目录
- Application.yml的自定义属性的读取
- 以前,接口定义常量
- spring中在application.yml中管理常量
- 方式1:@Value
- 方式2:@ConfigurationProperties
- 创建属性类的时候会有一个提示
- 总结
Application.yml的自定义属性的读取
以前我们会把一些常量,放在接口中,因为接口默认属性就是静态的,缺省了public static final
注意:既可以读取自定义的属性,也可以读取官方封装好的属性。
以前,接口定义常量
public interface WeixinPayConstants { // 接口里面默认属性就是静态常量,可以缺深public static fianl
// APID
String APPID = "45645x编程xx2";
// 商户号
String MCID = "48xxxxx787";
// 回调地址
String CALLBACK_URL = "https://wxxxxxlback";
// 私key
String APISECRET = "SDFLKxxxxx23423423";
}
- 方式1:@Value
- 方式2:@ConfigurationProperties
spring中在application.yml中管理常量
方式1:@Value
第一步:在application.yml中自定义属性
# 环境激活
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
#自定义属性,把上面接口的常量放这,冒号后面至少要有一个空格
ksd:
weixin:
appid: 456453sdfsd52342
mcid: 48878787
callbackurl: https://www.kuangstudy.com/pay/callback
apiscret: SDFLKSDJFKLSJKLJ23423423
第二步:使用@Value(“${}”)来注入使用
前提:注入的地方一定要已近交给了IOC容器管理
@Servic编程e
public class WeixinPayService {
@Value("${ksd.weixin.appid}")
private String appid;
@Value("${ksd.weixin.mcid}")
private String mcid;
@Value("${ksd.weixin.callbackurl}")
private String callbackurl;
@Value("${ksd.weixin.apisecret}")
private String apisecret;
public void testvalue(){
System.out.println(appid);
System.out.println(mcid);
System.out.println(callbackurl);
System.out.println(apisecret);
}
}
方式2:@ConfigurationProperties
这种方式具有面向对象的特性,把属性注入道属性类中,而不是上面@Value注入道某一个属性中。
第一步:@ConfigurationProperties(prefix =“路python径前缀”)定义一个配属性类,且属性一定要生成getter,setter方法
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix ="ksd.weixin")
public class WeixinPayProperties {
// appid
private String appid;
// 商户号
private String mcid;
// 回调地址
javascript private String callbackurl;
// api私钥
private String apisecret;
public String getAppid() {
return appid;
}
public void setAppid(String appid) {
this.appid = appid;
}
public String getMcid() {
return mcid;
}
public void setMcid(String mcid) {
this.mcid = mcid;
}
public String getCallbackurl() {
return callbackurl;
}
public void setCallbackurl(String callbackurl) {
this.callbackurl = callbackurl;
}
public String getApisecret() {
return apisecret;
}
public void setApisecret(String apisecret) {
this.apisecret = apisecret;
}
}
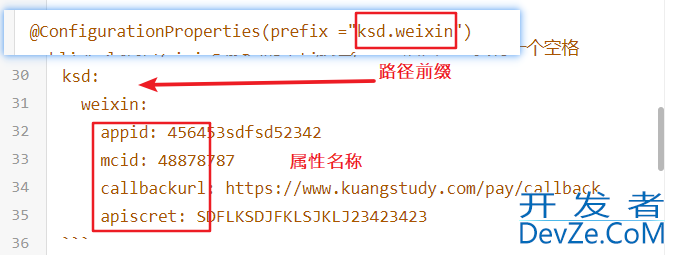
第二步:在启动类上或者属性类上加上注解@EnableConfigurationProperties(WeixinPayProperties.class)
@Configuration
这两个注解告诉springboot去加载这个属性配置类以及去完成属性注入
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix ="ksd.weixin")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WeixinPayProperties.class)
@Configuration
public class WeixinPayProperties {
......
}
第三步:注入.get方法使用
@Service
public class WeixinPayService {
@Autowired
private WeixinPayProperties weixinPayProperties;
public void testvalue2() {
System.out.println(weixinPayProperties.getAppid());
System.out.println(weixinPayProperties.getApisecret());
System.out.println(weixinPayProperties.getMcid());
System.out.println(weixinPayProperties.getCallbackurl());
}
}
创建属性类的时候会有一个提示
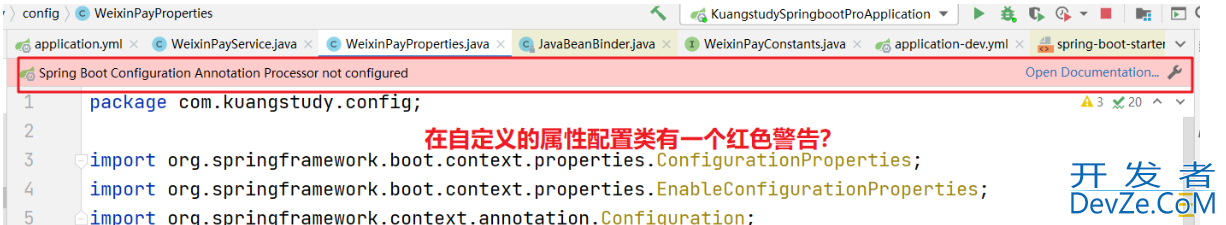
这个警告是告诉,springboot确实可以去帮你完成属性和配置文件中的属性自动注入,但是不能在配置文件中自动提示
解决:
添加依赖
<!--把项目中的springboot自定义属性配置类生成一个元素javascript数据文件,这个文件可以生成以后
在未来的配置文件中,我们就达到和官方一致效果,可以自动提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
然后关掉配置文件,再重写编译
手动编译:
mvn clean compile
用工具编译
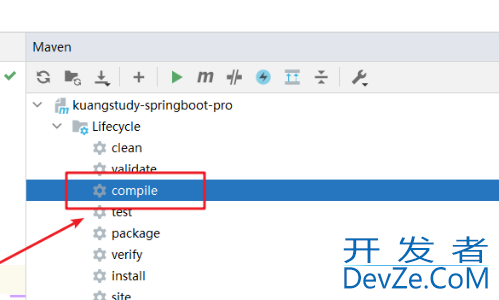
最终,实际开发中@Value用的较多
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)。
 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论