目录
- 引言
- 头文件的准备
- 函数代码的实现
- 1.某年某月天数的获取
- 2.全缺省的构造函数
- 3.拷贝构造函数
- 4.七个运算符的重载
- 5.四个日期计算函数
- 6.前置/后置的加加减减
- 7.计算两个日期之间的天数值
引言
我们日常生活中可能会有一个烦恼。
今天几月几号?过n天后又是几月几号?某年某月某天和x年x月x天相差几天?你和男/女朋友的相识了几天?等等。这些问题好麻烦,我不想去算,所以我们的日期计算机也就油然而生了。
头文件的准备
头文件的声明代码:
#pragma once
#include<IOStream>
#inclu<assert.h>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int days[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31,30,31 };
int day = days[month];
if (month == 2 &&
(year & 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))
{
day += 1;
}
return day;
}
//打印函数
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d);
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
// 析构函数
~Date();
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置--
Date operator--(iphpnt);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d);
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d);
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d);
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d);
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d);
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d);
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
函数代码的实现
1.某年某月天数的获取
第一个函数,我们定义在了头文件中
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
assert(month > 0 && month < 13);
static int DayA[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31,30,31 };
int day = DayA[month];
if (month == 2 &&
(year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))
{
day += 1;
}
return day;
}
这里我们直接建立一个数组,存储的是每月的天数。
第一个我们存储为0,毕竟第一个月我们没有经历满。
这里的数组我们前边加上了static,使其成为了全局变量。这里设置为全局变量是为了方便后边的使用/调用。
不要忽略了这里闰年的判定,最后返回我们的天数
2.全缺省的构造函数
Date::Date(int year,int month,int day)
{
year = _year;
month = _month;
day = _day;
}
这个函数就比较简单了,就是赋值。
值得注意的是:这里是源文件,我们在头文件声明是已经使用了缺省参数,所以在源文件中就不需要使用了。
3.拷贝构造函数
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._d编程客栈ay;
}
这个函数也比较简单,我们这里利用了this指针,所以传参只需要传递一个就可以了。也不过多讲解了。
4.七个运算符的重载
首先是==的重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
然后再写一个 < 的重载
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year)
{
if (_month < d._month)
return true;
else if (_month == d._month)
{
if (_day < d._day)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
写完这两个后,我们后边其他的重载就好写了。
这里我们不需要再去写这种麻烦的代码,我们偷个懒,转换一下思路。利用前边这两个去写其他的重载函数
小于等于就是符合小于的同时也符合等于
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return *this < d && *this == d;
}
大于就是不是小于等于
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
大于等于就是不是小于
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this < d);
}
不等于就是不是等于就可以
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
赋值运算符重载
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (*this != d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
这个我们在之前也讲解过,就不过多叙述了
5.四个日期计算函数
第一个:月份日期增加天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day +=day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
http://www.devze.com return *this;
}
首先先获取天数
如果天数大于月份的天数,我们就减去当前月份的天数,然后让月份加一。如果月份大于13了,我们就让年去加一。
写完+=,那么+就会好写很多
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date ret = *this;
ret += day;
return ret;
}
这里我们也用到了+=的重载。
但这两个都是用来加天数的,两者有什么不同呢?
首先呢,第一个重载的是运算符+=的重载,他们的本质是在原有的基础上进行改变,改变了*this指针的值
举个例子
int main()
{
Date d1(2024, 4, 24);
d1 += 3;//这里的d1应该是2024/4/27
d1.Print();
return 0;
}
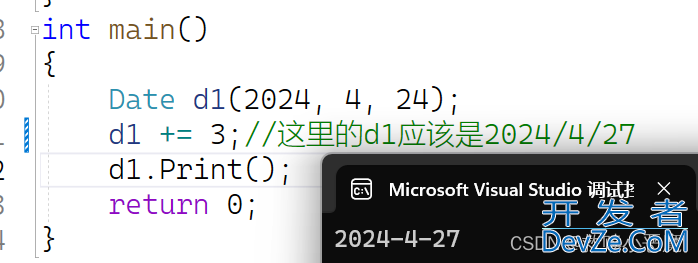
利用+=我们改变了d1原本的数值
再看一看+
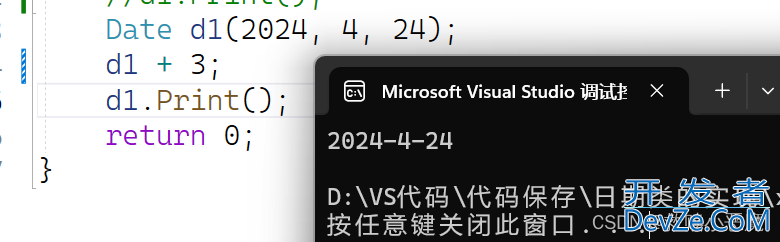
虽然d1加了3,但是并没有改变d1原本的数值
总结:
- Date& Date::operator+=(int day) 他的返回类型是Date的引用们可以进行链式操作,调用+=,是在原有的基础上进行增加天数,会改变原有变量的数值。
- Date Date::operator+(int day) 他的返回类型是一个新的Date,需要去利用变量去接受。调用+,返还的对象实在原有的基础上进行增加得到结果,不会改变原有变量的数值
那么问题又来了?
我这里显示写出+=,然后再+中去调用+=。
那么如果我们先写出+后,再重在+=中去调用+会怎么样呢???
这里就直接说结论了
不论是先写+=再写+,还是先写+再写+=,结果都是一样的,但是唯一不同的就是代码的书写量以及效率的高低。在这里我比较推荐我的写法,先写+=,再写+会提高一定的效率。
写完+有关的,我们开始写-有关的
接下来是月份日期的减少
Date& Date:js:operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operpythonator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
6.前置/后置的加加减减
这里需要注意的是,为了区分时前置和后置的区别,我们在传参时需要加入一个int
加入int参数的就是后置++
这里代码如下:
Date& Date::operator++()
{
_day += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
_day += 1;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator--()
{
_day -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
_day -= 1;
return tmp;
}
既然是加加就是day加一,这样的话我们也利用前边思路想法,前置我们利用引用去写,而后置我们不用引用,利用前边的运算符重载去写
7.计算两个日期之间的天数值
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
int flag = 1;
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (*this < d)
{
int flag = -1;
max = d;
min = *this;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
这个函数的逻辑也利用了假设法,其思路则是确定好大的日期后,让小的日期不断增加然后直至与大的日期相同。
讲解:
第一个点是确确定日期的大小。我们让max确保成为大日期,min确保成为小日期,这里就利用了假设法,设置完后,利用if语句,确保我们的判断是正确的,如果不正确就进行反转,并让flag成为-1。
第二个点就是计算两者之间差值的天数。我们通过循环,每次都让min不断增加,同时也见建立一个变量n,让它随着min增加,从而记录下两者之间的差值天数,最后n就是两者之间的差值。
第三个点就是返回值。我们这里的返回值最后需要乘上flag,其原因是,我们一开始我们让this指针为大日期,如果不对的话,就说明this指针的日期小,所以两者之间差值就是负的。
以上就是基于C++实现简单的日期计算机的详细内容,更多关于C++日期计算机的资料请关注编程客栈(www.devze.com)其它相关文章!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论