目录
- 一、官方提供方法
- 二、根据业务场景的方法
- 三、说明
- 1、获取输出流
- 2、获取模版文件
- 3、创建 ExcelWriter 和 WriteSheet
- 4、获取数据
- 5、填充数据
- 1.获取字典数据
- 2.填充列表外的数据
- 3.填充缺少的列名
- 4.填充主列表数据
- 5.设置输出流格式以及文件名
- 四、思想
- 总结
一、官方提供方法
easyexcel官方文档 填充Excel | Easy Excel
官方demo是利用本地模版文件填充并下载到本地
/**
* 复杂的填充
*
* @since 2.1.1
*/
@Test
public void complexFill() {
// 模板注意 用{} 来表示你要用的变量 如果本来就有"{","}" 特殊字符 用"\{","\}"代替
// {} 代表普通变量 {.} 代表是list的变量
String templateFileName =
TestFileUtil.getPath() + "demo" + File.separator + "fill" + File.separator + "complex.xlsx";
String fileName = TestFileUtil.getPath() + "complexFill" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx";
// 方案1
try (ExcelWriter excelWriter = EasyExcel.write(fileName).withTemplate(templateFileName).build()) {
WriteSheet writeSheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet().build();
// 这里注意 入参用了forceNewRow 代表在写入list的时候不管list下面有没有空行 都会创建一行,然后下面的数据往后移动。默认 是false,会直接使用下一行,如果没有则创建。
// forceNewRow 如果设置了true,有个缺点 就是他会把所有的数据都放到内存了,所以慎用
// 简单的说 如果你的模板有list,且list不是最后一行,下面还有数据需要填充 就必须设置 forceNewRow=true 但是这个就会把所有数据放到内存 会很耗内存
// 如果数据量大 list不是最后一行 参照下一个
FillConfig fillConfig = FillConfig.builder().forceNewRow(Boolean.TRUE).build();
excelWriter.fill(data(), fillConfig, writeSheet);
excelWriter.fill(data(), fillConfig, writeSheet);
Map<String, Object> map = MapUtils.newHashMap();
map.put("date", "2019年10月9日13:28:28");
map.put("total", 1000);
excelWriter.fill(map, writeSheet);
}
}
二、根据业务场景的方法
我用的是web项目,将输出改为了输出流 OutputStream
/**
* 导出质检任务详情
*
* @param id 任务主键,用于获取数据
*/
@Override
public void exportTask(Long id, HttpServletResponse response) {
ExcelWriter excelWriter = null;
try {
// outputStream:要导出的文件的输出流
OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
// 模版文件
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("template/taskTemplate.xlsx");
// 使用模版文件的两种方式:
// 1、文件路径:.withTemplate(templateFileName)
// 2、输入流:.withTemplate(inputStream)
String templateFileName = classPathResource.getFile().getPath();
InputStream inputStream = classPathResource.getInputStream();
excelWriter = EasyExcel.write(outputStream).withTemplate(inputStream).excelType(ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX).autoCloseStream(Boolean.FALSE).build();
WriteSheet writeSheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet().build();
// 获取数据 dataList columnList formData
Map<String, Object> mapDetail = qmsQcTaskDetailService.getDataListByTaskId(id);
// 调用微服务获取字典 determine 用来翻译判定结果
List<SysDictItem> determineItem = remoteDictService.getDictByType("determine").getData();
// 调用微服务获取字典 product_unit 用来翻译零件单位
List<SysDictItem> unitItem = remoteDictService.getDictByType("product_unit").getwww.devze.comData();
/* 1、List以外的数据 */
QmsQcTask formData = (QmsQcTask) mapDetail.get("formData");
determineItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(formData.getResult(), item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> formData.setResult(sysDictItem.getLabel()));
unitItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(formData.getMaterialUnit(), item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> formData.setMaterialUnit(phpsysDictItem.getLabel()));
excelWriter.fill(formData, writeSheet);
/* 2、List cols数据 */
List<Map<String, Object>> cols = new ArrayList<>();
// 查找抽检数是多少,即有几列
int num = formData.getSampleNum();
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 列名
map.put("label", "" + i);
cols.add(map);
}
// 横向填充
FillConfig fillConfigCols = FillConfig.builder().direction(WriteDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL).build();
excelWriter.fill(new FillWrapper("cols", cols), fillConfigCols, writeSheet);
/* 3、List details数据 */
// 这里注意 入参用了forceNewRow 代表在写入list的时候不管list下面有没有空行 都会创建一行,然后下面的数据往后移动。默认 是false,会直接使用下一行,如果没有则创建。
// forceNewRow 如果设置了true,有个缺点 就是他会把所有的数据都放到内存了,所以慎用
// 简单的说 如果你的模板有list,且list不是最后一行,下面还有数据需要填充 就必须设置 forceNewRow=true 但是这个就会把所有数据放到内存 会很耗内存
FillConfig fillConfig = FillConfig.builder().forceNewRow(Boolean.TRUE).build();
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList = (List<Map<String, Object>>) mapDetail.get("dataList");
for (int i = 0; i < dataList.size(); i++) {
Map<String, Object> data = dataList.get(i);
// 翻译判定合不合格(因为业务和字典不在一个数据库,所以放在代码里处理)
String determine = (String) data.get("determine");
determineItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(determine, item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> data.put("determine", sysDictItem.getLabel()));
// 如果没有质检标准,每一个质检值都要转为合不合格
if (StrUtil.isBlank((String) data.get("inspection_standard"))){
int samplingNum = Optional.ofNullable((Integer) data.get("sampling_num")).orElse(0);
for (int j = 1; j <= samplingNum; j++) {
String val = (String) data.get(""+j);
int finalJ = j;
determineItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(val, item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> data.put(""+ finalJ, sysDictI编程客栈tem.getLabel()));
}
}
// 给数据加上序号
data.put("index", i + 1);
}
excelWriter.fill(new FillWrapper("details", dataList), fillConfig, writeSheet);
// 设置输出流格式以及文件名:
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openXMLformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String fileName = URLEncoder.encode("质检任务", "UTF-8").replaceAll("\\+", "%20");
response.setHeader("Content-disposition", "attachment;filename*=utf-8''" + fileName + ".xlsx");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 千万别忘记close关闭流
if (excelWriter != null) {
excelWriter.close();
}
}
}
模版:
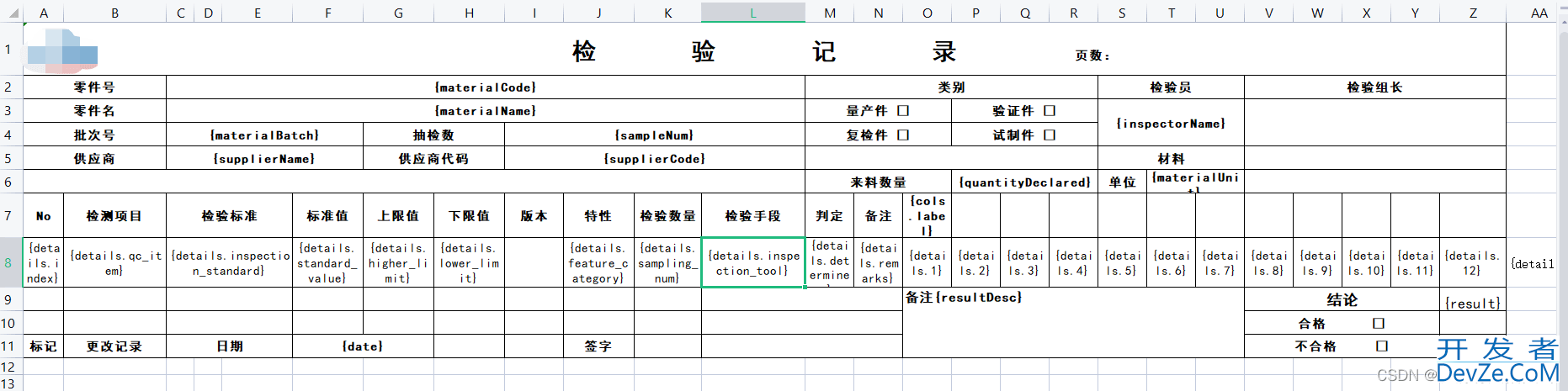
效果:
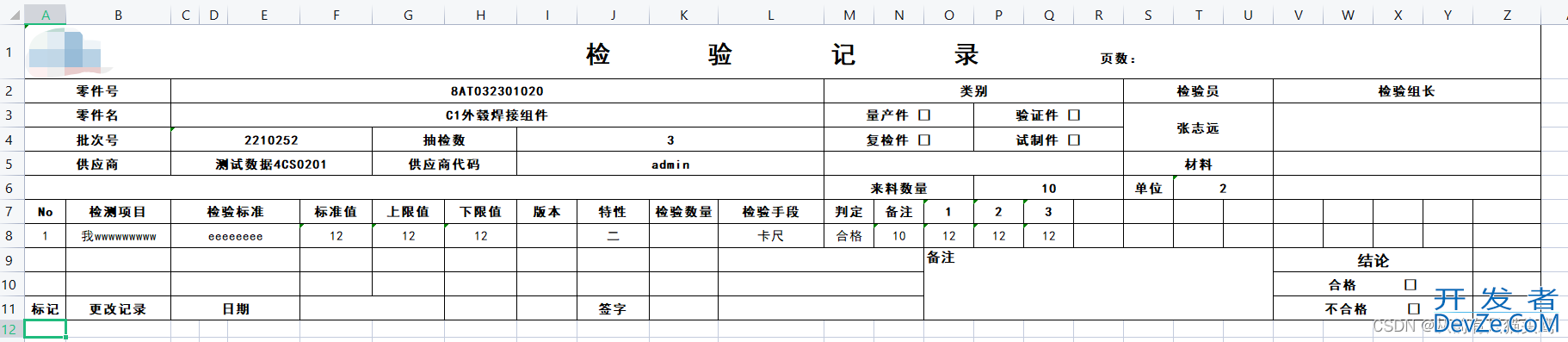
三、说明
1、获取输出流
// outputStream:要导出的文件的输出流 OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();python
2、获取模版文件
// 模版文件
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource("template/taskTemplate.xlsx");
// 方式一:路径
String templateFileName = classPathResource.getFile().getPath();
// 方式二:输入流
InputStream inputStream = classPathResource.getInputStream();
3、创建 ExcelWriter 和 WriteSheet
excelWriter = EasyExcel.write(outputStream).withTemplate(inputStream).excelType(ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX).autoCloseStream(Boolean.FALSE).build(); WriteSheet writeSheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet().build();
使用模版文件有两种方式,使用其中一种就可以:
1.文件路径:.withTemplate(templateFileName)
2.输入流:.withTemplate(inputStream)
4、获取数据
Map<String, Object> mapDetail = qmsQcTaskDetailService.getDataListByTaskId(id);
我这里直接调用了方法,map包含
dataList主要列表数据 formData 列表外的数据
5、填充数据
1.获取字典数据
// 调用微服务获取字典 determine 用来翻译判定结果
List<SysDictItem> determineItem = remoteDictService.getDictByType("determine").getData();
// 调用微服务获取字典 product_unit 用来翻译零件单位
List<SysDictItem> unitItem = remoteDictService.getDictByType("product_unit").getData();
我的业务数据和字典不在同一个数据库内,sql无法翻译,所以需要在代码里翻译
2.填充列表外的数据
/* 1、List以外的数据 */
QmsQcTask formData = (QmsQcTask) mapDetail.get("formData");
determineItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(formData.getResult(), item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> formData.setResult(sysDictItem.getLabel()));
unitItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(formData.getMaterialUnit(), item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> formData.setMaterialUnit(sysDictItem.getLabel()));
excelWriter.fill(formData, writeSheet);
只要对象属性名和模版里写的标记已知就可以了
3.填充缺少的列名
模版:
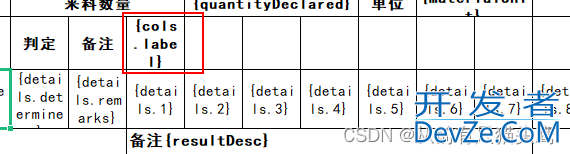
效果:
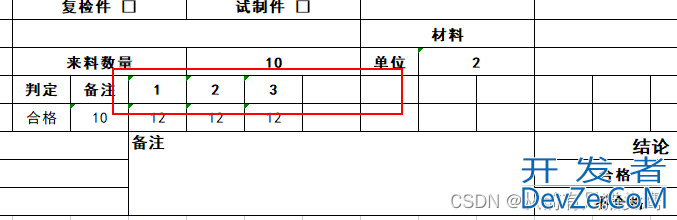
因为我后半部分列名涉及到行转列,且不固定列数,所以需要横着填充上列名。注意列表的名字“cols”要对应起来。
使用.direction(WriteDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL) 设置为横向填充。
/* 2、List cols数据 */
List<Map<String, Object>> cols = new ArrayList<>();
// 查找抽检数是多少,即有几列
int num = formData.getSampleNum();
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 列名
map.put("label", "" + i);
cols.add(map);
}
// 横向填充
FillConfig fillConfigCols = FillConfig.builder().direction(WriteDirectionEnum.HORIZONTAL).build();
excelWriter.fill(new FillWrapper("cols", cols), fillConfigCols, writeSheet);
4.填充主列表数据
/* 3、List details数据 */
// 这里注意 入参用了forceNewRow 代表在写入list的时候不管list下面有没有空行 都会创建一行,然后下面的数据往后移动。默认 是false,会直接使用下一行,如果没有则创建。
// forceNewRow 如果设置了true,有个缺点 就是他会把所有的数据都放到内存了,所以慎用
// 简单的说 如果你的模板有list,且list不是最后一行,下面还有数据需要填充 就必须设置 forceNewRow=true 但是这个就会把所有数据放到内存 会很耗内存
FillConfig fillConfig = FillConfig.builder().forceNewRow(Boolean.TRUE).build();
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList = (List<Map<String, Object>>) mapDetail.get("dataList");
/*以下为个人业务处理*/
for (int i = 0; i < dataList.size(); i++) {
Map<String, Object> data = dataList.get(i);
// 翻译判定合不合格(因为业务和字典不在一个数据库,所以放在代码里处理)
String determine = (String) data.get("determine");
determineItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(determine, item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> data.put("determine", sysDictItem.getLabel()));
// 如果没有质检标准,每一个质检值都要转为合不合格
if (StrUtil.isBlank((String) data.get("inspection_standard"))){
int samplingNum = Optional.ofNullable((Integer) data.get("sampling_num")).orElse(0);
for (int j = 1; j <= samplingNupythonm; j++) {
String val = (String) data.get(""+j);
int finalJ = j;
determineItem.stream().filter(item -> StrUtil.equals(val, item.getItemValue())).findFirst().ifPresent(sysDictItem -> data.put(""+ finalJ, sysDictItem.getLabel()));
}
}
// 给数据加上序号
data.put("index", i + 1);
}
/*以上为个人业务处理*/
excelWriter.fill(new FillWrapper("details", dataList), fillConfig, writeSheet);
最重要的三句话:
FillConfig fillConfig = FillConfig.builder().forceNewRow(Boolean.TRUE).build();
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList = (List<Map<String, Object>>) mapDetail.get("dataList");
excelWriter.fill(new FillWrapper("details", dataList), fillConfig, writeSheet);
这里注意 入参用了forceNewRow 代表在写入list的时候不管list下面有没有空行 都会创建一行,然后下面的数据往后移动。默认 是false,会直接使用下一行,如果没有则创建。forceNewRow 如果设置了true,有个缺点 就是他会把所有的数据都放到内存了,所以慎用简单的说 如果你的模板有list,且list不是最后一行,下面还有数据需要填充 就必须设置 forceNewRow=true 但是这个就会把所有数据放到内存 会很耗内存
5.设置输出流格式以及文件名
// 设置输出流格式以及文件名:
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String fileName = URLEncoder.encode("质检任务", "UTF-8").replaceAll("\\+", "%20");
response.setHeader("Content-disposition", "attachment;filename*=utf-8''" + fileName + ".xlsx");
四、思想
我的模版使用了动态的列,不确定有几列,所以我就写了一百多个。
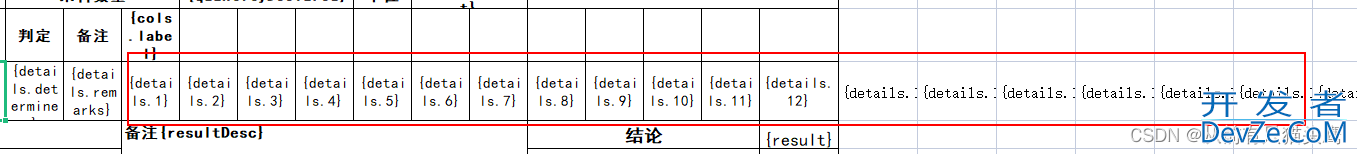
还有另外一种设想:
如果先把列表外的数据填充,然后将主列表的列填充完毕,再把主列表的标记写上,这些操作完毕之后把文件输出到另外的输出流上,再将此输出流转为输入流,再把主列表的数据填充,输出到response。
理论上可行,但我没试。
总结
到此这篇关于Java使用EasyExcel模版导出的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关使用EasyExcel模版导出内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论