目录
- threadpool.h
- 测试文件
接着上文,我们使用了基于C++11实现的手写线程池,自己实现了Any类,Semaphore类以及Result类的开发,其中很多细节是值得学习的,随着不断更新,在C++17中提供future类,使得代码更加轻量化。接下来我们来看一下源码剖析:
threadpool.h
在最终版,除去 submitTask 以及 threadFunc 其余部分和基于C++11是一样的,这里不自定义Any类,Semaphore类以及Result类,使用C++17中提供的future类,并且支持用户输入任意类型,任意参数数量的任务.
首先,定义了一个Task任务,不确定函数返回值类型using Task = std::function<void()>;
submitTask
template<typename Func,typename... Args> //右值引用,引用折叠,可变参
auto submitTask(Func&& func, Args&&... args) -> std::future<decltype(func(args...))>
{
//打包任务 放入任务队列里面
using RType = decltype(func(args...)); //返回值类型
auto task = std::make_shared<std::packaged_task<RType()>>(
std::bind(std::forward<Func>(func), std::forward<Args>(args)...)); //forward保持左值或者右值特性
std::future<RType> result = task->get_future(); //把参数全部绑定到函数上
//获取锁
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(taskQueMtx_);
if (!notFull_.wait_for(lock, std::chrono::seconds(1),
[&]()->bool {return taskQue_.size() < (size_t)taskQueMaxThresHold_; }))
{
std::cerr << "task queue is full,submit task fail." << std::endl;
auto task = std::make_shared<std::packaged_task<RType()>>(
[]()->RType { return RType(); });
(*task)();
return task->get_future();;
}
taskQue_.emplace([task]() {
(*task)(); });
taskSize_++;
notEmpty_.notify_all();
if (poolMode_ == PoolMode::MODE_CACHED
&& taskSize_ > idleThreadSize_
&& curThreadSize_ < threadSizeThresHold_)
{
std::cout << ">>> create new thread" << std::endl;
//创建thread线程对象
auto ptr = std::make_unique<Thread>(std::bind(&ThreadPool::threadFunc, this, std::placeholders::_1));
//threads_.emplace_back(std::move(ptr)); //资源转移
int threadId = ptr->getId();
threads_.emplace(threadId, std::move(ptr));
threads_[threadId]->start(); //启动线程
//修改线程个数相关的变量
curThreadSize_++;php
idleThreadSize_++;
}
//返回任务的Result对象
return result;
}
- 为了让submitTask可以接收任意任务函数和任意数量的参数,我们使用可变参模板编程
template<typename Func,typename... Args>; - submitTask返回的类型是由decltype推导出来的,func(args…) 参数传入函数,通过decltype可以推导出来类型,但是不会计算表达式;
- 打包任务 放入任务队列里面,使用 decltype(func(args…)); 来确定返回值类型RType;
- 确定task,把参数全部绑定到函数上
- 把参数全部绑定到函数上;
- 通过future类的
get_future();获取返回值
接下来就执行任务,由于using Task = std::function<void()>;任务队列的任务没有返回值,但是上面的task有返回值,所以使用中间层匿名函数对象,当调用匿名函数时,实际上就是调用(*task)();,task解引用以后就是packaged_task,然后()执行了task任务,在线程函数中,执行task()相当于就执行了packaged_task对象。
启动线程,执行线程函数
void threadFunc(int threadid)
{
auto lastTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock().now();
for (;;)
{
Task task;
{
//获取锁
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(taskQueMtx_);
std::cout << "tid:" << std::this_thread::get_id()<< "尝试获取任务..." << std::endl;
while (taskQue_.size() == 0)
{
if (!isPoolRuning_)
{
threads_.erase(threadid);
std::cout << "threadid:android" << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "exit!" << std::endl;
exitCond_.notify_all();
return;
}
if (poolMode_ == PoolMode::MODE_CACHED)
{ //超时返回std::cv_status::timeout
if (std::cv_status::timeout ==
notEmpty_.wait_for(lock, std::chrono::seconds(1)))
{
auto now = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock().now();
auto dur = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(now - lastTime);
if (dur.count() >= THREAD_MAX_IDLE_TIME&& curThreadSize_ > initThreadSize_)
{
threads_.erase(threadid);
curThreadSize_--;
idleThreadSize_--;
std::cout << "threadid:" << std::this_thread::get_id()<< "exit!" << std::endl;
return;
}
}
}
else
{
//等待notEmpty_条件
notEmpty_.wait(lock);
}
}
idleThreadSize_--;
std::cout << "tid:" << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "获取任务成功..." << std::endl;
//从任务队列中取一个任务出来
task = taskQue_.front();
taskQue_.pop();
taskSize_--;
//若依然有剩余任务,继续通知其他线程执行任务
if (taskQue_.size() > 0)
{
notEmpty_.notify_all();
}
notFull_.notify_all();
}
if (task != nullptr)
{
task(); //执行std::function<void()>;
}
idleThreadSize_++;
auto lastTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock().now();
}
}
除去执行任务的地方改变了,其余没变;
这里取出task,然后task(); 相当于执行了(*task)();也就是执行了packaged_task对象。
测试文件
#include <IOStream>
#include <functional>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <chrono>
#include "threadpool.h"
using namespace std;
int sum1(int a, int b)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(5));
return a + b;
}
int sum2(int a, int b,int c)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(5));
return a + b + c;
}
int main()
{
ThreadPool pool;
//pool.setMode(PoolMode::MODE_CACHED);
pool.start(2);
future<int> res1 = pool.submitTask(sum1, 1, 2);
future<int> res2 = pool.submitTask(sum2, 1, 2,3);
future<int> res3 = pool.submitTask([](int d, int e)->int {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = d; i < e; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
},1, 100);
future<int> res4 = pool.submitTask([]jOgIeb(int d, int e)->int {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = d; i < e; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}, 1, 100);
future<int> res5 = pool.submitTask([](int d, int e)->int {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = d; i < e; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}, 1, 100);
cout << res1.get() << endl;
cout << res2.get() << endl;
cout << res3.get() << endl;
cout << res4.get() << endl;
cout << res5.get() << endl;
}
ThreadPool定义对象,开启线程,2个线程
这里可以提交任意类型的,任意参数个数的任务以及匿名函数;
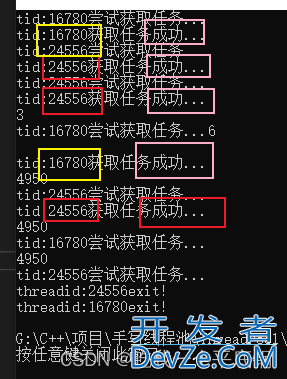
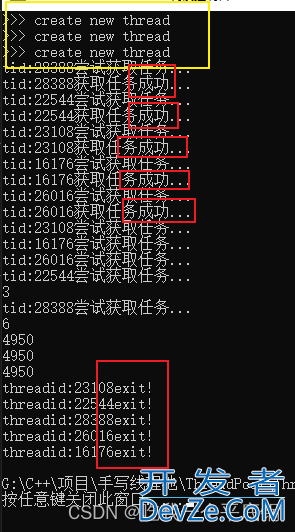
pool.setMode(PoolMode::MODE_CACHED); 下:
好了~ 基于C++17实现jOgIeb的线程池就剖析结束了,实际上使用了future类以及packaged_task(functiphpon函数对象),方便了我们项目的实现,更多相关C++17 手写线程池内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论