目录
- 1. set 的基本内容
- 1.基本特点
- 2.set() 实质
- 2. set 的基本方法
- 2.1 set 的普通基本方法
- 2.2 set 的逻辑基本方法
- 总结
1. set 的基本内容
1.基本特点
- (1) 无序性
- (2) 确定性
- (3) 不重复性
2.set() 实质
内部进行 可迭代性的 for 循环
例子:

2. set 的基本方法
2.1 set 的普通基本方法
2.1.1 增
add(self, *args, **kwargs) copy(self, *args, **kwargs)
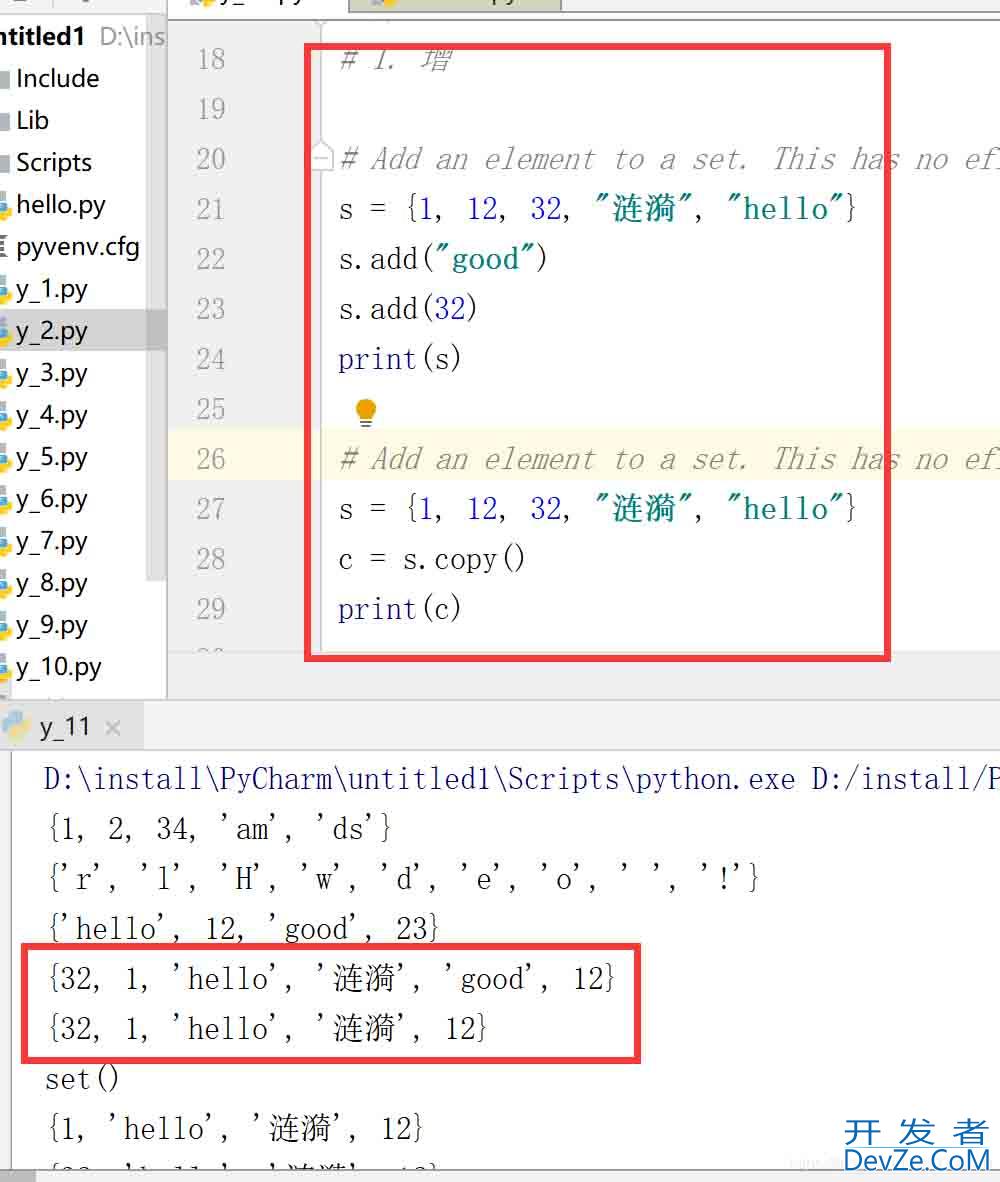
# 1. 增
# Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present.
s = {1, 12, 32, "涟漪", "hello"}
s.add("good")
s.add(32)
print(s)
# Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present.
s = {1, 12, 32, "涟漪", "hello"}
c = s.copy()
print(c)
结果:
2.1.1 删
clear(self, *args, **kwargs) pop(self, *args, **kwargs) remove(self, *args, **kwargs) discard(self, *args, **kwargs)
# 2. 删
# Remove all elements from this set.
s = {1, 12, 32, "涟漪", "hello"}
s.clear()
print(s)
# Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty.
s = {1, 12, 32, "涟漪", "hello"}
s.pop()
print(s)
# Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError.
s = {1, 12, 32, "涟漪", "hello"}
s.remove(1)
# s.remove("good")
print(s)
# Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing.
s = {1, 12, 32, "涟漪", "hello"}
s.discard(1)
s.discard("good")
print(s)
结果:
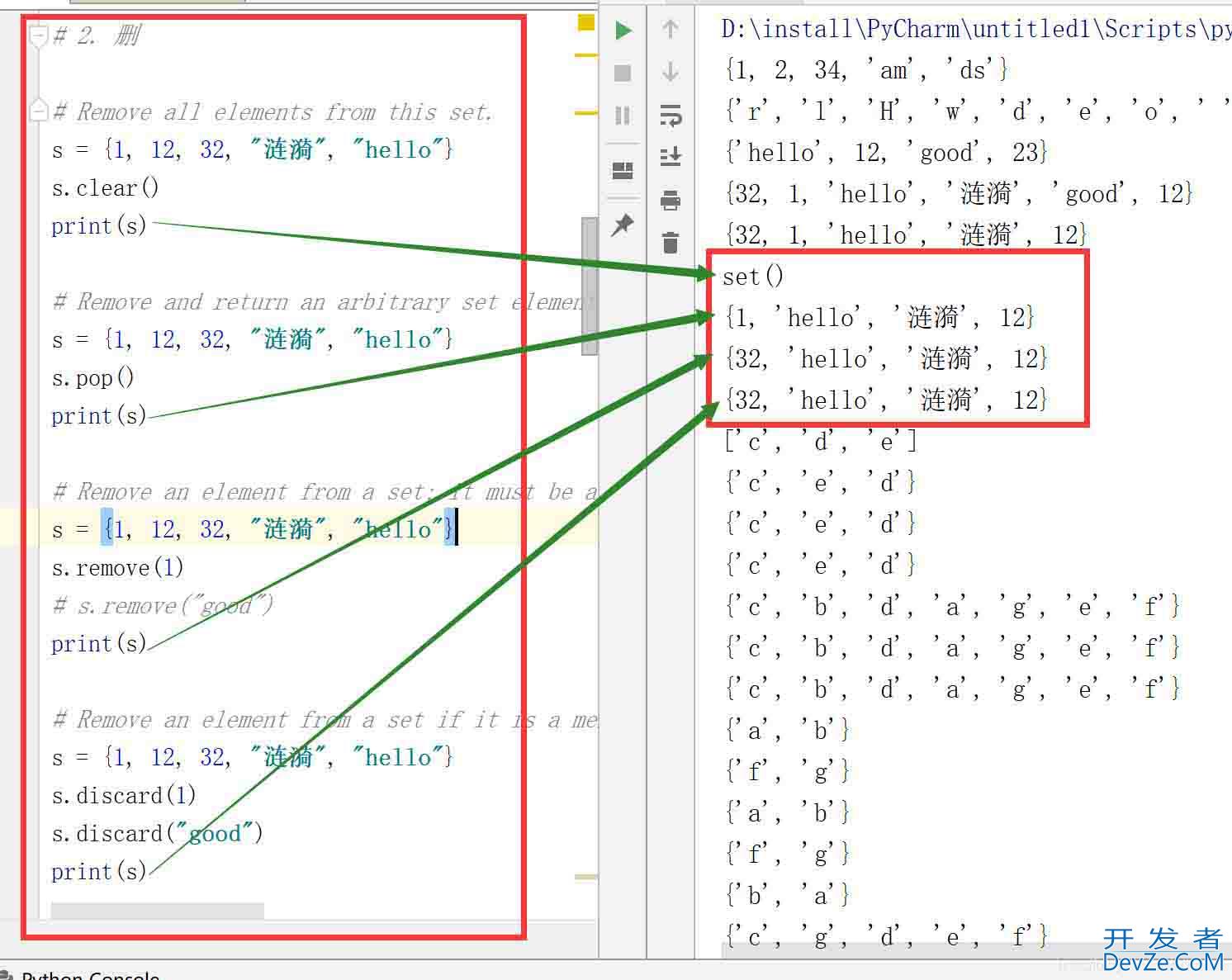
pop() 是随机删除。
remove() 和 discard() 指定删除,但是指定不存在的元素时,remove() 会报错,而 discard() 不会报错
2.2 set 的逻辑基本方法
2.2.1 set 交集运算
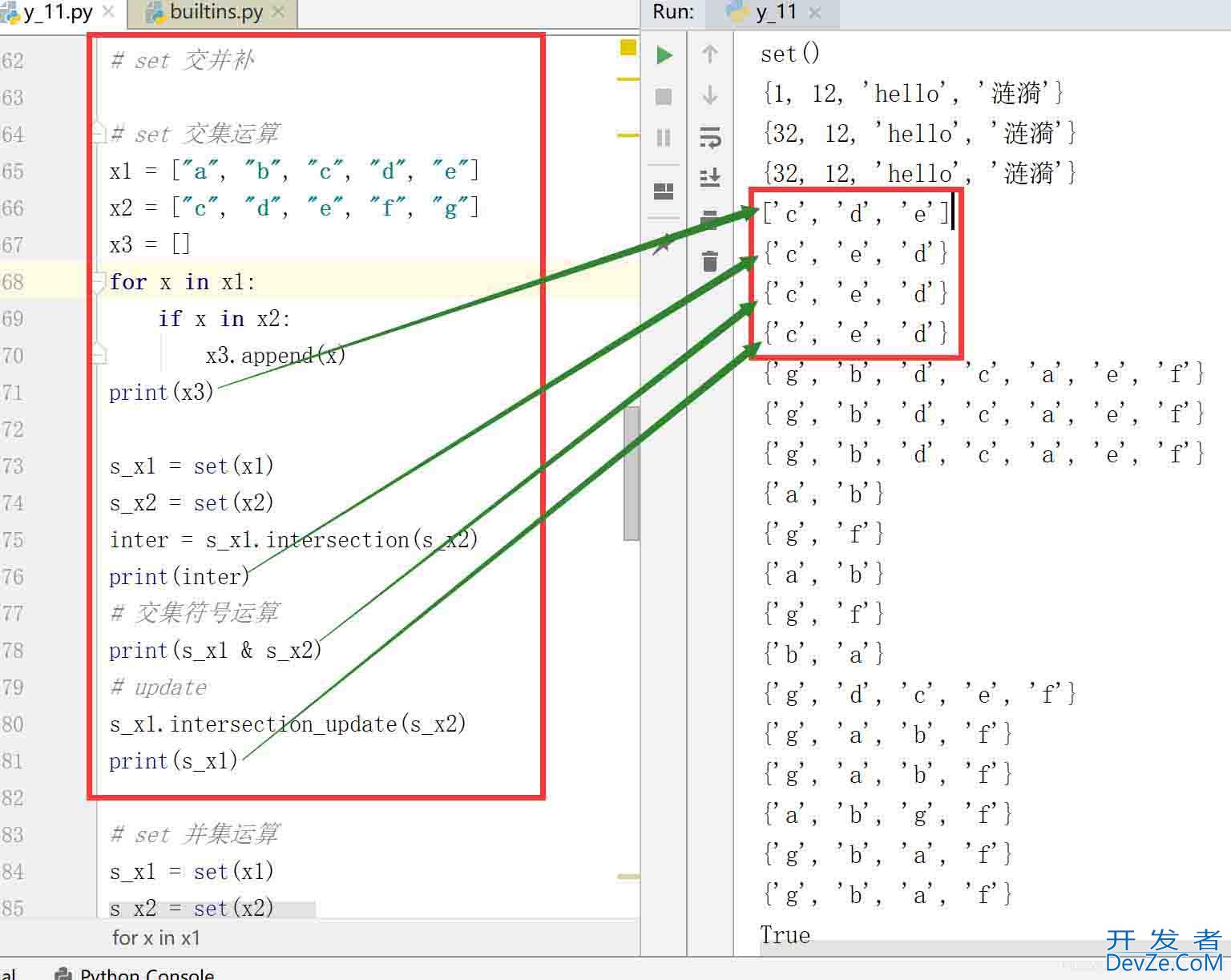
# set 交集运算
x1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"]
x2 = ["cDquKVKzGHA", "djavascript", "e", "f", "g"]
x3 = []
for x in x1:
if x in x2:
x3.appepythonnd(x)
print(x3)
s_x1 = set(x1)
s_x2 = set(x2)
inter = s_x1.intersection(s_x2)
print(inter)
# 交集符号运算
print(s_x1 & s_x2)
# update
s_x1.intersection_update(s_x2)
print(s_x1)
结果:
2.2.2 set 并集运算
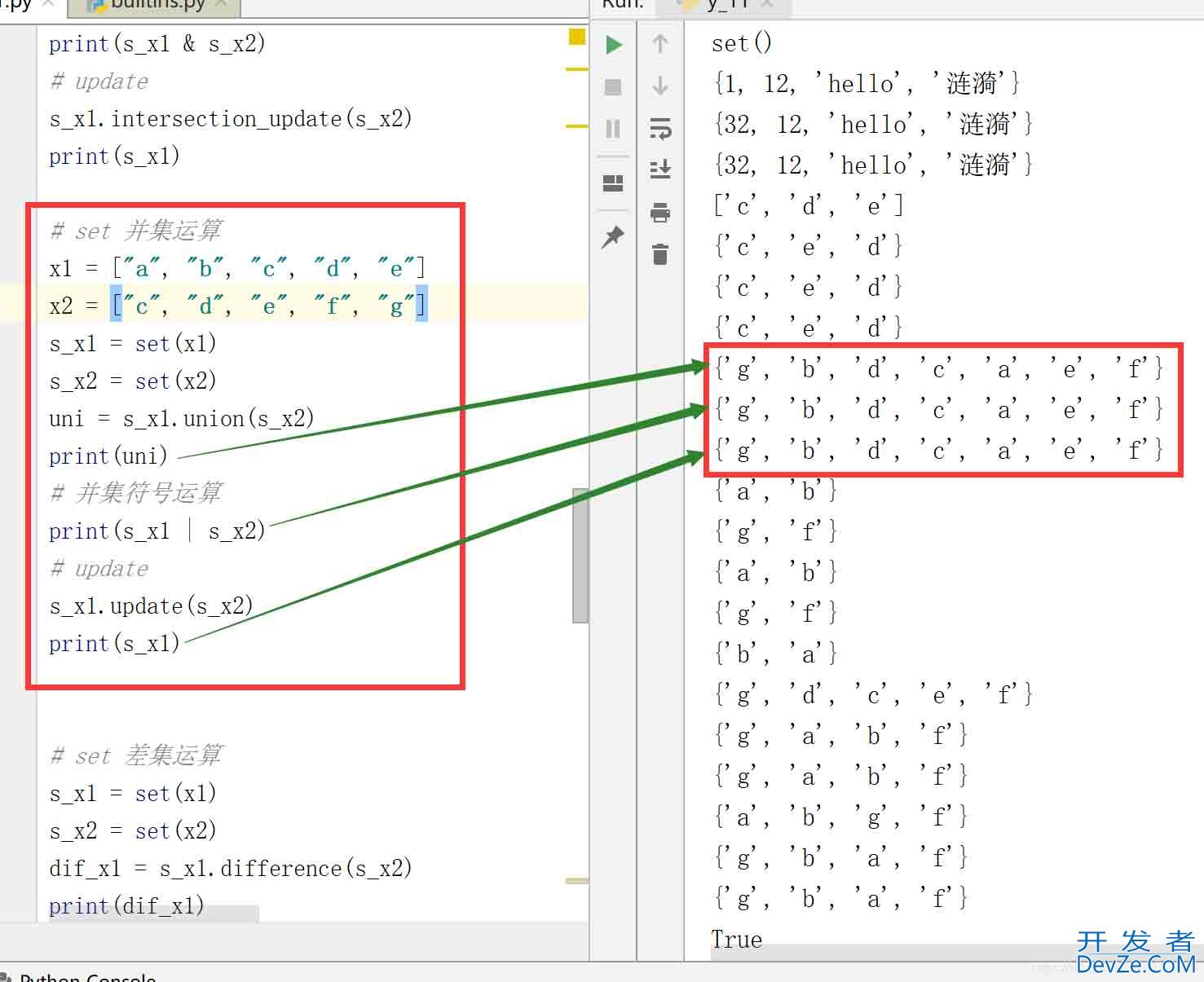
# set 并集运算 x1 = ["a", 编程客栈"b", "c", "d", "e"开发者_JAVA教程] x2 = ["c", "d", "e", "f", "g"] s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) uni = s_x1.union(s_x2) print(uni) # 并集符号运算 print(s_x1 | s_x2) # update s_x1.update(s_x2) print(s_x1)
结果:
2.2.3 set 差集运算
# set 差集运算 x1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"] x2 = ["c", "d", "e", "f", "g"] s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) dif_x1 = s_x1.difference(s_x2) print(dif_x1) dif_x2 = s_x2.difference(s_x1) print(dif_x2) # 差集符号运算 print(s_x1 - s_x2) print(s_x2 - s_x1) # update s_x1.difference_update(s_x2) print(s_x1) s_x2.difference_update(s_x1) print(s_x2)
结果:
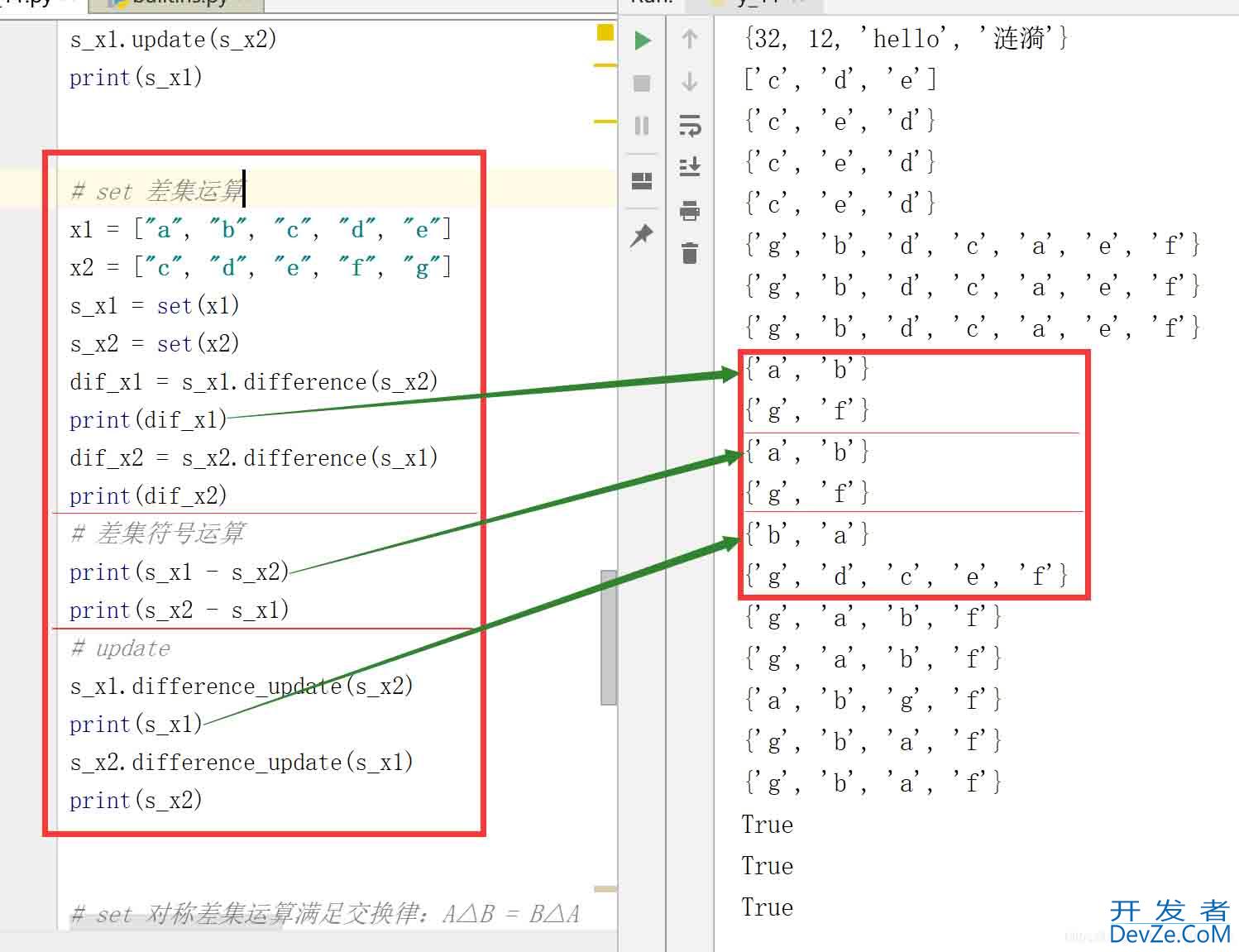
2.2.4 set 对称差集运算
# set 对称差集运算满足交换律:A△B = B△A s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) sym = s_x1.symmetric_difference(s_x2) print(sym) # 对称差集符号运算 print(s_x1 ^ s_x2) print(s_x1 - s_x2 | s_x2 - s_x1) print((s_x1 | s_x2) - (s_x2 & s_x1)) # update s_x1.symmetric_difference_update(s_x2) print(s_x1)
结果:

2.2.5 set 逻辑判断运算
# 判断
# Return True if two sets have a null intersection.
x1 = {"a", "b", "c"}
x2 = {"e", "f", "g"}
inter = x1.isdisjoint(x2)
print(inter)
# Report whether another set contains this set.
x1 = {"a", "b", "c"}
x2 = {"a", "b", "c", "e", "f", "g"}
inter = x1.issubset(x2)
print(inter)
# Report whether this set contains another set.
x1 = {"a", "b", "c", "e", "f", "g"}
x2 = {"a", "b", "c"}
inter = x1.issuperset(x2)
print(intejsr)
结果:

总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。


 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论