目录
- 一、使用Collections工具类
- 1、对基本类型排序
- 2、对字符串类型排序
- 3、对对象排序
- 二、使用stream流
- 三、使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
- 四、测试类整体代码
- 总结
一、使用Collections工具类
1、对基本类型排序
通过Collections.sort()对基本类型排序默认是以升序排序
// 1.Collections.sort()默认按照升序排序 List<编程客栈;Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(integerList,1,2,6,5,5,4,55,4,5,5,4,5,2,4,6,2,45); Collections.sort(integerList); System.out.println(integerList);
2、对字符串类型排序
对字符串类型排序默认按照首字母a-z排序
// 2.对字符串类型排序 List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(strings,"d","gsf","trh","fsd","an"); Collections.sort(strings); System.out.println(strings);
3、对对象排序
如何使用Collections对对象排序呢?
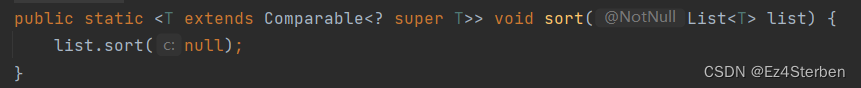
其实只需要让我们的数据类型实现Comparable接口即可,下面定义一个实现Comparable接口的学生类,并且实现compareTo方法,让学生类只比较年龄。
/**
* 学生
*
* @author ez4sterben
* @date 2023/07/18
*/
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Student(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// 这种是升序
return this.getAge() - o.getAge();
// 这种是降序
// return o.getAge() - this.getAge();
}
}
排序方法和正常使用一样,直接把整个list传入即可
// 3.对对象排序
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(students,
new Student(18),
new Student(26),
new Student(20),
new Student(16),
new Student(12));
System.out.println(students);
Collections.sort(students);
System.out.println(students);

二、使用stream流
// 2.lambda表达式
Stream<Integer> sorted = integerList.stream().sorted();
编程 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sorted.toArray()));

三、使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
// 3.直接使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
for(int i = 0; i < integerList.size() - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < integerList.size() - i - 1; j++){
if(integerList.get(j) > integerList.get(j + 1)){
Integer temp = integerList.get(j);
integerList.set(j, integerList.get(j + 1));
integerList.set(j + 1, temp);
}
}
}
System.out.println(integerList);

四、测试类整体代码
import Java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 数组列表排序
*
* @author ez4sterben
* @date 2023/07/19
*/
public class ArrayListSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(integerList,1,2,6,5,5,4,55,4,5,5,4,5,2,4,6,2,45);
// 1.Collections.sort()默认按照升序排序
Collections.sort(integerList);
System.out.println(integerList);
// 2.对字符串类型排序
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(strings,"d","gsf","trh","www.devze.comfsd","an");
Collections.sort(strings);
System.out.println(strings);
// 3.对对象排序
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(students,
new Student(18),
new Student(26),
new Student(20),
new Student(16),
new Student(12));
System.out.phpprintln(students);
Collections.sort(students);
System.out.println(students);
// 2.lambda表达式
Stream<Integer> sorted = integerList.stream().sorted();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sorted.toArray()));
// 3.直接使用排序算法(以冒泡排序为例)
for(int i = 0; i < integerList.size() - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < integerList.size() - i - 1; j++){
if(integerList.get(j) > integerList.get(j + 1)){
Integer temp = integerList.get(j);
integerList.set(j, integerList.get(j + 1));
integerList.set(j + 1, temp);
}
}
}
System.out.println(integerList);
}
}
总结
到此这篇关于java对ArrayList中元素进行排序的几种方式总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java对ArrayList元python素排序内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论