目录
- 前言
- 1.使用 Comparable 排序
- 2.使用 Comparator 排序
- 2.1 新建 Comparator 比较器
- 2.2 匿名类比较器
- 3.使用 Stream 流排序
- 扩展:排序字段为 null
- 总结
前言
在我们程序的编写中,有时候我们需要在 Java 程序中对 List 集合进行排序操作。比如获取所有用户的列表,但列表默认是以用户编号从小到大进行排序的,而我们的系统需要按照用户的年龄从大到小进行排序,这个时候,我们就需要对 List 集合进行自定义排序操作了。
List 排序的常见方法有以下 3 种:
使用 Comparable 进行排序;
使用 Comparator 进行排序;
如果是 JDK 8 以上的环境,也可以使用 Stream 流进行排序。
下面我们分别来看各种排序方法的具体实现。
1.使用 Comparable 排序
创建一个包含了用户列表的 List 集合,并按用户的年龄从大到小进行排序,具体实现代码如下:
import com.fasterXML.jackson.core.jsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Comparable 自定的规则进行排序
Collections.sort(list);
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person p) {
return p.getAge() - this.getAge();
}
}
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
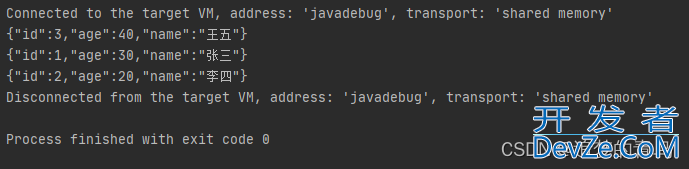
2.使用 Comparator 排序
Comparable 是类内部的比较方法,而 Comparator 是排序类外部的比较器。使用 Comparator 比较器,无需修改原 Person 类,只需要扩充一个 Person 类的比较器就行了,Comparator 的实现方法有以下两种:
新建 Comparator 比较器;
使用 Comparator 匿名类比较器。
其中,第二种实现方法要更简洁一些,我们通过下面的具体代码,来观察一下二者的区别。
2.1 新建 Comparator 比较器
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Comparator 比较器排序
Collections.sort(list, new PersonComparator());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
/**
* 新建 Person 比较器
*/
class PersonComparator implements Comparator<Person> {
@Override
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:

2.2 匿名类比较器
比较器 Comparator 可以使用更简洁的匿名类的方式,来实现排序功能,具体实现代码如下:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用匿名比较器排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {
return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
}
});
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();http://www.devze.com
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValuhttp://www.devze.comeAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:

3.使用 Stream 流排序
在 JDK 8 之后可以使用更加简单的方法 Stream 流来实现排序功能,它的实现只需要一行代码,具体实现如下:
package com.highcom.hc.api;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, 40, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Stream 排序
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private int age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
http://www.devze.com this.name = name;
}
}
其中 reversed() 表示倒序的意思,如果不使用此方法则是正序。
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:

扩展:排序字段为 null
使用 Stream 进行排序时,如果排序的字段出现 null 值就会导致异常发生,具体示例如下:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, null, "王五"));
}};
// 使用 Stream 排序
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, Integer age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:

想要解决上述问题,需要给 Comparator.comparing 传递第二个参数:Comparator.nullsXXX,如下代码所示:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ListSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建并初始化 List
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>() {{
add(new Person(1, 30, "张三"));
add(new Person(2, 20, "李四"));
add(new Person(3, null, "王五"));
}};
// 按照[年龄]排序,但年龄中有一个 null 值
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge,
Comparator.nullsFirst(Integer::compareTo)).reversed())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 打印 list 集合
list.forEach(p -> {
// 将JavaBean对象转换为JSON字符串
String jsonStr = null;
try {
android jsonStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(p);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(jsonStr);
});
}
}
class Person {
private int id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
android public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int id, Integer age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
Comparator.nullsFirst 表示将排序字段中的 null 值放到集合最前面,如果想要将 null 值放到集合最后面可以使用 Comparator.nullsLast。
以上代码的执行结果,如下图所示:
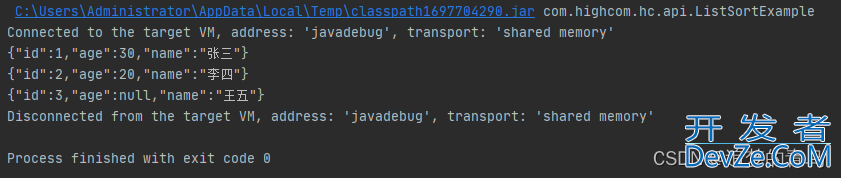
总结
本文介绍了 3 种 List 排序的方法,前两种方法常用于 JDK 8 之前的版本,其中比较器 Comparator 有两种实现的写法,而在 JDK 8 之后的版本,就可以使用 Comparator.comparing 实现排序了,如果排序字段中可能出现 null 值,要使用 Comparator.nullsXXX 进行排序处理(否则会报错)
到此这篇关于Java中List排序的3种常见方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java中List排序方式内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论