目录
- 1. 概述
- 1.1 适用场景
- 1.2 Hello world
- 2. 数据加载使用
- 2.1 CacheLoader.load(K key)
- 2.2 CacheLoader.loadAll(keys) 批量加载
- 2.3 Callable.call
- 2.4 手工写入
- 3. 缓存清除
- 3.1 基于maximumSize的清除
- 3.2 基于maximumWeight的清除
- 3.3 基于时间的清除
- 3.4 使用WeakReferenct、SoftReference保存Key和Value
- 3.5 显示的移除缓存
- 3.6 缓存清除监听
- 4. 缓存的清除时机
- 4.1 通过refresh优化读取性能
- 5. 缓存性能指标
- 6. 原理、长处和限制
- 7. 测试代码
1. 概述
1.1 适用场景
Cache在ConcurrentHashMap的基础上提供了自动加载数据、清除数据、get-if-absend-compute的功能,适用场景:
- 愿意花一些内存来提高访问速度
- 缓存的数据查询或计算代码高昂,但是需要查询不止一次
- 缓存的数据在内存中放得下,否则应该考虑Redis、Memcached
1.2 Hello world
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> graphs = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.removalListener(MY_LISTENER)
.build (
new CacheLoader<Key, Graph>() {
@Override
public Graph load(Key key) throws AnyException {
return createExpensiveGraph(key);
}
}
);
2. 数据加载使用
2.1 CacheLoader.load(K key)
LoadingCache是包含了数据加载方式的Cache,加载方式由CacheLoader指定,CacheLoader可以简单到只实现一个V load(K key)方法,如:
CacheLoader<Key,Graph> cacheLoader = new CacheLoader<Key,Graph> {
public Grapch load(Key key) throws AnyException {
return createExpensiveGraph(key);
}
}
LoadingCache和Cache都是通过CacheBuilder创建,唯一的区别是LoadingCache需要要提供CacheLoader实例。
LoadingCache<Key, Graph> graphs = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(1000).build(cacheLoader); graphs.get(key);
LoadingCache经典的使用方式是通过get(K)获取数据,有缓存则直接返回,否则调用CacheLoader.load(K)计算并写入缓存。
CacheLoader可以抛出异常,检查型异常会被封装为ExecutionException,RuntimeException会被封装为UncheckedExecutionException。
如果不想在客户端代码里处理异常,可以使用LoadingCache.getUnchecked(K)方法,该方法只会抛出UncheckedExecutionException,它是一个RuntimeException。
2.2 CacheLoader.loadAll(keys) 批量加载
在客户端调用LoadingCache.getAll的时候,会优先尝试CacheLoader.loadAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys)方法,这个方法默认实现是抛出UnsupportedLoadingOperationException,LocalCache默认优先尝试调用ClassLoader.loadAll,如果异常则挨个Key调用CacheLoader.load(K)并组成Map<Key,Value>返回。
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(100).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("going to load from data, key:" + s);
return s.matches("\\d+") ? Integer.parseInt(s) : -1;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Integer> loadAll(Iterable<? extends String> keys) throws Exception {
System.out.println("going to loadAll from data, keys:" + keys);
Map<String, Integer> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (String s : keys) {
result.put(s, s.matches("\\d+") ? Integer.parseInt(s) : -1);
}
result.put("99", 99);
result.put("WhatIsTheFuck", 100);
return result;
}
});
System.out.println(cache.get("10"));
List<String> ls = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "a");
System.out.println(cache.getAll(ls));
System.out.println(cache.get("WhatIsTheFuck"));
getAll调用CacheLoader.loadAll,该方法返回一个Map,可以包含非指定Key数据,整个Map会被缓存,但getAll只返回指定的Key的数据。
2.3 Callable.call
所有Guava Cache的实现类都支持get(K, Callable<V>)方法, 返回K对应的缓存,或者使用Callable<V>计算新值并存入缓存,实现get-if-absent-compute。
Cache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(10).build();
final String key = "2";
Integer value = cache.get(key, new Callable<Integer>() {
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Callable.call running, key:" + key);
return key.matches("\\d+") ? Integer.parseInt(key) : -1;
}
});
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(value);
2.4 手工写入
我们可以通过cache.put(key,value)直接写入缓存,写入会覆盖之前的值。 也可以通过cache.asMap()视图来操作数据。 cache.asMap()并不会促发缓存的自动加载,应该尽可能使用cache.put和cache.get。
Cache<String,Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.nwww.devze.comewBuilder().maximumSize(3).build();
cache.put("1",1);
cache.put("2",2);
cache.put("3",3);
cache.put("4",4);
System.out.println(cache.asMap().get("1")); // 因为最多缓存3个,get("1")数据被清除,返回null
System.out.println(cache.asMap().get("2"));
3. 缓存清除
现实实际我们总是不可能有足够的内存来缓存所有数据的,你总是需要关注缓存的清除策略。
3.1 基于maximumSize的清除
用于控制缓存的大小,通过CacheBuilder.maximumSize(long),当缓存的数据项解决maximum的数量时,采用类似LRU的算法过期历史数据。
Cache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).build();
cache.put("1", 1);
cache.put("2", 2);
cache.put("3", 3);
cache.put("4", 4);
System.out.println(cache.asMap().get("1")); // 因为最多js缓存3个,get("1")数据被清除,返回null
System.out.println(cache.asMap().get("2"));
3.2 基于maximumWeight的清除
和maximun类似,只是统计的weight而不是缓存的记录数。
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumWeight(10).weigher(new Weigher<String, Integer>() {
public int weigh(String s, Integer integer) {
return integer;
}
}).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading from CacheLoader, key:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
3.3 基于时间的清除
数据写入指定时间后过期(expireAfterWrite),也可以指定数据一段时间没有访问后清除(expireAfterAccess)。
final long start = System.nanoTime();
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.HOURS).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading data from CacheLoader, key:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
测试基于时间的清除,缓存一个小时,然后我们真的等一个小时后来验证是不现实的,Guava提供了Ticker类用于提供模拟时钟,返回的是时间纳秒数。
下面这个实例通过自定义Ticker,让1s变成10分钟(*600),缓存一个小时的数据,实际过6s后数据就会过期。
final long start = System.nanoTime();
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.HOURS).ticker(new Ticker() {
public long read() {
long current = System.nanoTime();
long diff = current - start;
System.out.println("diff:" + (diff / 1000 / 1000 / 1000));
long time = start + (diff * 600);
return time;
}
}).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading data from CacheLoader, key:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
3.4 使用WeakReferenct、SoftReference保存Key和Value
Guava允许设置弱引用(weak reference)和软银用(soft reference)来引用实际的Key、Value数据。
通过CacheBuilder.weakKeys、CacheBuilder.weakValues、CacheBuilder.softValues来运行JVM的垃圾回收,同时带来的问题是Cache的Key只用==来比较而不是equals,要想从Cache里取回之前的缓存,必须保存Key的Reference对象。
3.5 显示的移除缓存
删除单个Key、批量删除Key、清空缓存
Cache.invalidate(key) Cache.invalidateAll(keys) Cache.invalidateAll()
3.6 缓存清除监听
不是太实用,并不是Key一过期就会触发RemovalListener回调,你需要再次写入数据的时候才会触发同一个Segment的过期,Cache.get官网文档说特定条件下也会触发清空过期数据。
Cache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<String, Integer>() {
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<String, Integer> r) {
System.out.println("Key:" + r.getKey());
System.out.println("Value:" + r.getValue());
System.out.println("Cause:" + r.getCause());
}
}).build();
4. 缓存的清除时机
Cache不会自动的清除缓存,不会在数据过期后立即就清除,只有发生写入动作(如Cache.put)才会触发清除动作(包括LoadingCache.get新加载数据也会清除当前Segement过期数据)。
这样做的目的好处是不用额外维护一个线程做缓存管理动作,如果想要定期清除,开发者可以自行创建一个线程,定期调用Cache.cleanUp()方法。
4.1 通过refresh优化读取性能
LoadingCache.refresh(K)和清除缓存(eviction)不同,refresh会导致Cache重新加载Key对应的值,加载期间,老的值依然可用; 而清除(eviction)之后,其他现在再来取值会阻塞直至新数据加载完成。
CacheLoader.reload(K,V)方法是专门处理refresh提供的方法,refresh调用后实际会调用CacheLoader.reload(K,V)方法,这个方法的第2个入参实际是当前K的历史值。
通过CacheBuilder.refreshAfterWrite(long,TimeUnit)设定,Key在写入Cache指定时间区间后,自动刷新Key的值,而此时历史数据仍然对外提供服务。
CacheBuilder.refreshAfterWrite(long,TimeUnit)只会在下次查询的时候生效,你可以同时指定refreshAfterWrite和expireAfterWrite,这样在指定python的时间段过了之后,如果数据还没有被查询,数据会把清除。
final ScheduledExecutorService es = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).refreshAfterWrite(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading from load...s:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
@Override
public ListenableFuture<Integer> reload(final String key, final Integer oldValue) throws Exception {
if (oldValue > 5) { // 立即返回旧值
System.out.println("loading from reload immediate...key:" + key);
return Futures.immediateFuture(oldValue);
} else {
ListenableFutureTask<Integer> fi = ListenableFutureTask.create(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading from reload...key:" + key);
return oldValue;
}
});
es.execute(fi);
return fi;
}
}
});
5. 缓存性能指标
通过调用CacheBuilder.recordStats()可以打开统计功能,打开功能后可以通过Cache.stats()返回统计信息
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).recordStats().build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
CacheStats stats = cache.stats();
System.out.println(stats.hitRate()); // 缓存命中率
System.out.println(stats.averageLoadPenalty()); // 平均数加载时间,单位纳秒
System.out.println(stats.evictionCount()); // 缓存过期数据数
6. 原理、长处和限制
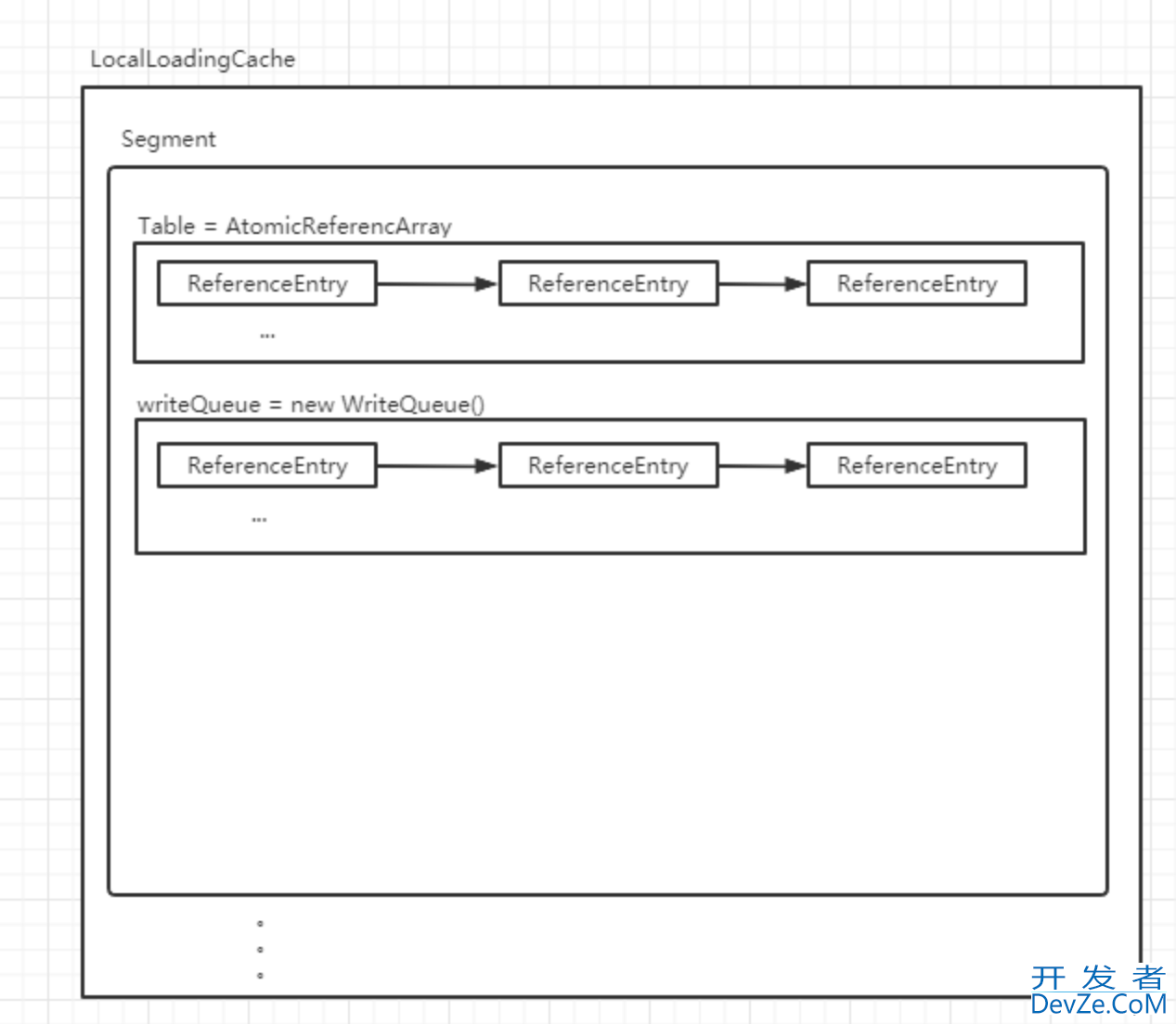
LocalLoadingCache通过公式Math.min(concurrencyLevel, maxWeight / 20)计算Segment数量,数据根据key的Hash值被分散到不同的Segment中。
LocalLoadingCache指定Capacity,默认是16,Capacity会转换为大于指定Capacity的最小的2幂次方。
SegmentCapacity等于Capacity/SegmentCount, 转换为大于SegmentCapacity的最小的2幂次方。
SegmentCapacity的值指定了Segment下AtomicReferenceArray的长度,AtomicReferenceArray每一个下标对应一个链表。
SegmentCount和SegmentCapacity决定了缓存数据被切分的份数,相当于决定了查找效率。
Segment内部还维护着writeQueue、accessQueue、recencyQueue每一次读写操作都会更新对应队列,后续expireAfterWrite、expireAfterAccess只需要顺着队列找即可,因为队列的顺序就是操作的顺序, writeQueue、accessQueue是特制的队列,只用简单的链表实现,从链表移除插入都很高效。
Segement还维护了keyReferenceQueue、valueReferenceQueue,他们是Java里的ReferenceQueue,当采用WeakReference、SoftReference做为Key/Value存储时,自动加入到keyReferenceQueue和valueReferenceQueue中,Guava处理并删除对应的缓存。
7. 测试代码
package com.hujiang.track.pageview;
import com.google.common.base.Ticker;
import com.google.common.cache.*;
import com.google.common.collect.Listshttp://www.devze.com;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.Futures;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureTask;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class TestCache {
@Test
public void testCache() throws ExecutionException {
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(100).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("going to load from data, key:" + s);
return s.matches("\\d+") ? Integer.parseInt(s) : -1;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Integer> loadAll(Iterable<? extends String> keys) throws Exception {
System.out.println("going to loadAll from data, keys:" + keys);
Map<String, Integer> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (String s : keys) {
result.put(s, s.matches("\\d+") ? Integer.parseInt(s) : -1);
}
result.put("99", 99);
result.put("WhatIsTheFuck", 100);
return result;
}
});
System.out.println(cache.get("10"));
System.out.println(cache.get("20"));
System.out.println(cache.get("a0"));
List<String> ls = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "a");
System.out.println(cache.getAll(ls));
System.out.println(cache.get("WhatIsTheFuck"));
}
@Test
public void testCallable() throws ExecutionException {
Cache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(10).build();
final String key = "2";
Integer value = cache.get(key, new Callable<Integer>() {
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Callable.call running, key:" + key);
return key.matches("\\d+") ? Integer.parseInt(key) : -1;
}
});
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(value);
}
@Test
public void testPut() {
Cache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).build();
cache.put("1", 1);
cache.put("2", 2);
cache.put("3", 3);
cache.put("4", 4);
System.out.println(cache.asMap().get("1")); // 因为最多缓存3个,get("1")数据被清除,返回null
System.out.println(cache.asMap().get("2"));
}
@Test
public void testWeight() throws ExecutionException {
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumWeight(10).weigher(new Weigher<String, Integer>() {
public int weigh(String s, Integer integer) {
return integer;
}
}).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading from CacheLoader, key:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
cache.get("1");
cache.get("3");
cache.get("5");
cache.get("1");
cache.get("7");
cache.get("1");
cache.get("3");
}
@Test
public void testTimeEviction() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("nano:" + System.nanoTime());
System.out.println("ms :" + System.currentTimeMillis());
final long start = System.nanoTime();
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.HOURS).ticker(new Ticker() {
public long read() {
long current = System.nanoTime();
long diff = current - start;
System.out.println("diff:" + (diff / 1000 / 1000 / 1000));
long time = start + (diff * 600);
return time;
}
}).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>(编程客栈) {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading data from CacheLoader, key:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
System.out.println(cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("time:" + (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())) + "-------" + cache.get("1"));
}
@Test
public void testWeakKeys() {
CacheBuilder.newBuilder().weakKeys().weakValues().build();
}
@Test
public void testRemovalListener() throws InterruptedException {
Cache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS).removalListener(new RemovalListener<String, Integer>() {
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<String, Integer> r) {
System.out.println("Key:" + r.getKey());
System.out.println("Value:" + r.getValue());
System.out.println("Cause:" + r.getCause());
}
}).build();
cache.put("1", 1);
cache.put("2", 2);
cache.put("3", 3);
cache.put("4", 4);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(11);
System.out.println("get-from-cache-2:" + cache.getIfPresent("2"));
cache.put("2", 3);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(11);
}
@Test
public void testEvict() throws ExecutionException {
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(2).removalListener(new RemovalListener<String, Integer>() {
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<String, Integer> r) {
System.out.println("Key:" + r.getKey() + ", Value:" + r.getValue() + ", Cause:" + r.getCause());
}
}).recordStats().build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CacheLoader.load key:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
System.out.println(cache.get("2"));
System.out.println(cache.get("5"));
System.out.println(cache.get("6"));
System.out.println(cache.get("1"));
}
@Test
public void testStatistics() {
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).recordStats().build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
});
CacheStats stats = cache.stats();
System.out.println(stats.hitRate()); // 缓存命中率
System.out.println(stats.averageLoadPenalty()); // 平均数加载时间,单位纳秒
System.out.println(stats.evictionCount()); // 缓存过期数据数
}
@Test
public void testRefresh() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
final ScheduledExecutorService es = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
LoadingCache<String, Integer> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(3).refreshAfterWrite(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS).build(new CacheLoader<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer load(String s) throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading from load...s:" + s);
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
@Override
public ListenableFuture<Integer> reload(final String key, final Integer oldValue) throws Exception {
if (oldValue > 5) { // 立即返回旧值
System.out.println("loading from reload immediate...key:" + key);
return Futures.immediateFuture(oldValue);
} else {
ListenableFutureTask<Integer> fi = ListenableFutureTask.create(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("loading from reload...key:" + key);
return oldValue;
}
});
es.execute(fi);
return fi;
}
}
});
cache.get("5");
cache.get("6");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
cache.get("5");
cache.get("6");
}
}
到此这篇关于使用Guava Cache做缓存的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Guava Cache缓存内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程客栈(www.devze.com)!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论