目录
- 0. 需求
- 1. 采用一个配置文件的情况
- 1.1. 数据源类
- 1.2. 数据源配置类
- 1.3 DAO层用到数据源
- 1.4. 配置文件
- 1.5. 测试代码
- 1.6. 测试结果
- 1.6.1 配置文件中的spring.profiles=dev
- 1.6.2 配置文件中的spring.profiles=test
- 1.6.3 配置文件中的spring.profiles=prod
- 2. 采用多个配置文件的情况
- 2.1 . 三个环境对应的配置文件
- 2.1.1 dev环境的配置信息
- 2.1.2 test环境的配置信息
- 2.1.3 prod环境的配置信息
- 2.2. 数据源类
- 2.3. DAO层需要用到数据源
- 2.4. 在主配置文件中开启需要使用哪个环境的配置文件
- 2.4.1. 开启dev
- 2.4.2. 开启test
- 2.4.3. 开启prod
- 3. 使用建议
0. 需求
通常项目开发过程中,会经历多种环境转换,典型的如开发环境(dev)、测试环境(test)和生产环境(prod)。在这三种不同的环境下,连接数据库时使用的配置信息是不同的,即三个不同环境对应三个不同的数据库。
现在的需求是:当在不同的环境下,想通过修改配置文件来连接不同的数据库。比如在开发过程中启动项目时,想连接开发环境对应的数据库,可以在配置文件中指定 environment = dev。其他环境类似,此时就需要用到Spring为我们提供的Profile功能。
1. 采用一个配置文件的情况
当SpringBoot项目只使用一个配置文件(application.yml或application.properties)时,如果想在这个配置文件中通过配置切换不同数据源,可以按照如下步骤:
1.1. 数据源类
package com.shg.spring.ioc.bean;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class MyDataSource {
private String username;
private String password;
private String url;
private String driver;
}
1.2. 数据源配置类
package com.shg.spring.ioc.config;
import com.shg.spring.ioc.bean.MyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
@Configuration
public class MyDataSourceConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.user.dev}")
private String usernameForDev;
@Value("${jdbc.password.dev}")
private String passwordForDev;
@Value("${jdbc.jdbcUrl.dekznoMAilOcv}")
private String urlForDev;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClass.dev}")
private String driverForDev;
@javascriptValue("${jdbc.user.test}")
private String usernameForTest;
@Value("${jdbc.password.test}")
private String passwordForTest;
@Value("${jdbc.jdbcUrl.test}")
private String urlForTest;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClass.test}")
private String driverForTest;
@Value("${jdbc.user.prod}")
private String usernameForProd;
@Value("${jdbc.password.pro}")
private String passwordForProd;
@Value("${jdbc.jdbcUrl.pro}")
private String urlForProd;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClass.pro}")
private String driverForProd;
@Profile(value = {"default", "dev"})
@Bean
public MyDataSource dev() {
MyDataSource myDataSource = new MyDataSource();
myDataSource.setDriver(driverForDev);
myDataSource.setUrl(urlForDev);
myDataSource.setUsername(usernameForDev);
myDataSource.setPassword(passwordForDev);
return myDataSource;
}
@Profile(value = {"test"})
@Bean
public MyDataSource test() {
MyDataSource myDataSource = new MyDataSource();
myDataSource.setDriver(driverForTest);
myDataSource.setUrl(urlForTest);
myDataSource.setUsername(usernameForTest);
myDataSource.setPassword(passwordForTest);
return myDataSource;
}
@Profile(value = {"prod"})
@Bean
public MyDataSource prod() {
MyDataSource myDataSource = new MyDataSource();
myDat编程aSource.setDriver(driverForProd);
myDataSource.setUrl(urlForProd);
myDataSource.setUsername(usernameForProd);
myDataSource.setPassword(passwordForProd);
return myDataSource;
}
}
1.3 DAO层用到数据源
package com.shg.spring.ioc.dao;
import com.shg.spring.ioc.bwww.devze.comean.MyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class HelloDao {
// DAO层需要注入数据源
@Autowired
private MyDataSource myDataSource;
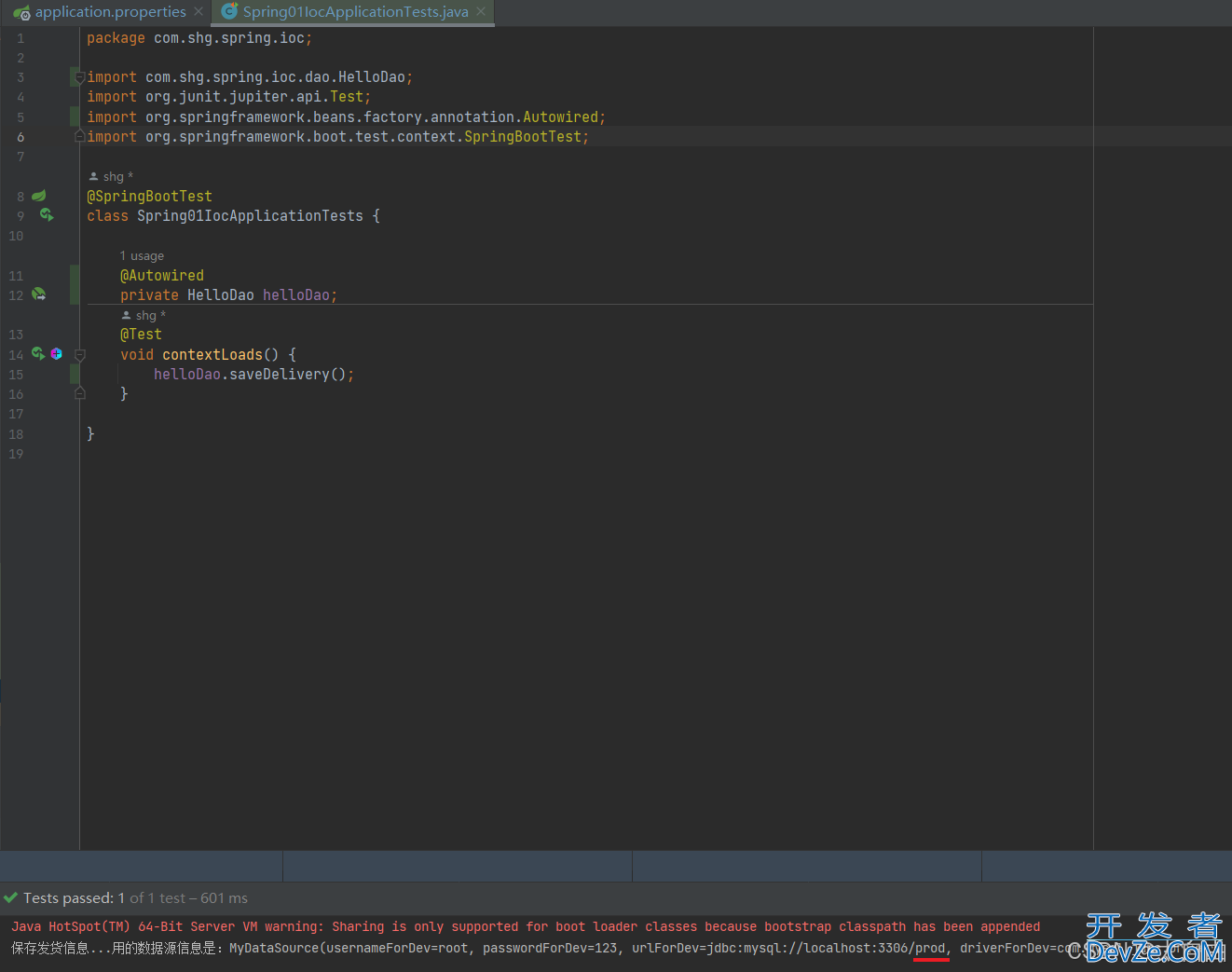
// 保存发货信息
public void saveDelivery() {
System.out.println("保存发货信息...用的数据源信息是:" + myDataSource);
}
}
1.4. 配置文件
spring.application.name=spring-01-ioc spring.profiles.active=dev jdbc.jdbcUrl.dev=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dev jdbc.driverClass.dev=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.user.dev=root jdbc.password.dev=123 jdbc.jdbcUrl.test=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test jdbc.driverClass.test=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.user.test=root jdbc.password.test=123 jdbc.jdbcUrl.prod=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/prod jdbc.driverClass.prod=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.user.prod=root jdbc.password.prod=123
1.5. 测试代码
package com.shg.spring.ioc;
import com.shg.spring.ioc.dao.HelloDao;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Spring01IocApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc = SpringApplication.run(Spring01IocApplication.class, args);
HelloDao helloDao = ioc.getBean(HelloDao.class);
helloDao.saveDelivery();
}
}
1.6. 测试结果
1.6.1 配置文件中的spring.profiles=dev
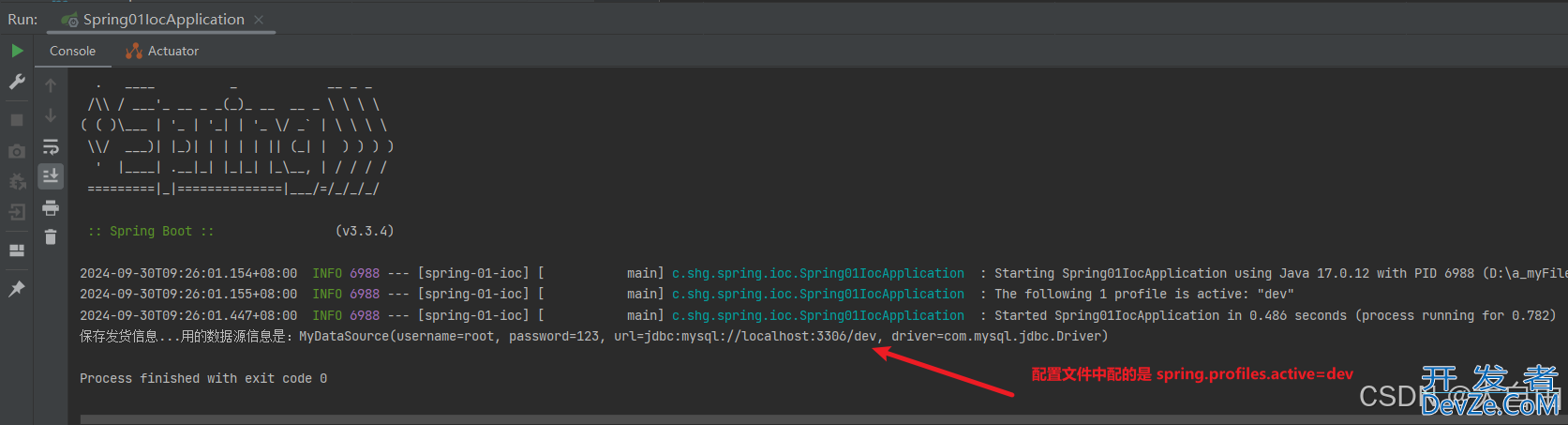
1.6.2 配置文件中的spring.profiles=test
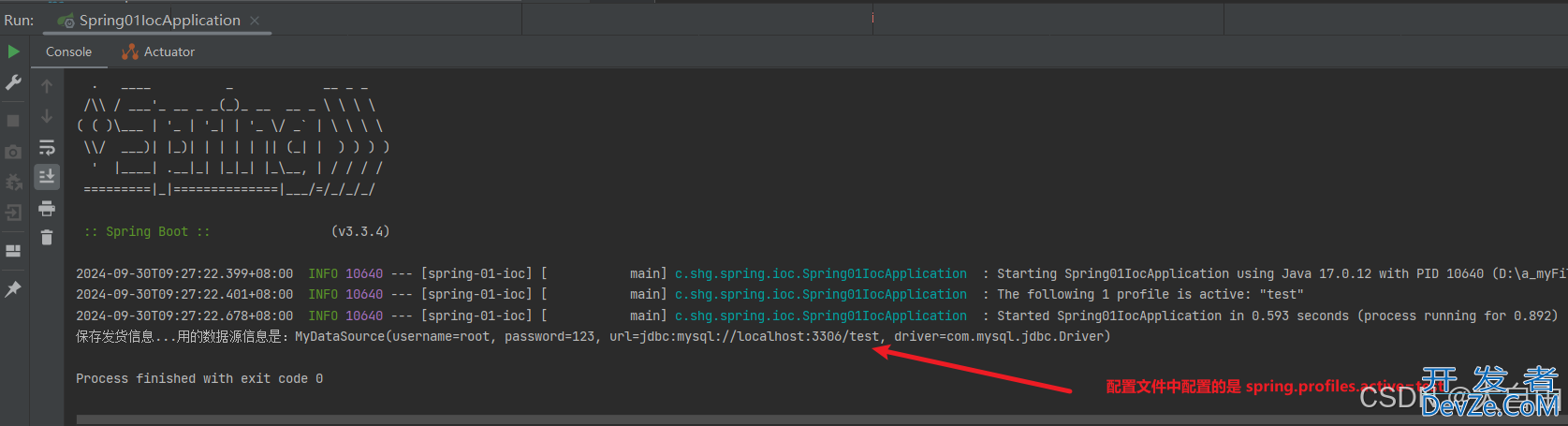
1.6.3 配置文件中的spring.profiles=prod
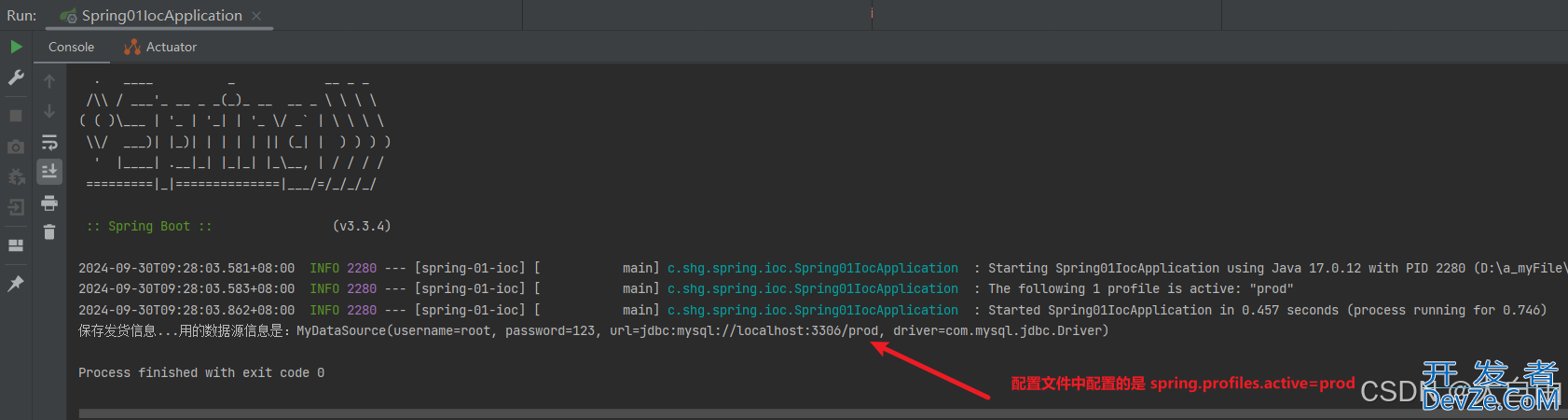
2. 采用多个配置文件的情况
上面的例子中,只使用一个配置文件。需要在这个配置文件中配置三种环境的配置信息,感觉不太好...
【你也可能会反驳说,我直接使用一组配置信息,不分什么dev,test和prod环境,在配置类中也不用标注@Profile注解,而是在部署对应环境的时候,修改这个数据源的配置信息,这当然也是可以的,但是不要忘了我们现在是在讨论 Profile这个功能,这样举例子会更加清楚明了】
下面我们采用另一种方式,来实现我们的需求,即:在不同的环境下,可以直接通过修改配置文件来连接不同的数据库。
2.1 . 三个环境对应的配置文件
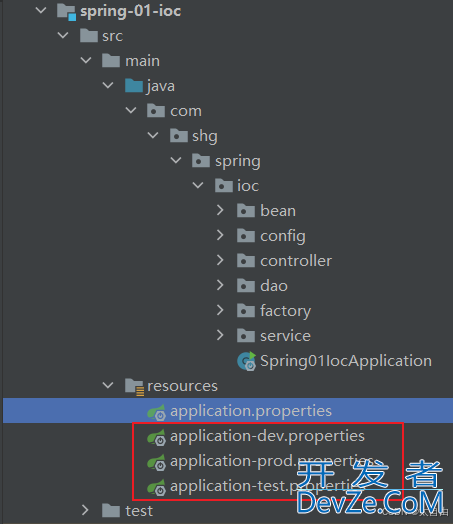
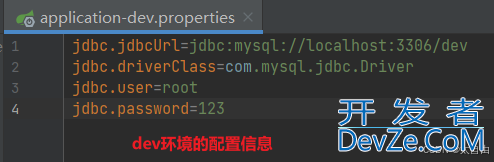
2.1.1 dev环境的配置信息
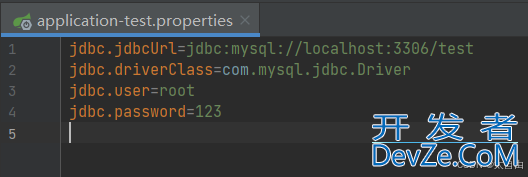
2.1.2 test环境的配置信息
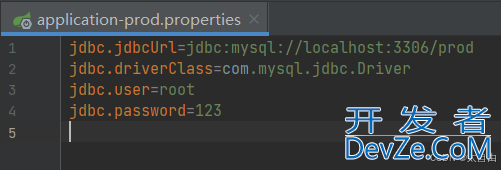
2.1.3 prod环境的配置信息
2.2. 数据源类
package com.shg.spring.ioc.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
public class MyDataSource {
@Value("${jdbc.user}")
private String usernameForDev;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String passwordForDev;
@Value("${jdbc.jdbcUrl}")
private String urlForDev;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClass}")
private String driverForDev;
}
2.3. DAO层需要用到数据源
package com.shg.spring.ioc.dao;
import com.shg.spring.ioc.bean.MyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class HelloDao {
// DAO层需要注入数据源
@Autowired
private MyDataSource myDataSource;
// 保存发货信息
publjavascriptic void saveDelivery() {
System.out.println("保存发货信息...用的数据源信息是:" + myDataSource);
}
}
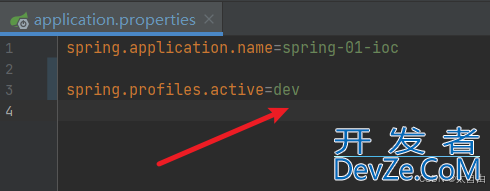
2.4. 在主配置文件中开启需要使用哪个环境的配置文件
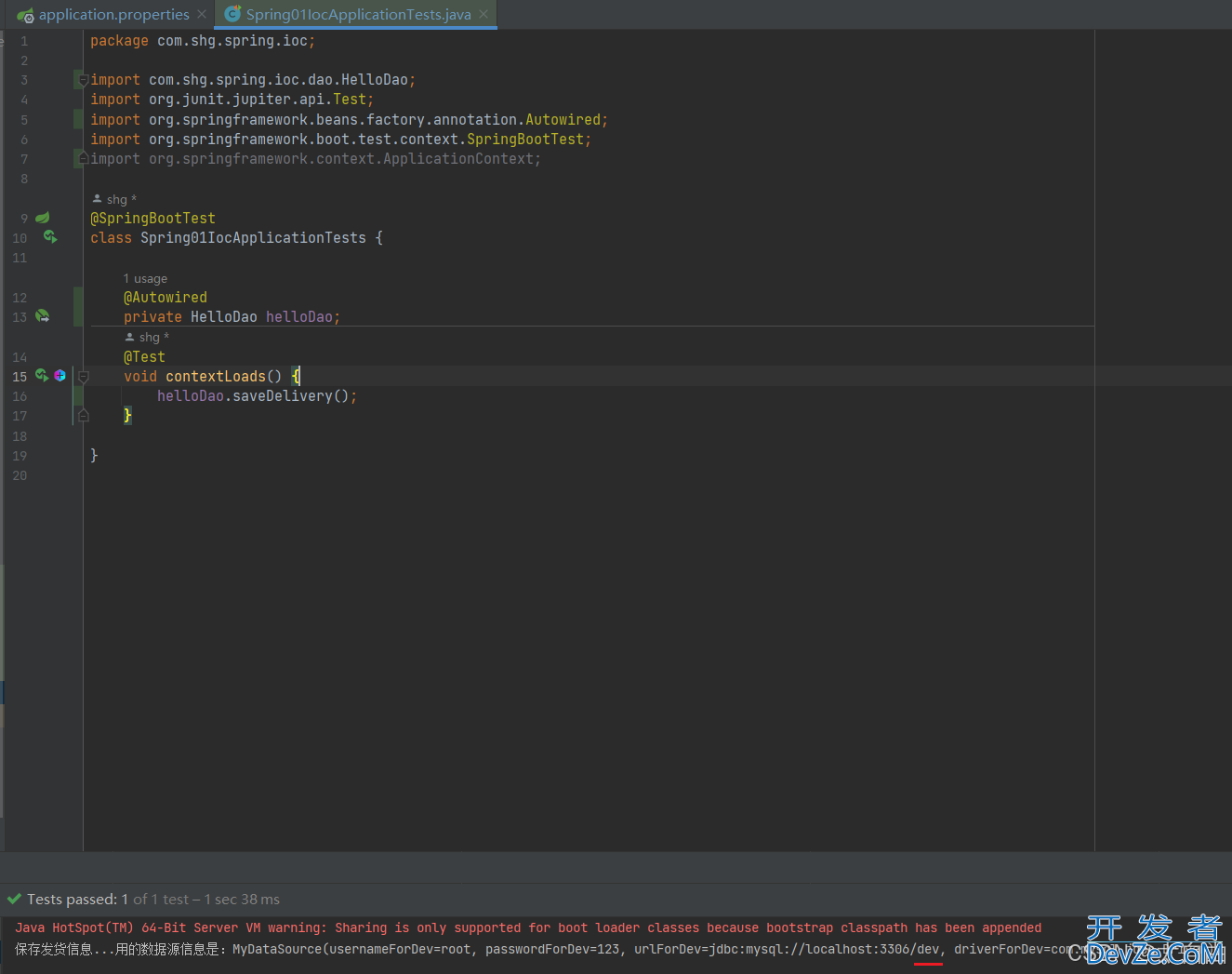
2.4.1. 开启dev
测试结果:
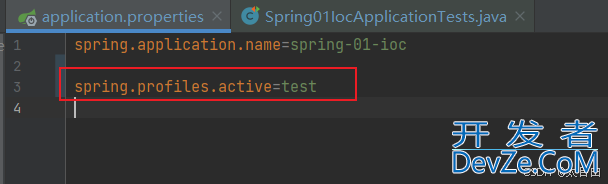
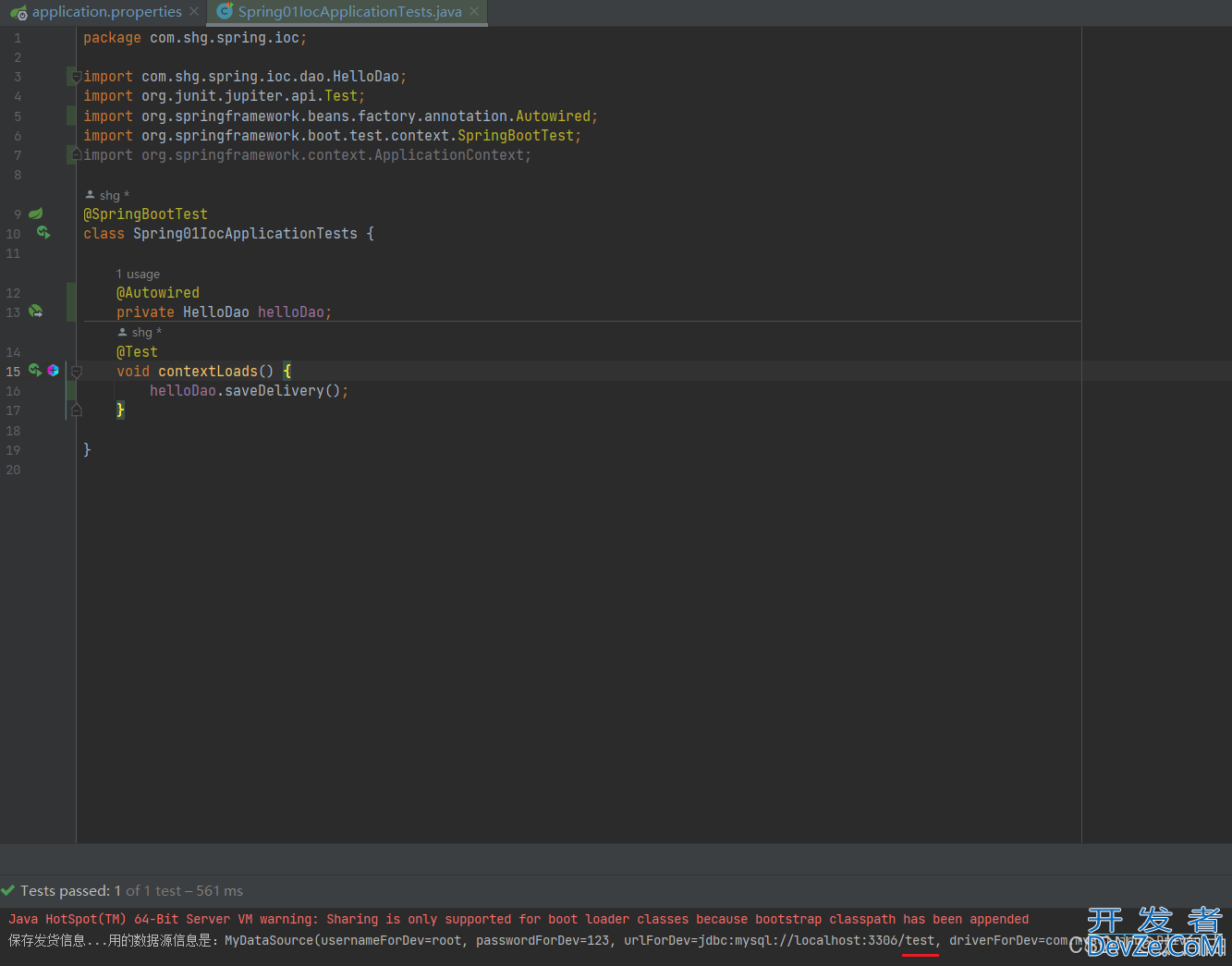
2.4.2. 开启test
测试结果:
2.4.3. 开启prod
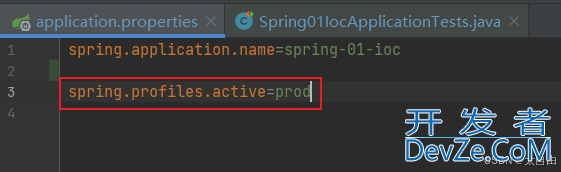
测试结果:
3. 使用建议
在实际项目中,推荐在不同环境使用不同的配置文件。
以上就是SpringBoot之Profile的两种使用方式详解的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot Profile使用方式的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论