目录
- 一、__getattribute__()
- 二、__setattr__()
- 三、__getattr__()
一、__getattribute__()
顾名思义,当访问object的属性会调用该方法,可以测试:
class A(object):
def __init__(self, name,age):
self.name = name
www.devze.comself.age = age
def __getattribute__(self, attr):
print("__getattribute__ is called")
try:
return super().__getattribute__(attr)
except AttributeError:
print(f'have no attr of {attr}')
if _js_name__ == '__main__':
a = A('jyz',200)
print(a.name)
print(a.age)
print(a.gender)
输出:
__getattribute__ is called
jyz__getattribute__ is called200__getattribute__ is calledhave no attr of genderNone
可以看出,当我们通过object.attrname的形式访问实例属性时,实际上我们是通过__getattribute__得到了该属性,是不是联想到了OOP中封装的思想?别急,下面会看到更多的oop设计思想。值得一提的是,在重写__getattribute__()方法时,一定要知道你在做什么,否则可能导致无法正确访问实例对象。另外,官方文档建议始终使用基类方法来设置属性,否则会陷入无限递归,最终栈溢出:

比如可以尝试:
class A(object):
def __init__(self, name,age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def __getattribute__(self, attr):
return self.name
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = A('jyz',200)
print(a.name)
输出:
[Previous line repeated 996 more times]
RecursionError: maximum recursion depth exceeded
究其原因,是因为当使用self.name访问属性时会调用__getattribute__,而__getattribute__又要访问self.name,因此会无限递归下去。正确的做法是使用基类方法,对于该例子由于继承的是基类,因此使用super().__getattribute__(attr)或object.__getattribute__(self,attr)均可。
二、__setattr__()
实例初始化过程中,为实例属性赋值时会调用该方法。
class A(object):
def __init__(self, name,age):
self.name = name
php self.age = age
def __getattribute__(self, attr):
print("__getattribute__ is called")
try:
return super().__getattribute__(attr)
except AttributeError:
print(f'have no attr of {attr}')
def __setattr__(self, key, value):
print(f"__setattr__() is called, key is {key}")
object.__setattr__(self, key, value)
输出:
__setattr__() is called, key is name
__setattr__() is called, key is age
与__getattribute__同理,在__setattr__中也尽量使用基类的该方法来设置一些属性,否则可能发生无限递归。
三、__getattr__()
从字面意思理解跟__getattribute__差不多,事实上,该方法是__getattribute__的补充,当访问某些属性不存在,或**__getattribute__显示地抛出AttributeError**,会自动转到该方法做进一步处理。
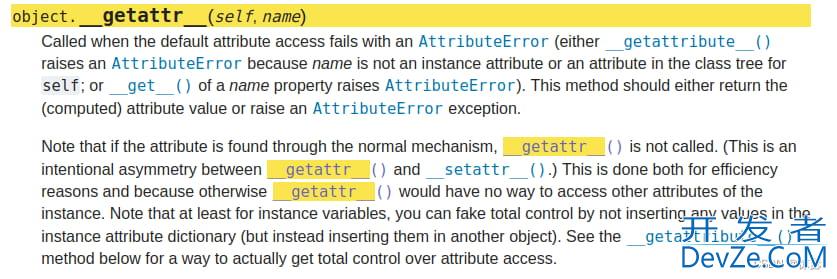
可以测试:
class A(object):
def __init__(self, name,age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def __getattr__(self, attr):
print(f"__getattr__() is called,but {attr} is not exist!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = A('jyz',200)
print(a.gender)
输出:
__getattr__() is called,but gender is not exist!
None
测试通过主动抛出异常的方式触发__getattr__():
class A(object):
dephpf __init__(self, name,age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def __getattribute__(self, attr):
if attr not in ['name','age']:
raise AttributeError
else:
return object.__getattribute__(self, attr)
def __getattr__(self, attr):
print(f"__getattr__() is called,but {attr} is not exist!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = A('jyz',200)
print(a.name)
print(a.gender)
输出:
jyz
__getattr__() is called,but gender is not exist!None
可以看到,上面两种方式都可以触发,__getattr__()。
到此这篇关于python中的getattribute 、getattr、setattr方法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关getattjavascriptribute 、getattr、setattr方法内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!
 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论