目录
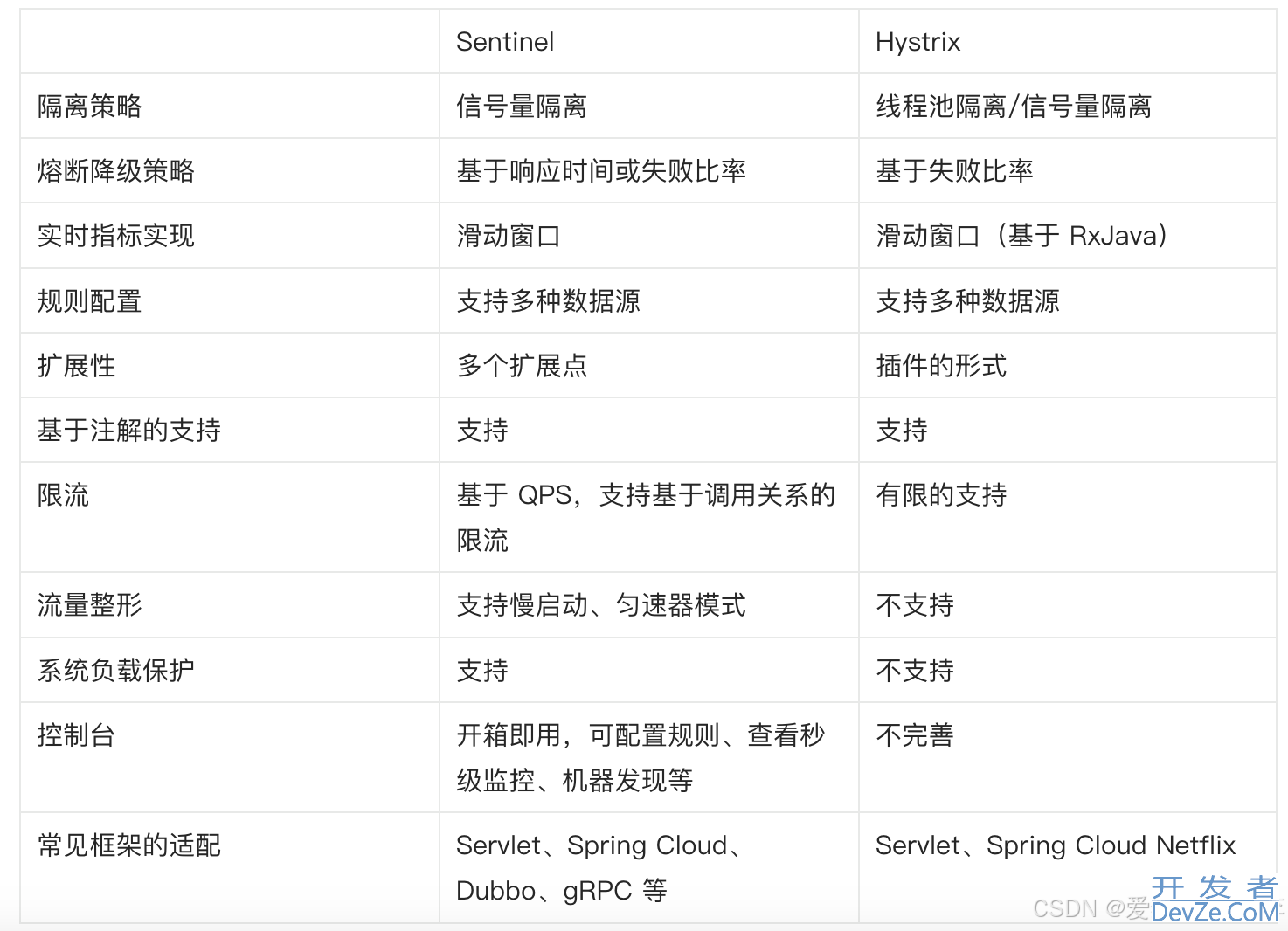
- 技术选型
- 限流
- QPS限流
- warmup限流
- Throttling策略
- 熔断
- 熔断策略
- 慢调用比例策略 (SlowRequestRatio)
- 错误比例策略 (ErrorRatio)
- 错误计数策略 (ErrorCount)
- gin集成sentinel限流
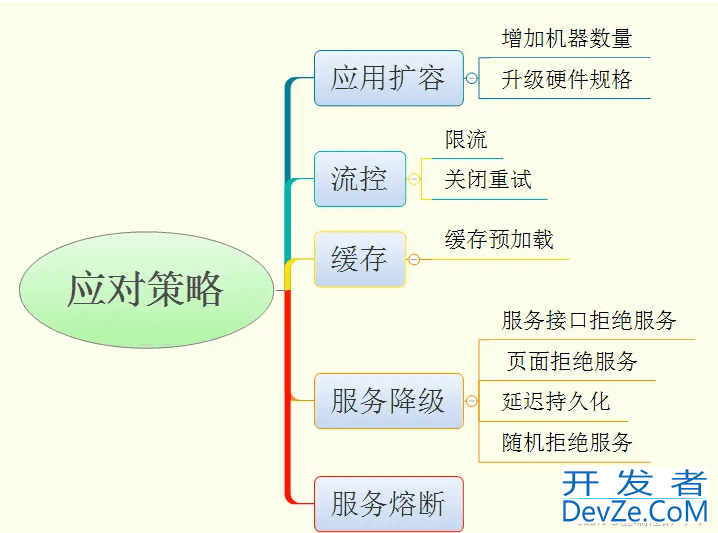
限流 - 2k 但是我的服务能力只有1k,所以这个时候多出来的流量怎么办: 1. 拒绝 2. 排队等待。用户体验不太好: 当前访问用户过多,请稍后重试和你的服务直接挂了
用户体验降级了 - 原本是访问流畅,下单流畅 -> 当前访问用户过多,请稍后重试
熔断 - 比如A服务访问B服务,这个时候B服务很慢 - B服务压力过大,导致了出现了不少请求错误,调用方很容易出现一个问题: 每次调用都超时 2k,结果这个时候数据库出现了问题, 超时重试 - 网络 2k的流量突然变成了3k。这让原本就满负荷的b服务雪上加霜,如果这个时候调用方有一种机制:比如说 1. 发现了大部分请求很慢 - 50%请求都很慢, 2. 发现我的请求有50%都错误了 3. 错误数量很多,比如1s出现了20个错误 。上述三种情况出现,在一段时间内不发给B服务,直接拒绝。一段时间之后再发送。以此来缓解B服务的压力,避免B服务挂掉的可能。
技术选型
sentinel官方文档
限流
QPS限流
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/base"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/flow"
)
const resName = "example-flow-qps-resource"
func main() {
//初始化sentinel
err := sentinel.InitDefault()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
//配置编程限流规则
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: resName,
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.Direct,
ControlBehavior: flow.Reject,
Threshold: 10,
StatIntervalInMs: 1000,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
ch := make(chan struct{})
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry(resName, sentinel.WithTrafficType(base.Inbound))
if b != nil {
// blocked. We could get the block reason from the BlockError.
fmt.Println("被限流")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%10) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
// Passed, wrap the logic here.
fmt.Println("成功")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%10) * time.Millisecond)
// Be sure the entry is exited finally.
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
}
// Simulate a scenario in which flow rules are updated concurrently
go func() {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 10)
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: resName,
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.Direct,
ControlBehavior: flow.Reject,
Threshold: 80,
StatIntervalInMs: 1000,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
}()
<-ch
}
warmup限流
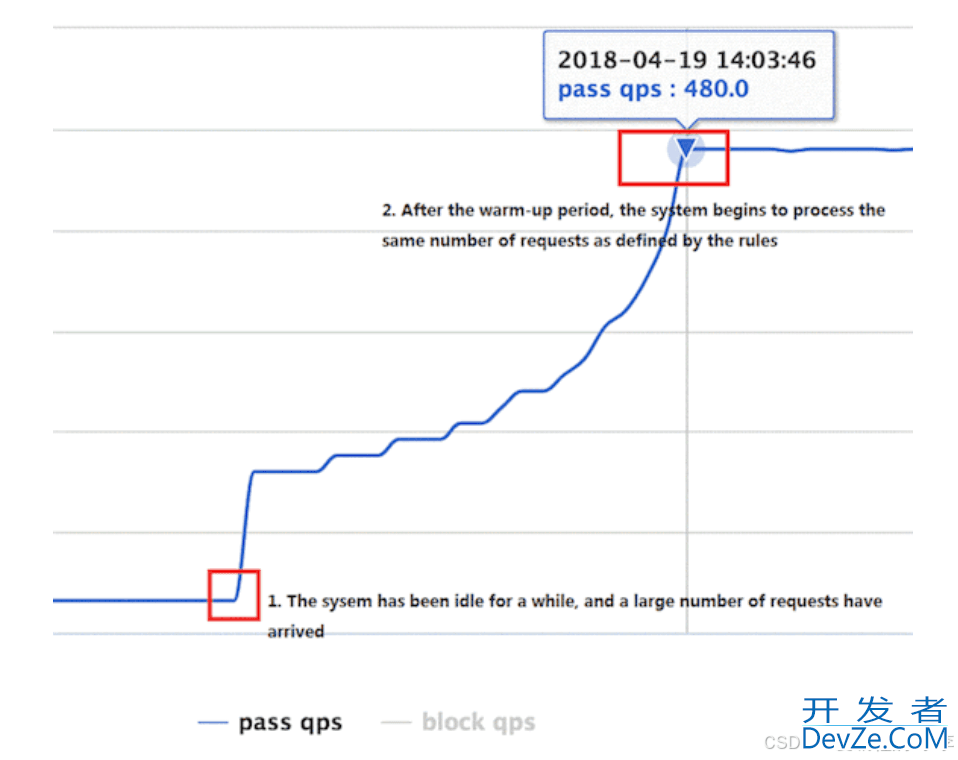
WarmUp 方式,即预热/冷启动方式。当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过"冷启动",让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。这块设计和 Java 类似。通常冷启动的过程系统允许通过的 QPS 曲线如下图所示:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"sync"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/base"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/flow"
)
const resName = "example-flow-qps-resource"
func main() {
//初始化sentinel
err := sentinel.InitDefault()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
//配置限流规则
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: resName,
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.WarmUp, //冷启动策略
ControlBehavior: flow.Reject, //直接拒绝
Threshold: 10, //1s10个并发
WarmUpPeriodSec: 30, //60s预热
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
var mutex sync.Mutex
lastSecond := time.Now().Second()
total := 0
totalRestrict := 0
totalPass := 0
ch := make(chan struct{})
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry(resName, sentinel.WithTrafficType(base.Inbound))
if b != nil {
// Blocked. We could get the block reason from the BlockError.
mutex.Lock()
totalRestrict++
mutex.Unlock()
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%10) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
// Passed, wrap the logic here.
mutex.Lock()
totalPass++
mutex.Unlock()
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%10) * time.Millisecond)
// Be sure the entry is exited finally.
e.Exit()
}
mutex.Lock()
total++
mutex.Unlock()
if time.Now().Second() != lastSecond {
mutex.Lock()
lastSecond = time.Now().Second()
fmt.Println("total=", total, ",totalRestrict=", totalRestrict, ",totalPass=", totalPass)
total = 0
totalRestrict = 0
totalPass = 0
mutex.Unlock()
}
}
}()
}
<-ch
}
趋势逐渐增加,一直到达每秒10个左右
Throttling策略
计算时间间隔,每过了时间间隔才允许通过
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/base"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/flow"
)
const resName = "example-flow-qps-resource"
func main() {
//初始化sentinel
err := sentinel.InitDefault()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
//配置限流规则
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: resName,
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.Direct,
ControlBehavior: flow.Throttling,
Threshold: 10,
StatIntervalInMs: 1000,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
ch := make(chan struct{})
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry(resName, sentinel.WithTrafficType(base.Inbound))
if b != nil {
// Blocked. We could get the block reason from the BlockError.
fmt.Println("被限流")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%10) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
// Passed, wrap the logic here.
fmt.Println("成功")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%10) * time.Millisecond)
// Be sure the entry is exited finally.
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
}
// Simulate a scenario in which flow rules are updated concurrently
go func() {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 10)
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: resName,
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.Direct,
ControlBehavior: flow.Reject,
Threshold: 80,
StatIntervalInMs: 1000,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
}()
<-ch
}

package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/base"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core编程客栈/flow"
)
const resName = "example-flow-qps-resource"
func main() {
//初始化sentinel
err := sentinel.InitDefault()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
//配置限流规则
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: resName,
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.Direct,
ControlBehavior: flow.Throttling,
Threshold: 10,
StatIntervalInMs: 1000,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
e, b := sentinel.Entry(resName, sentinel.WithTrafficType(base.Inbound))
if b != nil {
// Blocked. We could get the block reason from the BlockError.
fmt.Println("被限流")
} else {
// Passed, wrap the logic here.
fmt.Println("成功")
// Be sure the entry is exited finally.
e.Exit()
}
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
}
}

熔断
Sentinel 熔断降级基于熔断器模式 (circuit breaker pattern) 实现。熔断器内部维护了一个熔断器的状态机,状态机的转换关系如下图所示:
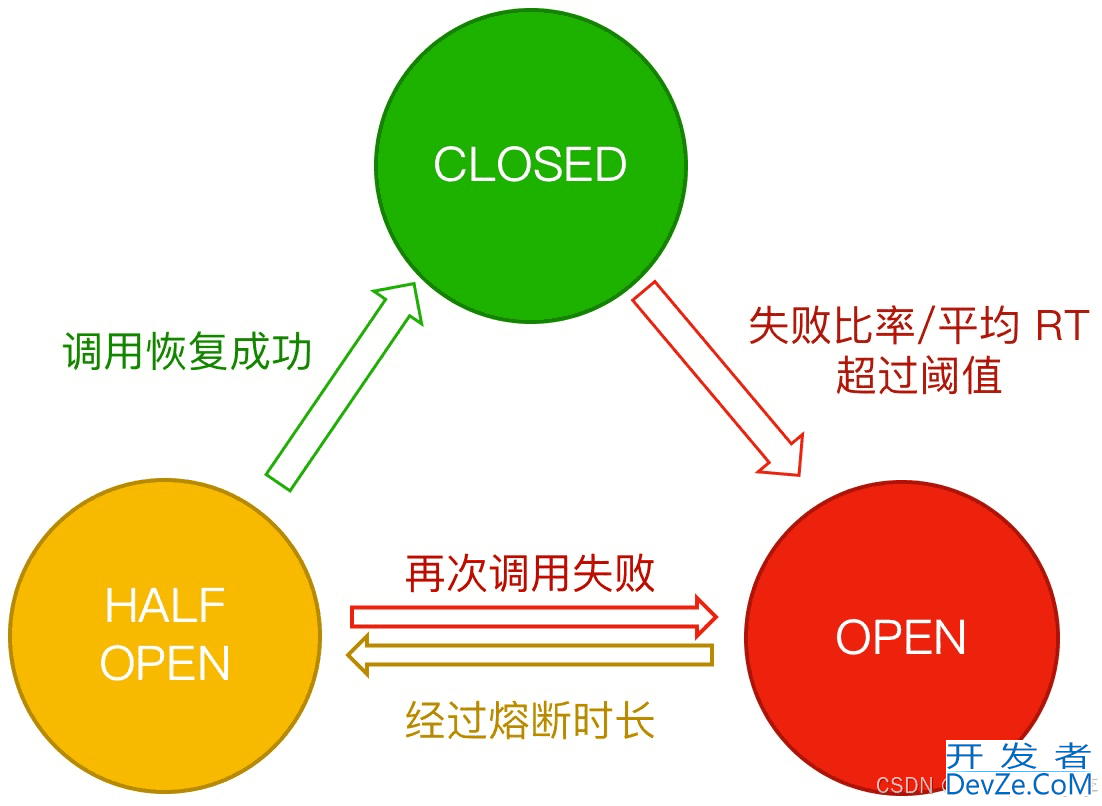
熔断器有三种状态:
1.Closed 状态:也是初始状态,该状态下,熔断器会保持闭合,对资源的访问直接通过熔断器的检查。2.Open 状态:断开状态,熔断器处于开启状态,对资源的访问会被切断。3.Half-Open 状态:半开状态,该状态下除了探测流量,其余对资源的访问也会被切断。探测流量指熔断器处于半开状态时,会周期性的允许一定数目的探测请求通过,如果探测请求能够正常的返回,代表探测成功,此时熔断器会重置状态到 Closed 状态,结束熔断;如果探测失败,则回滚到 Open 状态。这三种状态之间的转换关系这里做一个更加清晰的解释:
1.初始状态下,熔断器处于 Closed 状态。如果基于熔断器的统计数据表明当前资源触发了设定的阈值,那么熔断器会切换状态到 Open 状态;2.Open 状态即代表熔断状态,所有请求都会直接被拒绝。熔断器规则中会配置一个熔断超时重试的时间,经过熔断超时重试时长后熔断器会将状态置为 Half-Open 状态,从而进行探测机制;3.处于 Half-Open 状态的熔断器会周期性去做探测。Sentinel 提供了监听器去监听熔断器状态机的三种状态的转换,方便用户去自定义扩展:熔断策略
Sentinel 熔断器的三种熔断策略都支持静默期 (规则中通过MinRequestAmount字段表示)。静默期是指一个最小的静默请求数,在一个统计周期内,如果对资源的请求数小于设置的静默数,那么熔断器将不会基于其统计值去更改熔断器的状态。静默期的设计理由也很简单,举个例子,假设在一个统计周期刚刚开始时候,第 1 个请求碰巧是个慢请求,这个时候这个时候的慢调用比例就会是 100%,很明显是不合理,所以存在一定的巧合性。所以静默期提高了熔断器的精准性以及降低误判可能性。
Sentinel 支持以下几种熔断策略:慢调用比例策略 (SlowRequestRatio)
Sentinel 的熔断器不在静默期,并且慢调用的比例大于设置的阈值,则接下来的熔断周期内对资源的访问会自动地被熔断。该策略下需要设置允许的调用 RT 临界值(即最大的响应时间),对该资源访问的响应时间大于该阈值则统计为慢调用。
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/circuitbreaker"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/config"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/logging"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/util"
)
type stateChangeTestListener struct {
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToClosed(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Closed, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToOpen(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule, snapshot interface{}) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Open, snapshot: %.2f, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), snapshot, util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToHalfOpen(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Half-Open, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func main() {
conf := config.NewDefaultConfig()
// for testing, logging output to console
conf.Sentinel.Log.Logger = logging.NewConsoleLogger()
err := sentinel.InitWithConfig(conf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
ch := make(chan struct{})
// Register a state change listener so that we could observer the state change of the internal circuit breaker.
circuitbreaker.RegisterStateChangeListeners(&stateChangeTestListener{})
_, err = circuitbreaker.LoadRules([]*circuitbreaker.Rule{
// Statistic time span=5s, recoveryTimeout=3s, slowRtUpperBound=50ms, maxSlowRequestRatio=50%
{
Resource: "abc",
Strategy: circuitbreaker.SlowRequestRatio,
RetryTimeoutMs: 3000,
MinRequestAmount: 10,
StatIntervalMs: 5000,
StatSlidingWindowBucketCount: 10,
MaxAllowedRtMs: 50, //大于50ms是慢查询
Threshold: 0.5,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
logging.Info("[CircuitBreaker SlowRtRatio] Sentinel Go circuit breaking demo is running. You may see the pass/block metric in the metric log.")
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry("abc")
if b != nil {
// g1 blocked
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%20) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
if rand.Uint64()%20 > 9 {
// Record current invocation as error.
sentinel.TraceError(e, errors.New("biz error"))
}
// g1 passed
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%80+10) * time.Millisecond)
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry("abc")
if b != nil {
// g2 blocked
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%20) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
// g2 passed
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%80+10) * time.Millisecond)
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
<-ch
}
错误比例策略 (ErrorRatio)
Sentinel 的熔断器不在静默期,并且在统计周期内资源请求访问异常的比例大于设定的阈值,则接下来的熔断周期内对资源的访问会自动地被熔断。
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/circuitbreaker"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/config"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/logging"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/util"
)
type stateChangeTestListener struct{}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToClosed(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Closed, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToOpen(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule, snapshot interface{}) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Open, snapshot: %.2f, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), snapshot, util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToHalfOpen(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Half-Open, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func main() {
total := 0
totalPass := 0
totalBlock := 0
totalErr := 0
conf := config.NewDefaultConfig()
// for testing, logging output to console
conf.Sentinel.Log.Logger = logging.NewConsoleLogger()
err := sentinel.InitWithConfig(conf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
ch := make(chan struct{})
// Register a state change listener so that we could observer the state change of the internal circuit breaker.
circuitbreaker.RegisterStateChangeListeners(&stateChangeTestListener{})
_, err = circuitbreaker.LoadRules([]*circuitbreaker.Rule{
// Statistic time span=5s, recoveryTimeout=3s, maxErrorCount=50
{
Resource: "abc",
Strategy: circuitbreaker.ErrorRatio,
RetryTimeoutMs: 3000,
MinRequestAmount: 10,
StatIntervalMs: 5000,
StatSlidingWindowBucketCount: 10,
Threshold: 0.4,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
logging.Info("[CircuitBreaker ErrorCount] Sentinel Go circuit breaking demo is running. You may see the pass/block metric in the metric log.")
go func() {
for {
total++
e, b := sentinel.Entry("abc")
if b != nil {
// g1 blocked
totalBlock++
fmt.Println("熔断")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%20) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
if rand.Uint64()%20 > 9 {
totalErr++
// Record current invocation as error.
sentinel.TraceError(e, errors.New("biz error"))
}
totalPass++
// g1 passed
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%80+10) * time.Millisecond)
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry("abc")
if b != nil {
// g2 blocked
totalBlock++
fmt.Println("写成熔断了")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%20) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
// g2 passed
totalPass++
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint6js4()%80) * time.Millisecond)
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
go func() {
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Println(float64(totalErr) / float64(total))
}
}()
<-ch
}
错误计数策略 (ErrorCount)
Sentinel 的熔断器不在静默期,并且在统计周期内资源请求访问异常数大于设定的阈值,则接下来的熔断周期内对资源的访问会自动地被熔断。
注意:这里的错误比例熔断和错误计数熔断指的业务返回错误的比例或则计数。也就是说,如果规则指定熔断器策略采用错误比例或则错误计数,那么为了统计错误比例或错误计数,需要调用API: api.TraceError(entry, err) 埋点每个请求的业务异常。
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"time"
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/circuitbreaker"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/config"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/logging"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/util"
)
type stateChangeTestListener struct {
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToClosed(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Closed, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToOpen(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule, snapshot interface{}) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Open, snapshot: %d, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), snapshot, util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func (s *stateChangeTestListener) OnTransformToHalfOpen(prev circuitbreaker.State, rule circuitbreaker.Rule) {
fmt.Printf("rule.steategy: %+v, From %s to Half-Open, time: %d\n", rule.Strategy, prev.String(), util.CurrentTimeMillis())
}
func main() {
total := 0
totalPass := 0
totalBlock := 0
totalErr := 0
conf := config.NewDefaultConfig()
// for testing, logging output to console
conf.Sentinel.Log.Logger = logging.NewConsoleLogger()
err := sentinel.InitWithConfig(conf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
ch := make(chan struct{})
// Register a state change listener so that we could observer the state change of the internal circuit breaker.
circuitbreaker.RegisterStateChangeListeners(&stateChangeTestListener{})
_, err = circuitbreaker.LoadRules([]*circuitbreaker.Rule{
// Statistic time span=5s, recoveryTimeout=3s, maxErrorCount=50
{
Resource: "abc",
Strategy: circuitbreaker.ErrorCount,
RetryTimeoutMs: 3000,
MinRequestAmount: 10,
StatIntervalMs: 5000,
StatSlidingWindowBucketCount: 10,
Threshold: 50,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
logging.Info("[CircuitBreaker ErrorCount] Sentinel Go circuit breaking demo is running. You may see the pass/block metric in the metric log.")
go func() {
for {
total++
e, b := sentinel.Entry("abc")
if b != nil {
// g1 blocked
totalBlock++
fmt.Println("熔断")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%20) * time.Millisecond)
} else {
if rand.Uint64()%20 > 9 {
totalErr++
// Record current invocation as error.
sentinel.TraceError(e, errors.New("biz error"))
}
totalPass++
// g1 passed
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%80+10) * time.Millisecond)
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
go func() {
for {
e, b := sentinel.Entry("abc")
if b != nil {
// g2 blocked
totalBlock++
fmt.Println("写成熔断了")
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%20) * time.Millisecond)
www.devze.com} else {
// g2 passed
totalPass++
time.Sleep(time.Duration(rand.Uint64()%80) * time.Millisecond)
e.Exit()
}
}
}()
go func() {
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Println(totalErr)
}
}()
<-ch
}
gin集成sentinel限流
初始化
package initialize
import (
sentinel "github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/api"
"github.com/alibaba/sentinel-golang/core/flow"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
func InitSentinel() {
//初始化sentinel
err := sentinel.InitDefault()
if err http://www.devze.com!= nil {
zap.S().Fatal(err)
}
//配置限流规则
//这种配置从nacos读取
_, err = flow.LoadRules([]*flow.Rule{
{
Resource: "test",
TokenCalculateStrategy: flow.Direct,
ControlBehavior: flow.Reject,
Threshold: 10,
StatIntervalInMs: 1000,
},
})
if err != nil {
zap.S().Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
}
调用
initialize.InitSentinel()
限流
e, b := sentinel.Entry("goods-list", sentinel.WithTrafficType(base.Inbound))
if b != nil {
ctx.jsON(http.StatusTooManyRequests, gin.H{
"msg": "请求过于频繁,请稍后重试",
})
return
}
r, err := global.GoodsSrvClient.GoodsList(context.WithValue(context.Background(), "ginContext", ctx), request)
if err != nil {
zap.S().Errorw("[List] 查询 【商品列表】失败")
return
}
e.Exit()
到此这篇关于golang 熔断限流降级实践的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关golang 熔断限流降级内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论