目录
- 一、介绍
- 1.1 工作原理
- 1.2 重要概念
- 二、基本应用
- 2.1 构建项目
- 2.2 添加yaml路由配置
- 2.3 测试
- 三、核心原理解析
- 3.1 GatewayAutoConfiguration
- 3.2 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
- 3.3 FilteringWebHandler
- 3.4 NettyRoutingFilter
一、介绍
SpringCloud Gateway 是 Spring 官方基于 Spring Spring Boot 和 Project Reactor 等技术开发的网关,Gateway 旨在为微服务架构提供一种简单而有效的统一的API路由管理方式。Gateway作为 Spring Cloud 生态系中的网关,目标是替代 ZUUL,其不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/埋点,和限流等。
1.1 工作原理
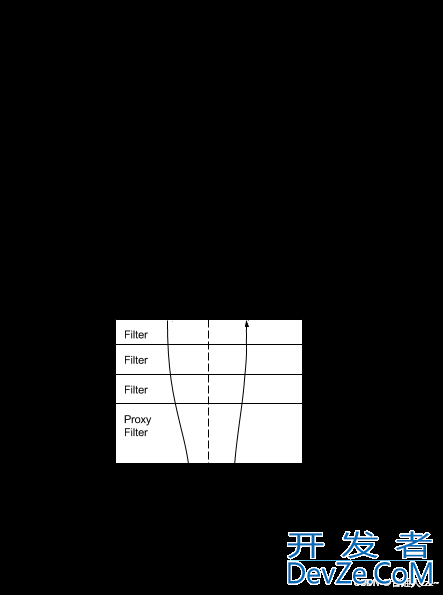
1.2 重要概念
- 路由(Route): 路由是Gateway的基础构建块。它由ID、目标URL、一组断言和过滤器定义。如果断言评估为true,则路由匹配并执行相关的过滤器链。
- 断言(Predicate): 输入的请求会被一组断言评估,如果断言为true,则路由匹配。常用的断言包括路径匹配、查询参数匹配、请求头匹配等。
- 过滤器(Filter): 过滤器在特定的生命周期中拦截并修改请求和响应。过滤器可以作用在代理前、代理后、或者出错时。常见的过滤器有:添加响应头、限流、日志记录等。
二、基本应用
2.1 构建项目
pom.XML
<properties>
<Java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.6.13</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2021.0.5</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2021.0.5</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.2 添加yaml路由配置
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
# 网关路由配置
routes:
# 路由id,自定义,只要唯一即可
- id: provider-baidu
# 路由的目标地址
uri: https://www.baidu.com
predicates: # 路由断言,判断请求是否符合路由规则的条件
- Path=/s/** # 按照路径匹配(PathRoutePredicateFactory),以/s/开头的请求就符合要求
- id: provider-csdn
# 路由的目标地址
uri: https://blog.csdn.net/
predicates: # 路由断言,判断请求是否符合路由规则的条件
- Path=/csdn/** # 按照路径匹配(PathRoutePredicateFactory),以/csdn/开头的请求就符合要求
2.3 测试
访问 http://localhost:8080/s?wd=1,则自动显示 https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=1 内容,结果如下:
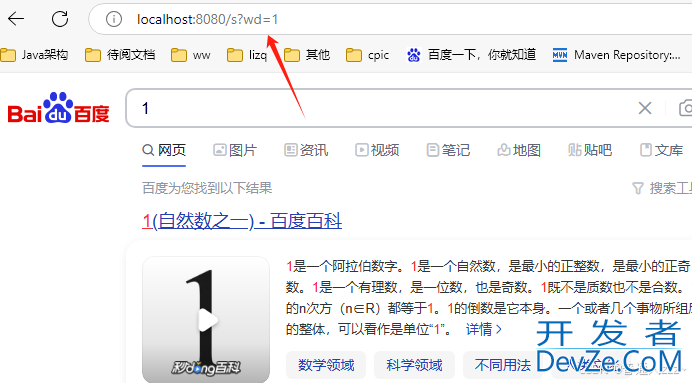
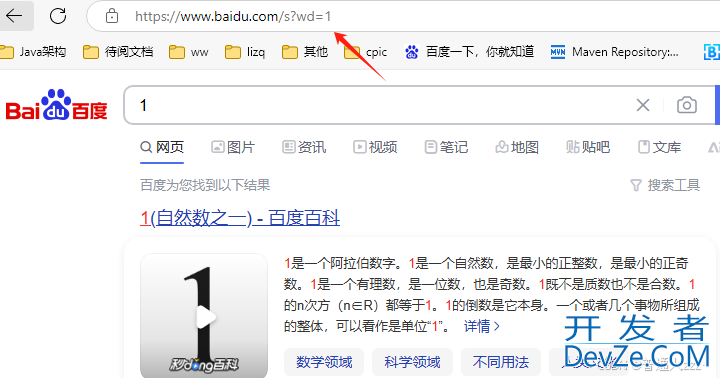
三、核心原理解析
3.1 GatewayAutoConfiguration
根据约定大于配置思想,结合springboot start原理,可以找到 Gateway自动注入类。
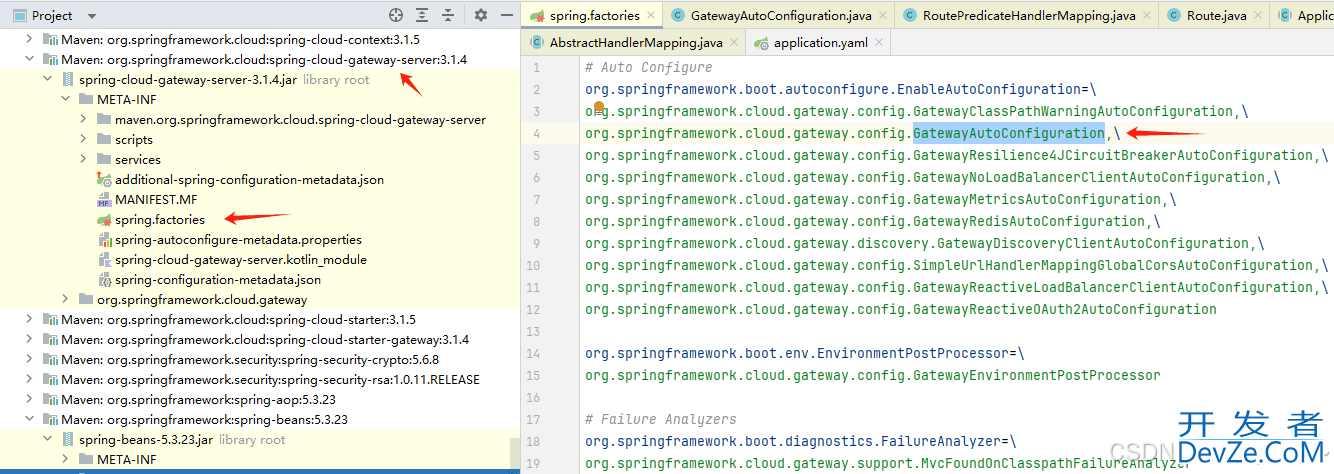
结合SpringMVC底层原理分析,Url的匹配,是在 HandlerMapping 中找到对应的 HandlerAdaptor 后进行处理,Gateway也运用了这一点,核心存在一个 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 类,用于根据请求url以及配置的所有路由,查找到一个 Route(路由),在进行相关处理后,进行Http调用。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.cloud.gateway.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@AutoConfigureBefore({ HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter({ GatewayReactiveLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration.class,
GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguration.class })
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherHandler.class)
public class GatewayAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RoutePredicateHandlerMapping routePredicateHandlerMapping(FilteringWebHandler webHandler,
RouteLocator routeLocator, GlobalCorsProperties globalCorsProperties, Environment environment) {
return new RoutePredicateHandlerMapping(webHandler, routeLocator, globalCorsProperties, environment);
}
}
3.2 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
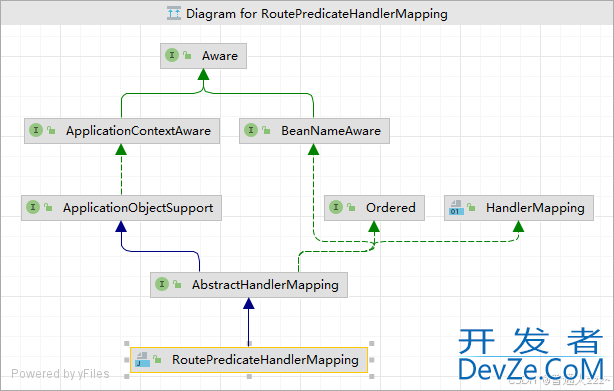
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 继承了 AbstractHandlerMapping 类,实现了
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends ApplicapythontionObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
@Override
public Mono<Object> getHandler(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return getHandlerInternal(exchange).map(handler -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(exchange.getLogPrefix() + "Mapped to " + handler);
}
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) www.devze.com{
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ?
this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(exchange) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, exchange);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
if (!this.corsProcessor.process(config, exchange) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return NO_OP_HANDLER;
}
}
return handler;
});
}
/**
* 查找给定请求的处理程序,如果未找到特定的处理程序,则返回空的
*/
protected abstract Mono<?> getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange);
}
则 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping#getHandlerInternal 核心代码如下:
public class RoutePredicateHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMapping {
@Override
protected Mono<?> getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// don't handle requests on management port if set and different than server port
if (this.managementPortType == DIFFERENT && this.managementPort != null
&& exchange.getRequest().getURI().getPort() == thpythonis.managementPort) {
return Mono.empty();
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_HANDLER_MAPPER_ATTR, getSimpleName());
return lookupRoute(exchange) // 查找路由
// .log("route-predicate-handler-mapping", Level.FINER) //name this
.flatMap((Function<Route, Mono<?>>) r -> {
exchange.getAttributes().remove(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "] to " + r);
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR, r);
return Mono.just(webHandler);
}).switchIfEmpty(Mono.empty().then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
exchange.getAttributes().remove(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No RouteDefinition found for [" + getExchangeDesc(exchange) + "]");
}
})));
}
/**
* 查找路由
*/
protected Mono<Route> lookupRoute(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return this.routeLocator.getRoutes()
// individually filter routes so that filterWhen error delaying is not a
// problem
.concatMap(route -> Mono.just(route).filterWhen(r -> {
// add the current route we are testing
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR, r.getId());
return r.getPredicate().apply(exchange);
})
// instead of immediately stopping main flux due to error, log and
// swallow it
.doOnError(e -> logger.error("Error applying predicate for route: " + route.getId(), e))
.onErrorResume(e -> Mono.empty()))
// .defaultIfEmpty() put a static Route not found
// or .switchIfEmpty()
// .switchIfEmpty(Mono.<Route>empty().log("noroute"))
.next()
// TODO: error handling
.map(route -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Route matched: " + route.getId());
}
validateRoute(route, exchange);
return route;
});
}
}
其中,final RouteLocator routeLocator; 对象存储了所有配置的路由(route),如下:

Gateway会根据断言Predicate进行匹配,找到对应的Route,再进行路由等其他处理。
Route
public class Route implements Ordered {
private final String id;
private final URI uri;
private final int order;
private final AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate;
private final List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters;
private final Map<String, Object> metadata;
private Route(String id, URI uri, int order, AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate,
List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters, Map<String, Object> metadata) {
this.id = id;
this.uri = uri;
this.order = order;
this.predicate = predicate;
this.gatewayFilters = gatewayFilters;
this.metadata = metadata;
}
}
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping#getHandler 如果匹配成功,最终会返回一个处理 FilteringWebHandler 类,如下:
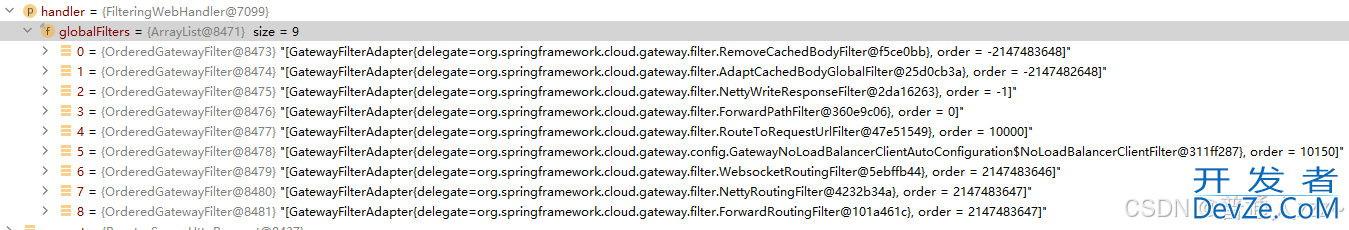
3.3 FilteringWebHandler
WebHandler
/**
* 用于处理 Web 请求的协定。
*/
public interface WebHandler {
/**
* Handle the web server exchange.
* @param exchange the current server exchange
* @return {@code Mono<Void>} to indicate when request handling is complete
*/
Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange);
}
则最终会调用到 FilteringWebHandler#handle 方法中:
public class FilteringWebHandler implements WebHandler {
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
Route route = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
// 获取当前 Route 配置的Filter
List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = route.getFilters();
// 获取全局的Filter
List<GatewayFilter> combined = new ArrayList<>(this.globalFilters);
combined.addAll(gatewayFilters);
// TODO: needed or cached?
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(combined);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Sorted gatewayFilterFactories: " + combined);
}
// 构建一个FilterChain,最终进行调用
return new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(combined).filter(exchange);
}
private static class DefaultGatewayFilterChain implements GatewayFilterChain {
private final int index;
private final List<GatewayFilter> filters;
DefaultGatewayFilterChain(List<GatewayFilter> filters) {
this.filters = filters;
this.index = 0;
}
private DefaultGatewayFilterChain(DefaultGatewayFilterChain parent, int index) {
this.filters = parent.getFilters();
this.index = index;
}
public List<GatewayFilter> getFilters() {
return filters;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return Mono.defer(() -> {
if (this.index < filters.size()) {
GatewayFilter filter = filters.get(thiphps.index);
DefaultGatewayFilterChain chain = new DefaultGatewayFilterChain(this, this.index + 1);
return filter.filter(exchange, chain);
}
else {
return Mono.empty(); // complete
}
});
}
}
}
handle 方法处理逻辑为:
- 获取当前 Route 配置的Filter;
- 获取全局的Filter;
- 将所有的Filter排序后,构建成一个FilterChain;
- 在所有的Filter中,根据具体协议选择最终的Filter,进行最终路由;
3.4 NettyRoutingFilter
NettyRoutingFilter 为最终进行Http路由的类。
public class NettyRoutingFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("Duplicates")
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
URI requestUrl = exchange.getRequiredAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
Strinandroidg scheme = requestUrl.getScheme();
if (isAlreadyRouted(exchange) || (!"http".equalsIgnoreCase(scheme) && !"https".equalsIgnoreCase(scheme))) {
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
setAlreadyRouted(exchange);
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
final HttpMethod method = HttpMethod.valueOf(request.getMethodValue());
final String url = requestUrl.toASCIIString();
HttpHeaders filtered = filterRequest(getHeadersFilters(), exchange);
final DefaultHttpHeaders httpHeaders = new DefaultHttpHeaders();
filtered.forEach(httpHeaders::set);
boolean preserveHost = exchange.getAttributeOrDefault(PRESERVE_HOST_HEADER_ATTRIBUTE, false);
Route route = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
// 获取HttpClient,并进行send
Flux<HttpClientResponse> responseFlux = getHttpClient(route, exchange).headers(headers -> {
headers.add(httpHeaders);
// Will either be set below, or later by Netty
headers.remove(HttpHeaders.HOST);
if (preserveHost) {
String host = request.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.HOST);
headers.add(HttpHeaders.HOST, host);
}
}).request(method).uri(url).send((req, nettyOutbound) -> {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
nettyOutbound.withConnection(connection -> log.trace("outbound route: "
+ connection.channel().id().asShortText() + ", inbound: " + exchange.getLogPrefix()));
}
return nettyOutbound.send(request.getBody().map(this::getByteBuf));
}).responseConnection((res, connection) -> {
// Defer committing the response until all route filters have run
// Put client response as ServerWebExchange attribute and write
// response later NettyWriteResponseFilter
exchange.getAttributes().put(CLIENT_RESPONSE_ATTR, res);
exchange.getAttributes().put(CLIENT_RESPONSE_CONN_ATTR, connection);
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
// put headers and status so filters can modify the response
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
res.responseHeaders().forEach(entry -> headers.add(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
String contentTypeValue = headers.getFirst(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(contentTypeValue)) {
exchange.getAttributes().put(ORIGINAL_RESPONSE_CONTENT_TYPE_ATTR, contentTypeValue);
}
setResponseStatus(res, response);
// make sure headers filters run after setting status so it is
// available in response
HttpHeaders filteredResponseHeaders = HttpHeadersFilter.filter(getHeadersFilters(), headers, exchange,
Type.RESPONSE);
if (!filteredResponseHeaders.containsKey(HttpHeaders.TRANSFER_ENCODING)
&& filteredResponseHeaders.containsKey(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_LENGTH)) {
// It is not valid to have both the transfer-encoding header and
// the content-length header.
// Remove the transfer-encoding header in the response if the
// content-length header is present.
response.getHeaders().remove(HttpHeaders.TRANSFER_ENCODING);
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(CLIENT_RESPONSE_HEADER_NAMES, filteredResponseHeaders.keySet());
response.getHeaders().addAll(filteredResponseHeaders);
return Mono.just(res);
});
Duration responseTimeout = getResponseTimeout(route);
if (responseTimeout != null) {
responseFlux = responseFlux
.timeout(responseTimeout,
Mono.error(new TimeoutException("Response took longer than timeout: " + responseTimeout)))
.onErrorMap(TimeoutException.class,
th -> new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.GATEWAY_TIMEOUT, th.getMessage(), th));
}
return responseFlux.then(chain.filter(exchange));
}
}
到此这篇关于SpringCloud Gateway路由核心原理解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringCloud Gateway路由内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论