目录
- 一、MongoDB简介
- 二、MongoDB与mysql的区别
- 三、使用
- 1、安装
- 2、在Java中使用
- 3、多表连接查询
- 总结
一、mongoDB简介
MongoDB 是由 C++ 语言编写的,基于分布式文件存储的数据库,是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是最接近于关系型数据库的 NoSQL 数据库。
MongoDB 将数据存储为一个文档,数据结构由键值(key=>value)对组成。MongoDB 文档类似于jsON对象。字段值可以包含其他文档,数组及文档数组
类似于

2. MongoDB优点:数据处理能力强,内存级数据库,查询速度快,扩展性强,只是不支持事务。
3. 使用场景:
1、应用不需要事务;
2、数据模型无法确定,经常发生变更;
3、应用存储的数据很大达到TB级别以上;
4、应用需要大量的地理位置查询简单的来说就是数据量比较大,而且主要是查询操作,而且不需要事务支持
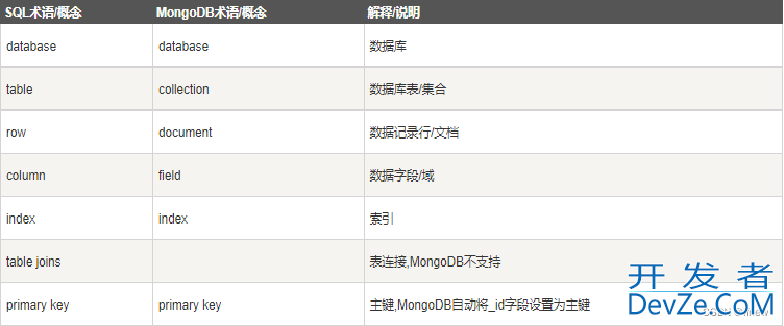
编程二、MongoDB与Mysql的区别
三、使用
1、安装
安装地址: http://www.mongodb.org/
github: https://github.com/mongodb/
2、在java中使用
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置连接参数
data:
mongodb:
host: 10.0.26.194
username: wanttop2
password: Testwanttop2
port: 27017
authentication-database: wanttop2
database: wanttop2
直接使用mongoTemplate
当然也可以自己封装一个工具类
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
单表查询
// 判断 dataType 是否存在,如果存在则添加到查询条件中
if (performanceRank.getDataType() != null) {
query.addCriteria(Criteria.where("dataType").is(performanceRank.getDataType()));
}
// 判断 divisionCode 是否存在,如果存在则添加到查询条件中
if (performanceRank.getDivisionCode() != null) {
query.addCriteria(Criteria.where("divisionCode").is(performanceRank.getDivisionCode()));
}
List<SysDimensionDataMarket> sysDimensionDataMarketList = MongoDBUtil.conditionalQuery(query, SysDimensionDataMarket.class, "SysDimensionDataMarket");
3、多表连接查询
mongoDB中没有sql的left join 和right join 的类似的概念而是用到了lookup管道操作符
mongoDB3.2版本新增(聚合管道$lookup操作)
完整代码
//连表
LookupOperation cusAndIndyosVZfoLookup = LookupOperation.newLookup().
from("SysProduct").//1.副表表名字
localField("prodItemCode").//2.主表的关联字段
foreignField("productCode").//3.副表的关联字段
as("SysProduct");//4.建议和1一致,结果的别名
//如果需要多连表就在写一个
//LookupOperation cusAndInfoLookup1 = LookupOperation.newLookup().
// from("SysProduct").//1.副表表名字
// localField("prodItemCode").//2.主表的www.devze.com关联字段
// foreignField("productCode").//3.副表的关联字段
// as("SysProduct");//4.建议和1一致,结果的别名
//多表的关联条件,查询条件均传入到此
//创建查询条件
Criteria criteria = new Criteria();
if (totalPerformanceCross.getDataCrossType() != null) {
criteria.and("dataCrossType").is(totalPerformanceCross.getDataCrossType());
}
// 判断 areaCode 是否存在,如果存在则添加到查询条件中
if (totalPerformanceCross.getAreaCode() != null) {
criteria.and("areaCode").is(totalPerformanceCross.getAreaCode());
}
android // 判断 companyCode 是否存在,如果存在则添加到查询条件中
if (totalPerformanceCross.getCompanyCode() != null) {
criteria.and("companyCode").is(totalPerformanceCross.getCompanyCode());
}
//如果查询的字段为附表则需要加上附表名字
if (totalPerformanceCross.getDateType() != null) {
criteria.and("SysProduct.dateType").is(totalPerformanceCross.getDateType());
}
//多表的关联条件,查询条件均传入到此
Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(
//连表条件
cusAndInfoLookup,
//cusAndInfoLookup1,
//查询条件
Aggregation.match(criteria),
//最后查询结果集显示字段
Aggregation.project("pmLineCode", "prodItemCode", "prodItemName", "performance", "growthRate", "monthPerformance", "fullMonthPerformance", "SysProduhttp://www.devze.comct.productPicUrl"));
总结
到此这篇关于在Java中使用MongoDB的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java使用MongoDB内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论