目录
- 正文
- 第一步 建立控制台应用
- 第二步 引用System.Threading.Thread
- 第三步:完成代码
- 运行结果
- 拓展:C#多线程刷新界面卡死测试
- 小结
正文
不带参数的多线程实现
第一步 建立控制台应用
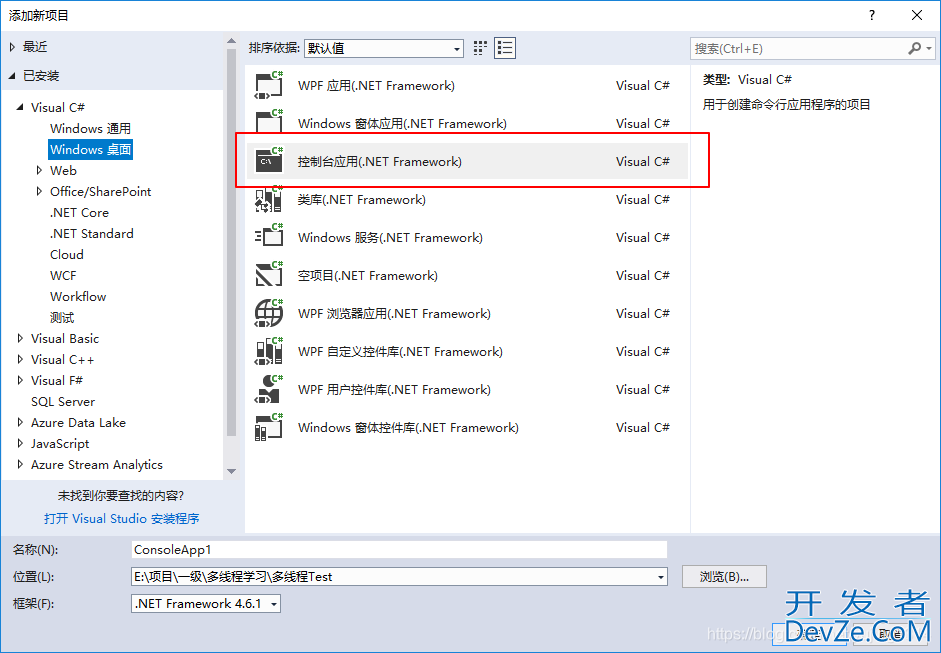
第二步 引用System.Threading.Thread
using System.Threading;
在 C# 中,System.Threading.Thread 类用于线程的工作。它允许创建并访问多线程应用程序中的单个线程。进程中第一个被执行的线程称为主线程。
第三步:完成代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace 多线程Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int num = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
//无参的多线程
noParmaThread();
}
}
private static void StartThread()
{
Console.WriteLine("------开始了新线程------");
Thread.Sleep(2000);//wait
Console.WriteLine("------线程结束------");
}
/// <summary>
///不需要传递参数
/// </summary>
private static void noParmaThread()
{
ThreadStart threadStart = new ThreadStart(StartThread);
var thread = new Thread(threadStart);
thread.Start();//开始线程
}
}
}
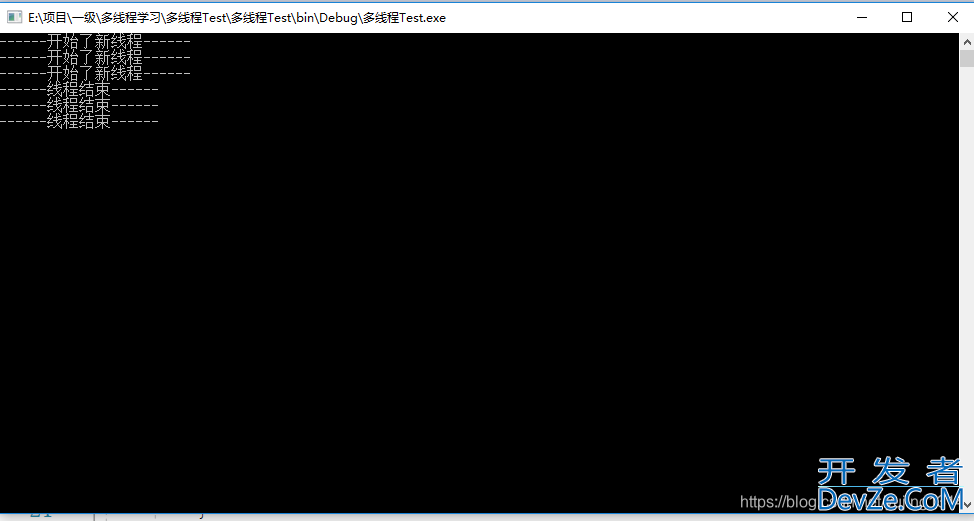
运行结果
拓展:C#多线程刷新界面卡死测试
背景
在上位机程序开发过程中,不可避免的会用到多线程,如处理Socket通信、PLC读取、界面数据实时刷新等。在某个项目中由于开启的线程很多,出现了不定期界面卡死状况,但后台线程还在运行,日志还在输出。为了解决这个问题,特写了模拟程序进行问题复现。顺便把过程分享一下。
要点
1、区分Control.BeginInvoke和Control.Invoke的用法
2、区分System.Timers.Timer、System.Threading.ThreadPool、System.Threading.Thread
Demo
创建一个WinForm应用程序,把工程属性的输出类型设置为控制台应用程序,方便运行时查看日志。
关键代码
BasicInvoker
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WinApp
{
/// <summary>
/// 调用器
/// </summary>
public class BasicInvoker
{
public delegate void Invoke();
private Form form = null;
private TextBox txt = null;
private object value = String.Empty;
public BasicInvoker(Form form, TextBox txt, object value)
{
this.form = form;
this.txt = txt;
this.value = value;
}
public void SetValue()
{
if (this.form != null && !this.form.IsDisposed)
{
if (this.form.InvokeRequired)
{
Delegate d = new Invoke(this.DoWork);
try
{
this.form.Invoke(d, null);
//this.form.BeginInvoke(d);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
else
{
this.DoWork();
}
}
}
public void DoWork()
{
if (this.txt != null)
{
this.txt.Text = this.value.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff}", DateTime.Now) + " " + this.value.ToString() + "...1");
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(200);
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff}", DateTime.Now) + " " + this.value.ToString() + "...2");
}
}
}
}
FrmTest
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WinApp
{
public partial class FrmTester : Form
{
#region 变量定义
private System.Timers.Timer timer1 = null;
private System.Timers.Timer timer2 = null;
private System.Timers.Timer timer3 = null;
private System.Threading.Thread thread1 = null;
private System.Threading.Thread thread2 = null;
private System.Threading.Thread thread3 = null;
#endregion
#region 构造方法
public FrmTester()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
#endregion
#region 事件处理
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (timer1 == null)
{
timer1 = new System.Timers.Timer();
timer1.Interval = 500;
timer1.Elapsed += t1_Elapsed;
timer1.Start();
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (timer2 == null)
{
timer2 = new System.Timers.Timer();
timer2.androidInterval = 500;
timer2.Elapsed += t2_Elapsed;
timer2.Start();
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (timer3 == null)
{
timer3 = new System.Timers.Timer();
timer3.Interval = 500;
timer3.Elapsed += t3_Elapsed;
timer3.Start();
}
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Threading.ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new System.Threading.WaitCallback(this.CallBack1));
}
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Threading.ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new System.Threading.WaitCallback(this.CallBack2));
}
private void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Threading.ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new System.Threading.WaitCallback(this.CallBack3));
}
private void button7_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.thread1 == null)
{
this.thread1 = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart(this.CallBack1));
this.thread1.Start();
}
}
private void button8_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.thread2 == null)
{
this.thread2 = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart(this.CallBack2));
this.thread2.Start();
}
}
private void button9_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.thread3 == null)
{
this.thread3 = new System.Threading.Thread(new System.Threading.ThreadStart(this.CalphplBack3));
this.thread3.Start();
}
}
private void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("FormClosing...");
if (this.timer1 != null)
{
this.timer1.Stop();
this.timer1.Dispose();
}
if (this.timer2 != null)
{
this.timer2.Stop();
this.timer2.Dispose();
}
if (this.timer3 != null)
{
this.timer3.Stop();
this.timer3.Dispose();
}
if (this.thread1 != null)
{
//if (this.thread1.ThreadState == System.Threading.ThreadState.Running)
{
this.thread1.Abort();
}
}
if (this.thread2 != null)
{
//if (this.thread2.ThreadState == System.Threading.ThreadState.Running)
{
this.thread2.Abort();
}
}
if (this.thread3 != null)
{
//if (this.thread3.ThreadState == System.Threading.ThreadState.Running)
{
this.thread3.Abort();
}
}
}
private void Form1_FormClosed(object sender, FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("FormClosed...");
}
#endregion
#region 定时处理方法定义
private void t1_Elapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
//lock(Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock (Stjsring.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, Guid.NewGuid().ToString());
invoker.SetValue();
}
}
private void t2_Elapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock (String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");
invoker.SetValue();
}
}
private void t3_Elapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock (String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, "BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB");
invoker.SetValue();
}
}
public void CallBack1(object state)
{
js while(true)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock(String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, Guid.NewGuid().ToString());
invoker.SetValue();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
public void CallBack2(object state)
{
while (true)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock(String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");
invoker.SetValue();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
public void CallBack3(object state)
{
while (true)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock(String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, "BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB");
invoker.SetValue();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
public void CallBack1()
{
while (true)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock (String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, Guid.NewGuid().ToString());
invoker.SetValue();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
public void CallBack2()
{
while (true)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock (String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");
invoker.SetValue();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
public void CallBack3()
{
while (true)
{
//lock (Global.PublicVar.Instance.Locker1)
lock (String.Empty)
{
BasicInvoker invoker = new BasicInvoker(this, this.textBox1, "BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB");
invoker.SetValue();
}
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
#endregion
}
}
运行图:
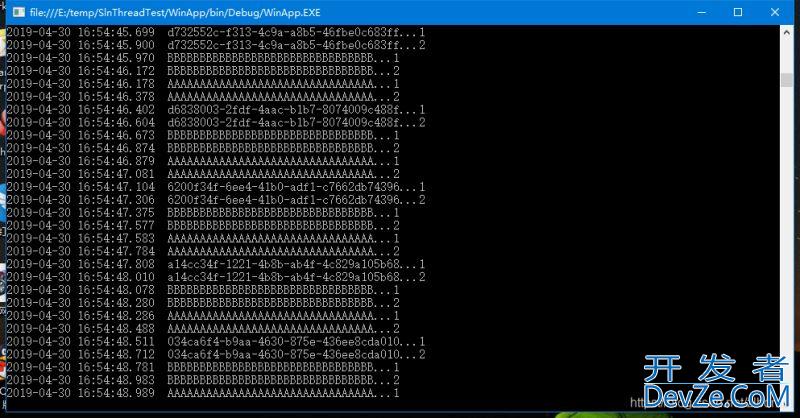
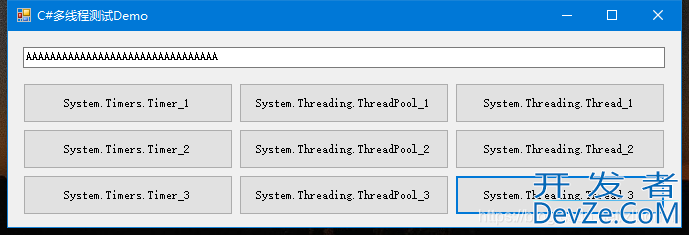
运行结果:
一、使用Control.BeginInvoke的情况
public void SetValue()
{
if (thttp://www.devze.comhis.form != null && !this.form.IsDisposed)
{
if (this.form.InvokeRequired)
{
Delegate d = new Invoke(this.DoWork);
try
{
//this.form.Invoke(d, null);
this.form.BeginInvoke(d);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
else
{
this.DoWork();
}
}
}
1.1、System.Timers.Timer开启2以上很快界面卡死,日志正常输出。
1.2、System.Threading.ThreadPool开启3个时,运行一会界面卡死,日志正常输出。
1.3、System.Threading.Thread开启3个时,运行一会界面卡死,日志正常输出。
二、使用Control.Invoke的情况
public void SetValue()
{
if (this.form != null && !this.form.IsDisposed)
{
if (this.form.InvokeRequired)
{
Delegate d = new Invoke(this.DoWork);
try
{
this.form.Invoke(d, null);
//this.form.BeginInvoke(d);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
else
{
this.DoWork();
}
}
}
2.1、System.Timers.Timer开启3个时很快界面卡死,日志正常输出。
2.2、System.Threading.ThreadPool开启3个时,界面正常操作,日志正常输出。
2.3、System.Threading.Thread开启3个时,界面正常操作,日志正常输出。
测试总结:
1、System.Threading.ThreadPool与System.Threading.Thread运行效果基本相同。
2、在多线程刷新界面时尽量通过Control.Invoke调用委托实现。
小结
到此这篇关于详解C#如何解决程序卡顿的问题(多线程初步学习)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C#解决程序卡顿内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论