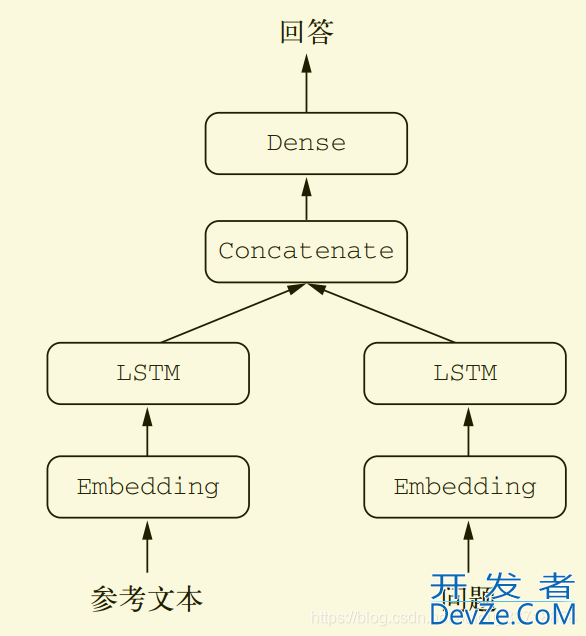
from keras.models import Model
from keras import layers
from keras import Input
text_vocabulary_size = 10000
question_vocabulary_size = 10000
answer_vocabulary_size = 500
# 文本输入是一个长度可变的整数序列。注意,你可以选择对输入进行命名
text_input = Input(shape=(None,), dtype='int32', name='text')
embedded_text = layers.Embedding(
text_vocabulary_size, 64)(text_input)
encoded_text = layers.LSTM(32)(embedded_text)
question_input = Input(shape=(None,), dtype='int32', name='question')
embedded_question = layers.Embedding(
question_vocabulary_size, 32)(question_input)
encoded_question = layers.LSTM(16)(embedded_question)
# 将编码后的问题和文本连接起来
concatenated = layers.concatenate([encoded_text, encoded_question],
axis=-1)
answer = layers.Dense(answer_vocabulary_size,
activation='softmax')(concatenated)
# 在模型实例化时,指定两个输入和输出
model = Model([text_input, question_input], answer)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['acc'])
import numpy as np
num_samples = 1000
max_length = 100
text = np.random.randint(1, text_vocabulary_size,
size=(num_samples, max_length))
question = np.random.randint(1, question_vocabulary_size,
size=(num_samples, max_length))
answers = np.random.randint(answer_vocabulary_size, size=(num_samples))
answers = keras.utils.to_categorical(answers, answer_vocabulary_size)
model.fit([text, question], answers, epochs=10, batch_size=128)
# 使用输入组成的字典来拟合(只有对输入进行命名之后才能用这种方法)使用输入组成的列表来拟合
model.fit({'text': text, 'question': question}, answers,
epochs=10, batch_size=128)
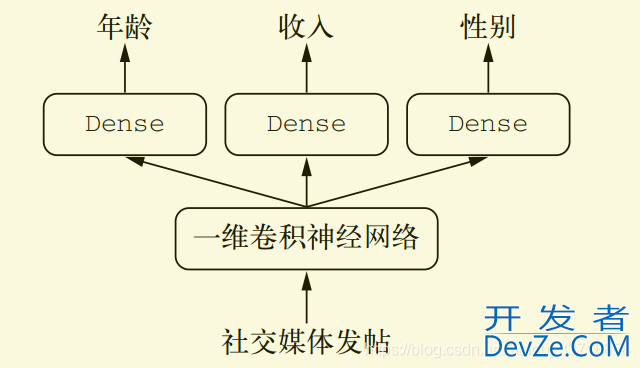
from keras import layers
from keras import Input
from keras.models import Model
vocabulary_size = 50000
num_income_groups = 10
posts_input = Input(shape=(None,), dtype='int32', name='posts')
embedded_posts = layers.Embedding(256, vocabulary_size)(posts_input)
x = layers.Conv编程客栈1D(128, 5, activation='relu')(embeddewww.devze.comd_posts)
x = layers.MaxPooling1D(5)(x)
x = layers.Conv1D(256, 5, activation='relu')(x)
x = layers.Conv1D(256, 5, activation='relu')(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling1D(5)(x)
x = layers.Conv1D(256, 5, activation='relu')(x)
x = layers.Conv1D(256, 5, activation='relu')(x)
x = layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D()(x)
x = layers.Dense(128, activation='relu')(x)
# 注意,输出层都具有名称
age_prediction = layers.Dense(1, name='age')(x)
income_prediction = layers.Dense(num_income_groups,
activation='softmax',
name='income')(x)
gender_prediction = layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='gender')(x)
model = Model(posts_input,
[age_prediction, income_prediction, gender_prediction])
#制定不同的损失函数
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss=['mse', 'categorical_crossentropy', 'binary_crossentropy'])
# 与上述写法等效(只有输出层具有名称时才能采用这种写法)
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss={'age': 'mse',
'income': 'categorical_crossentropy',
'gender': 'binary_crossentropy'})
#假设 age_targets、income_targets 和gender_targets 都是 Numpy 数组
model.fit(posts, [age_targets, income_targets, gender_targets],
epochs=10, batch_size=64)
# 等效
model.fit(posts, {'age': age_targets,
'income': income_targets,
'gender': gender_targets},
epochs=10, batch_size=64)
由于,年龄回归任务的均方误差(MSE)损失值通常在 3~5 左右,而用于性别分类任务的交叉熵损失值可能低至 0.1。在这种情况下,为了平衡不同损失的贡献,我们可以让交叉熵损失的权重取 10,而 MSE 损失的权重取 0.5
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss=['mse', 'categorical_crossentropy', 'binary_crossentropy'],
loss_weights=[0.25, 1., 10.])
# 等效
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss={'age': 'mse',
'income': 'categorical_crossentropy',
'gender'php: 'binary_crossentropy'},
loss_weights={'age': 0.25,
'income': 1.,
'gender': 10.})
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论