目录
- 前言
- 一、前期准备
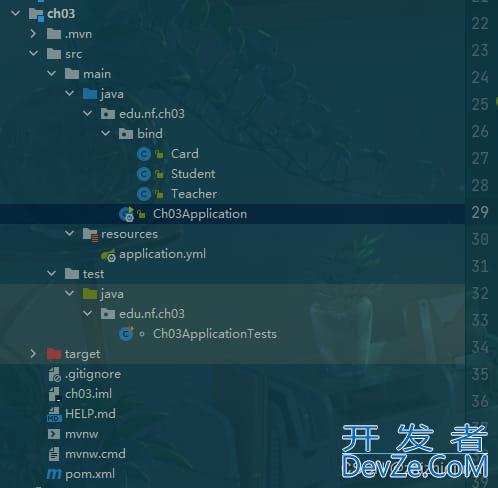
- 1、新建项目,结构如下
- 2、导入依赖
- 二、第一种,值绑定
- 1、新建一个 Student 类
- 2、测试
- 三、第二种,松散绑定
- 1、还是使用 Student 类
- 2、绑定实体
- 3、绑定数组
- 4、绑定 map
- 5、复杂的值绑定
- 四、值绑定和松散绑定到优点和缺点
前言
Spring Boot 提供了强大的配置能力,通过 YAML 文件进行数据绑定是一种常见且便捷的方式。在本示例中,我们将演示如何利用 Spring Boot 的特性,通过 phpYAML 文件实现数据绑定。借助于 YAML 的简洁语法和结构化特性,我们能够轻松地管理应用程序的配置信息,使得配置文件更加清晰易读。通过本示例,您将了解如何利用 Spring Boot 快速、高效地实现 YAML 数据绑定,为您的应用程序提供灵活且可维护的配置管理。让我们开始吧,深入探索 Spring Boot 中 YAML 数据绑定的精髓!
一、前期准备
1、新建项目,结构如下
2、导入依赖
<?XML version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.17</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>edu.nf</groupId>
<artifactId>ch03</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<namhttp://www.devze.come>ch03</name>
<description>ch03</description>
<properties>
<Java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<image&g编程客栈t;
<builder>paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-base:latest</builder>
</image>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
这是一个 Maven 的 pom.xml 文件,它描述了一个 Spring Boot 项目的依赖关系和构建方式。
在这个文件中,我们定义了两个依赖项:
spring-boot-starter:这是一个 Spring Boot 的核心依赖,它包含了 Spring MVC、Spring Data JPA、Spring Security 等常用模块,并且自动配置了这些模块所需的环境。通过引入这个依赖,我们可以快速搭建一个基于 Spring Boot 的 Web 应用程序。
spring-boot-starter-test:这是一个 Spring Boot 的测试依赖,它提供了许多用于测试的工具和框架,例如 JUnit、Mockito、Hamcrest 等。通过引入这个依赖,我们可以轻松地编写和执行单元测试和集成测试。
此外,我们还定义了一个 Maven 插件 spring-boot-maven-plugin,用于将应用程序打包成一个可执行的 JAR 文件,以便于部署和运行。在这个插件中,我们还可以配置容器、端口等参数,以满足不同的应用程序需求。
总之,pom.xml 文件是www.devze.com Spring Boot 项目的配置文件,它定义了项目的依赖关系和构建方式,并且通过 Maven 插件实现了对应用程序的打包和部署
二、第一种,值绑定
值绑定,使用 @value 注解精确指定节点的名称
1、新建一个 Student 类
@Component
@Data
public class Student {
// 使用 @Value 注解和spell表达式将yml的节点值绑定到类的字段上
@Value("${student.userId}")
private Integer stuId;
@Value("${student.userName}")
private String stuName;
@Value("${student.age}")
private Integer age;
}
这段代码是一个Spring组件,用于将YAML配置文件中的值映射到Java对象的字段上。
首先,使用了@Data注解,它会自动生成getter和setter方法、equals方法、hashCode方法以及toString方法。
然后,通过@Value注解来绑定YAML配置文件中的各个节点值到类的字段上。@Value注解中的"${student.userId}"等,是SpEL表达式,它会在运行时从YAML配置文件中读取对应节点的值,并将其赋值给类的字段。
例如,如果在YAML配置文件中有以下内容:
student: userId: 1001 userName: qiu age: 18
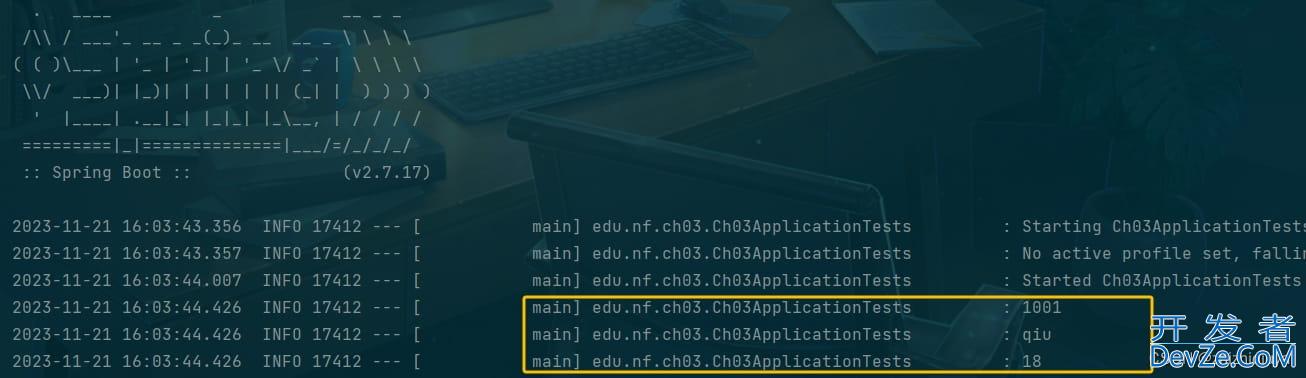
那么在运行时,Student对象的stuId字段将被赋值为123,stuName字段将被赋值为"tom",age字段将被赋值为18。
总之,这段代码可以让你轻松地将YAML配置文件中的值映射到Java对象的字段上,方便你的代码使用。
2、测试
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class Ch03ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
log.info(student.getStuId().toString());
log.info(student.getStuName());
log.info(student.getAge().toString());
}
}
这段代码是一个Spring Boot的测试类,用于测试应用程序的上下文加载和配置是否正确。
首先,使用了@SpringBootTest注解,它表示这是一个Spring Boot的集成测试类。它会自动加载应用程序的上下文,并进行必要的配置。
然后,使用@Slf4j注解,它是Lombok库提供的注解,可以自动生成日志变量log。
接下来,通过@Autowired注解将Student对象注入到测试类中的student字段上。这样就可以在测试方法中使用该对象。
在contextLoads()方法中,通过调用student对象的getter方法,获取并打印stuId、stuName和age字段的值。这主要用于验证是否成功将YAML配置文件中的值绑定到Student对象的相应字段上。
通过日志输出,你可以在测试运行时查看stuId、stuName和age字段的值。
总结起来,这段代码用于测试Spring Boot应用程序的上下文加载和配置是否正确,并验证是否成功将YAML配置文件中的值绑定到相应的Java对象字段上。
运行结果:
三、第二种,松散绑定
使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解,松散绑定只需要绑定指定节点的前缀即可,子节点在 yml 中可以依据约定, 使用驼峰模式(如:userName)、“—”线(如:允(user-name)、或者全大写加下划线(如:USER_NAME) 进行绑定即可。
1、还是使用 Student 类
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student.info")
public class Student {
private Integer stuId;
private String stuName;
private Integer age;
}
这段代码定义了一个名为 Student 的 Java 类,使用了 @Component 和 @Data 注解,并且使用了 @ConfigurationProperties 注解对该类进行了配置。
@Component 注解表示这个类是 Spring 中的一个组件,会被 Spring 容器所管理。@Data 注解是 lombok 提供的注解,自动生成一些常用方法,如 getter、setter、toString 等等。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student.info") 注解指定了该类的属性值从以 student.info 为前缀的配置项中获取。例如,配置文件中有如下配置:
# 数据值绑定
student:
info:
stuId: 1001
stu-name: qiu
AGE: 18
则 Student 类中的 stuId 属性值为 1001,stuName 属性值为 "qiu",age 属性值为 18。
这里指定字段的格式我使用了三种,为的是演示可以这样去写,在实际开发中,大家最好是选择一种去使用,统一一点。
通过这种方式,我们可以将应用程序的配置信息与业务逻辑分离,使得配置文件更加清晰易读,同时也方便进行统一的配置管理。
测试的结果和值绑定到一样,就不测试了。需要注意的是,实体类的字段名称和yml配置的名称要一样,不能出现不一致的,不然会报错的。
2、绑定实体
1)新建一个 Card 实体类
@Data
public class Card {
private String cardNum;
}
使用 @Data 生成 get、set访问器就可以了。
2)在 Student 实体类中引入 Card 实体类为字段
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student.info")
public class Student {
private Integer stuId;
private String stuName;
private Integer age;
// 实体
private Card card;
}
在原有的 Student 类基础上,新增了一个名为 card 的属性,并且类型为 Card。
yml示例:
# 数据值绑定
student:
info:
stuId: 1001
stu-name: qiu
AGE: 18
card:
card-num: 4408812000
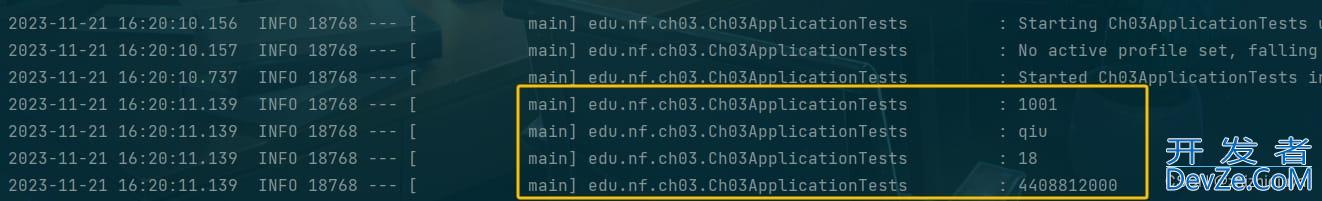
则 Student 类中的 stuId 属性值为 1001,stuName 属性值为 "qiu",age 属性值为 18。Card类中的 cardNum 为 4408812000.
3)测试
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class Ch03ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
log.info(student.getStuId().toString());
log.info(student.getStuName());
log.info(student.getAge().toString());
log.info(student.getCard().getCardNum());
}
}
在contextLoads()方法中,使用日志记录器log输出了student对象的一些属性信息。通过调用student对象的get方法获取学生的学号、姓名、年龄以及身份证号码,并通过log.info()方法将它们输出到日志中。
运行结果:
3、绑定数组
1)在 student 实体类中新建一个字段
// 数组
private String[] tels;
yml中绑定 tels 的值:
# 绑定 array,list,set 集合,多个值使用逗号分隔
tels: # 13223453421,14556766700
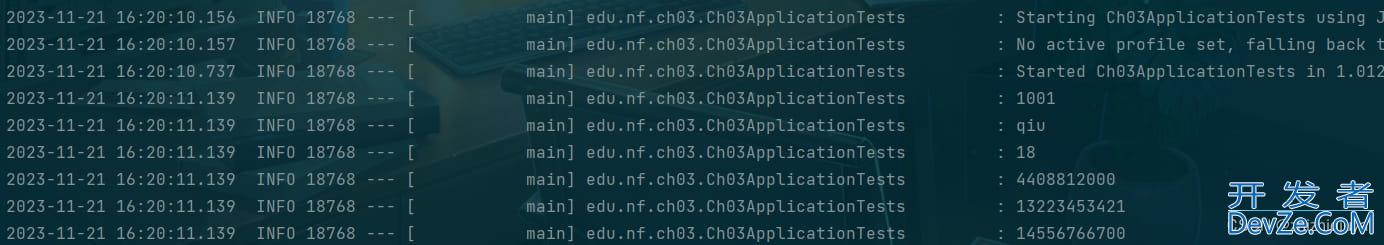
- 13223453421
- 14556766700
这里呢有两种写法,一种是用逗号隔开,一种是使用 “-”线加空格隔开,不加空格的话,输出的时候会把 “-” 也输出来。
2)测试
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class Ch03ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
log.info(student.getStuId().toString());
log.info(student.getStuName());
log.info(student.getAge().toString());
log.info(student.getCard().getCardNum());
for (String tel : student.getTels()) {
log.info(tel);
}
}
}
绑定了一个数组,拿出来只需要循环就可以啦。
运行结果:
4、绑定 map
1)在 Student 实体类中新建一个字段
// map
private Map<String,Integer> score;
yml 绑定 score 的值:
# 绑定 map
score:
chinese: 85
english: 60
因为 map 是一以键值对保存数据的,所以这里的 Chinese 就是键,85 就是这个键的值。
2)测试
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class Ch03ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
log.info(student.getStuId().toString());
log.info(student.getStuName());
log.info(student.getAge().toString());
log.info(student.getCard().getCardNum());
for (String tel : student.getTels()) {
log.info(tel);
}
student.getScore().forEach((k,v) -> log.info(k + " : " + v));
}
}
Map的forEach()方法,遍历了getScore()返回的Map对象,并通过日志输出了每个键值对的内容。
运行结果:
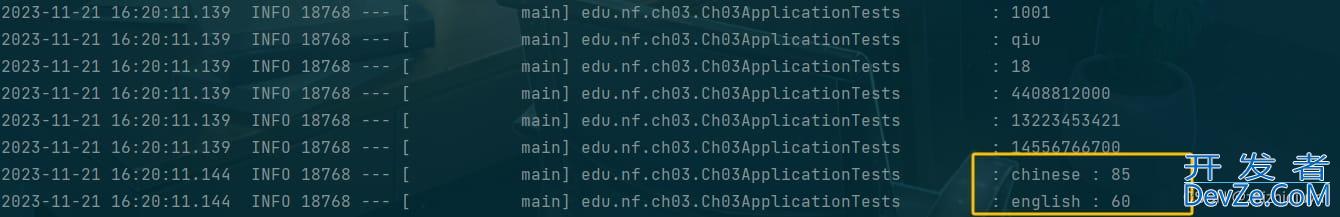
5、复杂的值绑定
1)新建一个 Teacher 实体类
@Data
public class Teacher {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
2)在 student 实体类中新加一个字段
// 集合里面有个对象
private List<Teacher> teaches;
yml绑定:
# 绑定复杂类型(集合中包含对象)
teaches:
- name: Mr.qiu
age: 21
- name: Ms.zhi
age: 22
这是一个 YAML 配置文件,其中 teaches 是一个复杂类型,包含了两个对象:Mr.qiu 和 Ms.zhi,它们都拥有 name 和 age 两个属性。
3)测试
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class Ch03ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
log.info(student.getStuId().toString());
log.info(student.getStuName());
log.info(student.getAge().toString());
log.info(student.getCard().getCardNum());
for (String tel : student.getTels()) {
log.info(tel);
}
student.getScore().forEach((k,v) -> log.info(k + " : " + v));
student.getTeaches().forEach( teach -> {
log.info(teach.getName());
log.info(teach.getAge().toString());
});
}
}
运行结果:
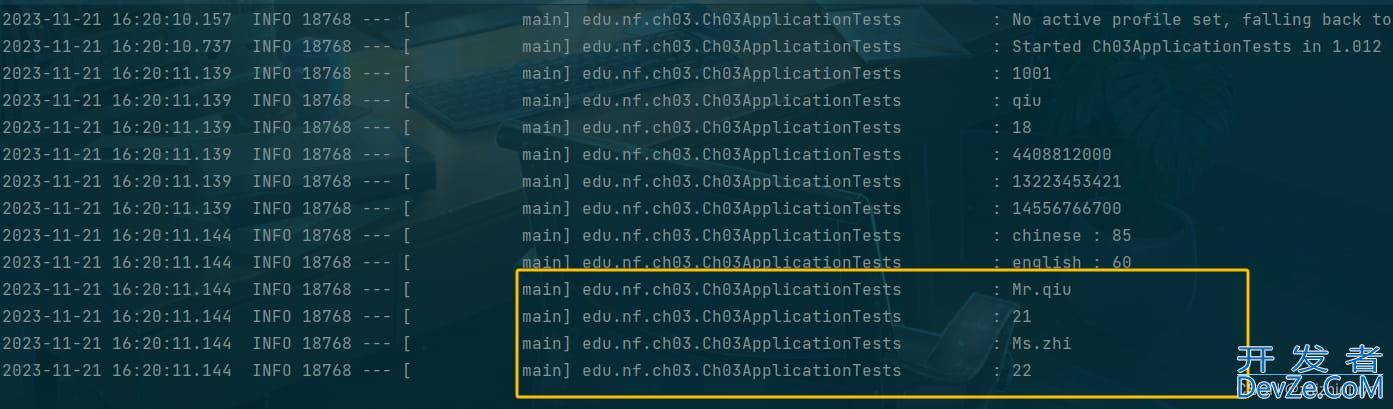
四、值绑定和松散绑定到优点和缺点
YAML 数据绑定的值绑定和松散绑定有以下优点:
- 简单易读:YAML 格式的数据配置文件相对于传统的属性文件更加简洁易读,且支持注释和多行文本。
- 灵活性:YAML 的灵活性允许我们在配置文件中使用复杂的数据类型,包括数组、对象、嵌套对象等。
- 易于维护:通过将配置文件中的值绑定到 Java 类上,我们可以使用 Java 对象的语法来访问这些值,使得代码更加易于维护和阅读。
- 配置管理:通过
@ConfigurationProperties注解,可以将应用程序的配置信息与业务逻辑分离,使得配置文件更加清晰易读,同时也方便进行统一的配置管理。
但是,YAML 数据绑定的值绑定和松散绑定也有以下缺点:
- 学习成本:相比于传统的属性文件,使用 YAML 格式的数据配置文件需要学习新的语法和规则,需要一些时间来适应。
- 错误处理:由于 YAML 的松散绑定特性,当配置文件中出现错误时,可能会造成不可编程预知的结果,需要开发者自己注意检查和处理。
- 性能问题:相比于传统的属性文件,使用 YAML 格式的数据配置文件解析和读取速度可能会稍慢一些,特别是在处理大量数据时。
综上所述,在使用 YAML 数据绑定时,需要根据具体情况权衡其优缺点,并选择适合自己的方式来处理配置信息。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot中yml的数据绑定示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot yml数据绑定内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论