目录
- 一. 什么是Spring Security
- 1. 登陆校验的流程
- 2. SpringSecurity基础案例
- 二. Spring Security原理流程
- 1. 大致流程
- 三. JWT
- 1. 什么是JWT?
- 2. SpringSecurity集成JWT
- 四. 总结
一. 什么是Spring Security
Spring Security是Spring家族的一个安全管理框架, 相比于另一个安全框架Shiro, 它具有更丰富的功能。一般中大型项目都是使用SpringSecurity做安全框架, 而Shiro上手比较简单
spring security 的核心功能:
- 认证(你是谁): 只有你的用户名或密码正确才能访问某些资源
- 授权(你能干嘛): 当前用户具有哪些功能, 将资源进行划分, 如在公司中分为普通资料和高级资料, 只有经理用户以上才能访文高级资料, 其他人只能拥有访问普通资料的权限。
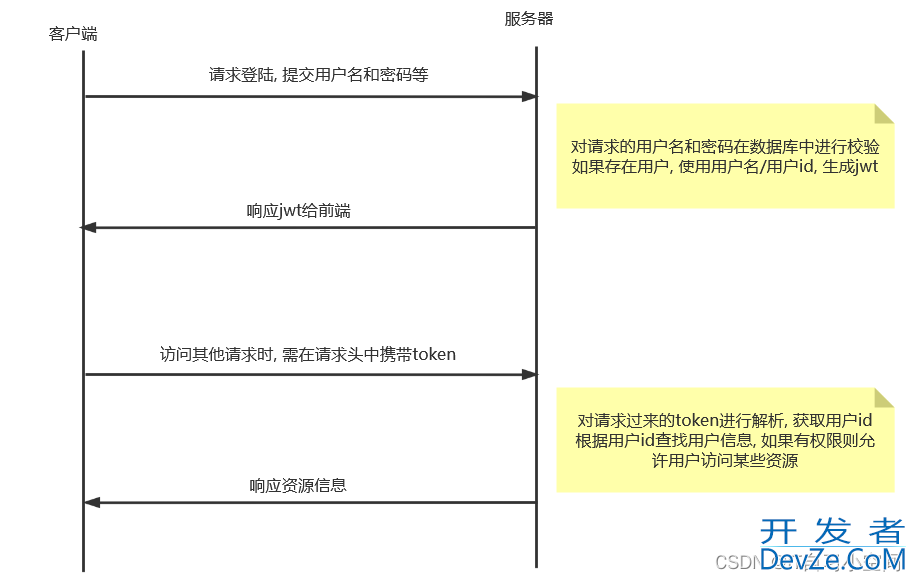
1. 登陆校验的流程
2. SpringSecurity基础案例
首先创建一个Springboot的项目
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
创建一个controller类
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
启动项目访问http://localhost:8080/login, 发现页面并没有hello字符, 下图是SpringSeurity默认的登陆界面, 默认用户名为user, 密码为启动项目时在输出框中的内容

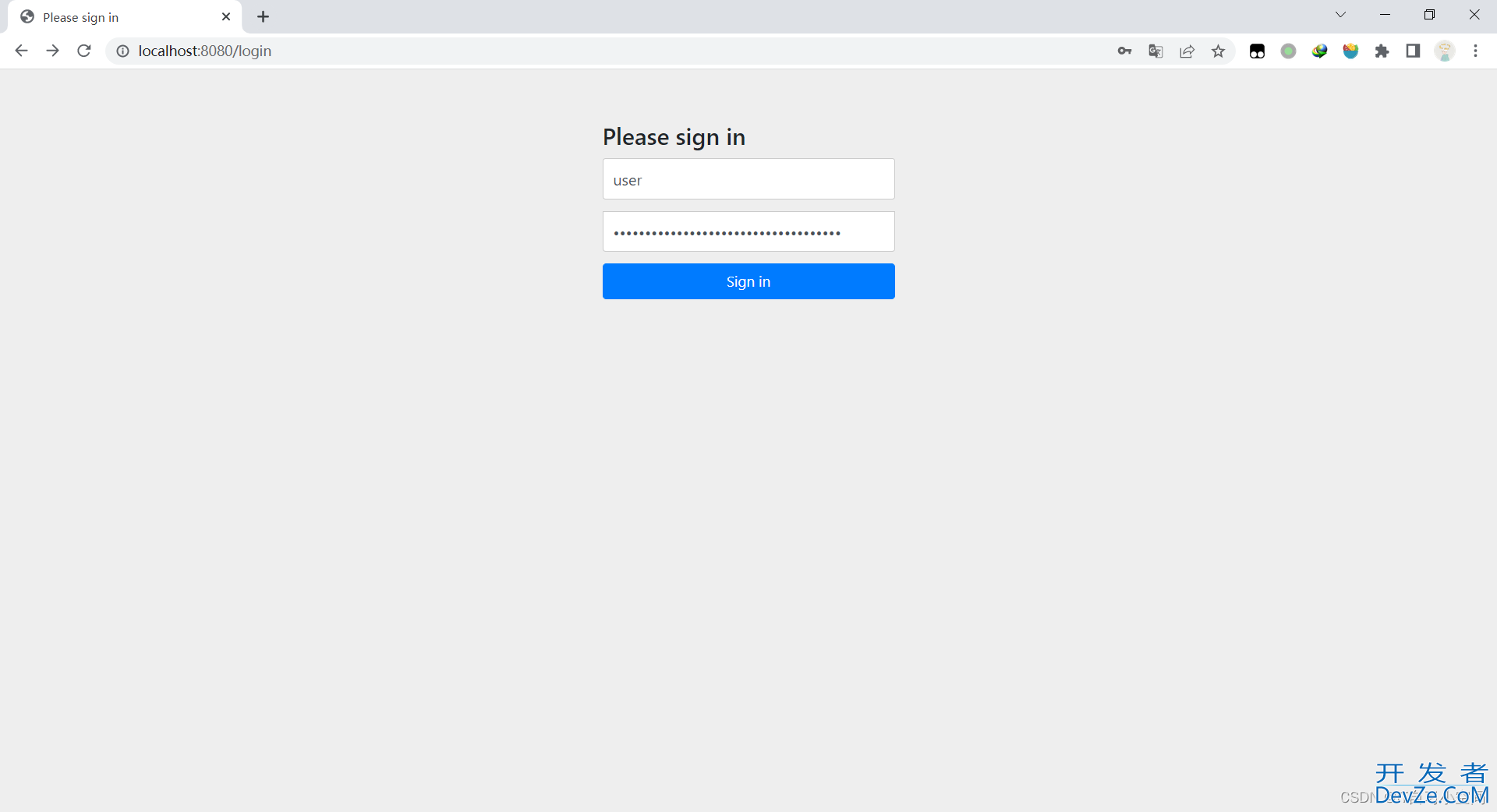
在实际项目中, 显然不能使用默认的登陆界面, 所以我们需要自定义登陆认证和授权
二. Spring Security原理流程
SpringSecurity底层实现是一系列过滤器链
默认自动配置的过滤器

| 过滤器 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter | 将WebAsyncManger与SpringSecurity上下文进行集成 |
| SecurityContextPersistenceFilter | 在处理请求之前, 将安全信息加载到SecurityContextHolder中 |
| HeaderWriterFilter | 处理头信息假如响应中 |
| CsrfFilter | 处理CSRF攻击 |
| LogoutFilter | 处理注销登录 |
| UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter | 处理表单登录 |
| DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter | 配置默认登录页面 |
| DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter | 配置默认注销页面 |
| BasicAuthenticationFilter | 处理HttpBasic登录 |
| RequestCacheAwareFilter | 处理请求缓存 |
| SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter | 包装原始请求 |
| AnonymousAuthenticationFilter | 配置匿名认证 |
| SessionManagementFilter | 处理session并发问题 |
| ExceptionTranslationFilter | 处理认证/授权中的异常 |
| FilterSecurityInterceptor | 处理授权相关 |
下图是主要的过滤器
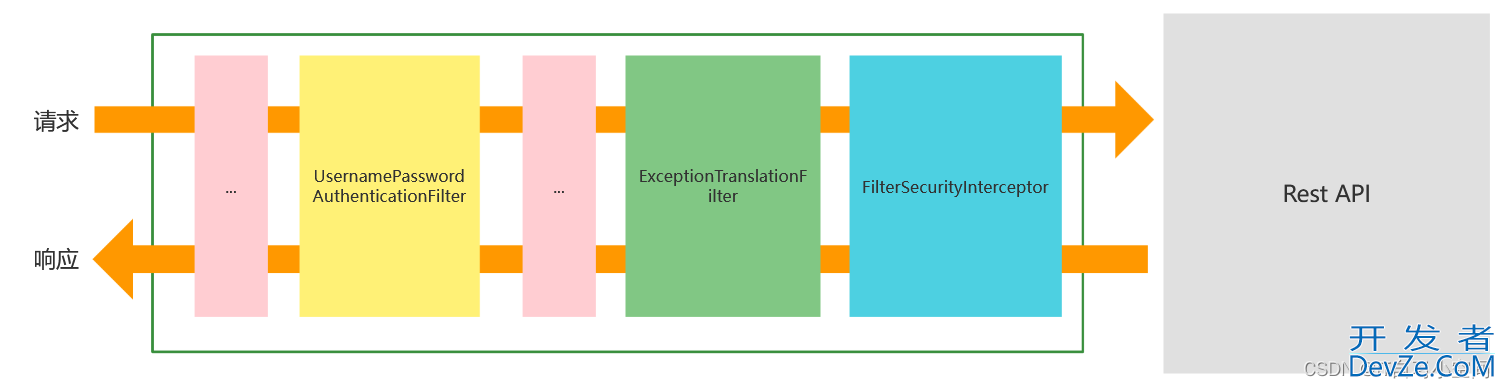
上图只画出了核心的过滤器
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter: 负责处理登陆页面填写的用户名和密码的登陆请求
ExceptionTranslationFilter: 处理过滤器链中抛出的任何AccessDeniedException和AuthenticationException异常
FilterSecurityInterceptor: 负责权限校验的过滤器
1. 大致流程
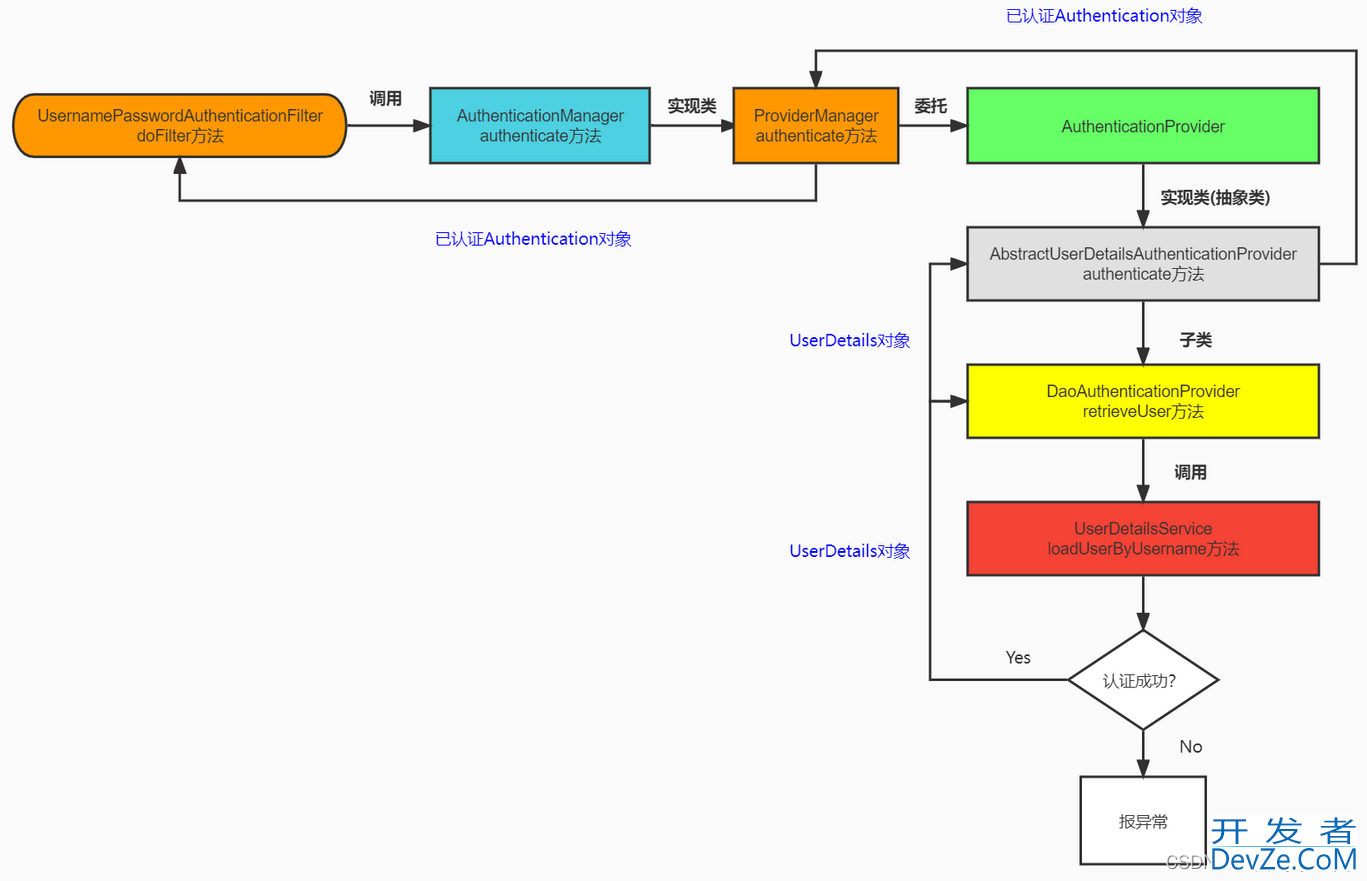
(1) 下面是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter中的attemptAuthentication方法, 该方法会将前端发送的用户名和密码封装为UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象, 该对象是Authentication对象的实现类
注意: attemptAuthentication方法主要处理视图表单认证, 现今都是前后端分离项目导致不能使用该方法进行拦截, 所以我们需要自己实现一个过滤器覆盖或者在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter之前做用户名和密码拦截处理.
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
(2) 返回getAuthenticationManager.authenticate(authRequest), 将未认证的Authentication对象传入AuthenticationManager , 进入authenticate方法我们看到AuthenticationManager是一个接口, 该接口主要做认证管理, 它的默认实现类是ProviderManager
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
}
(3) 在SpringSecurity中, 在项目中支持多种不同方式的认证方式, 不同的认证方式对应不同的AuthenticationProvider, 多个AuthenticationProvider 组成一个列表, 这个列表由ProviderManager代理, 在ProviderManager中遍历列表中的每一个AuthenticationProvider进行认证
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 迭代遍历认证列表
Iterator var8 = this.getProviders().iterator();
while(var8.hasNext()) {
// 取出当前认证
AuthenticationProvider provider = (AuthenticationProvider)var8.next();
// 当前认证是否支持当前的用户名和密码信息
if (provider.supports(toTest)) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using " + provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
// 开始做认证处理
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
// 认证成功时候返回
this.copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException | AccountStatusException var13) {
this.prepareException(var13, authentication);
throw var13;
} catch (AuthenticationException var14) {
lastException = var14;
}
}
}
// 不支持当前认证并且parent支持该认证
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
try {
result = parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
} catch (ProviderNotFoundException var11) {
} catch (AuthenticationException var12) {
parentException = var12;
lastException = var12;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && result instanceof CredentialsContainer) {
((CredentialsContainer)result).eraseCredentials();
}
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
} else {
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound", new Object[]{toTest.getName()}, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
if (parentException == null) {
this.prepareException((AuthenticationException)lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}
}
拓展:
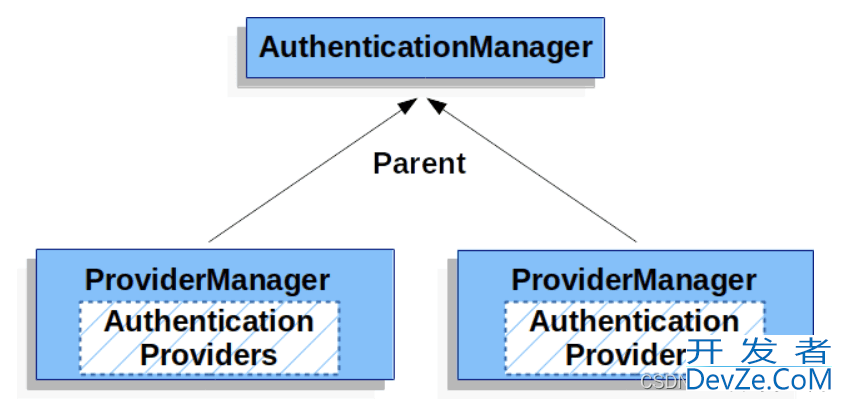
ProviderManager可以配置一个AuthenticationManager作为parent, 当ProviderManager认证失败后, 可以进入parent中再次进行认证, 通常由ProviderManager来充当parent的角色, 即ProviderManager是ProviderManager的parent
ProviderManager可以有多个, 而多个ProviderManager共用一个parent
(4) 当前AuthenticationProvider支持认证时, 会进入AuthenticationProvider的authenticate方法, 而AuthenticationProvider是一个接口, 它的实现类是AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
public Authentiwww.devze.comcation authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication, () -> {
return this.messages.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports", "Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported");
});
// 获取当前authentication的信息
String username = authentication.getPrincipal() == null ? "NONE_PROVIDED" : authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
// 在缓存中查看username
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
// 调用retrieveUser方法
user = this.retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)authentication);
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException var6) {
this.logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (this.hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
throw var6;
}
Assert.notNull(user, "retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
this.preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
this.additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)authentication);
} catch (AuthenticationException var7) {
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
throw var7;
}
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = this.retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)authentication);
this.preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 密码的加密处理
this.additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)authentication);
}
this.postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (this.forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
return this.createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
(5) retrieveUser在AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider中有retrieveUser方法, 但是实现该方法的对象是DaoAuthenticationProvider, 该对象重写了retrieveUser方法, 在retrieveUser方法中, 可以看到调用了UserDetailsService的loadUserByUsername()方法, 该方法用来根据用户名查询内存或者其他数据源中的用户. 默认是基于内存查找, 我们可以自定义为数据库查询. 查询后的结果封装成UserDetails 对象, 该对象包含用户名、加密密码、权限以及账户相关信息. 密码的加密处理是SpringSecurity帮我们处理
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
this.prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
// 调用该方法返回一个UserDetails 对象
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
} else {
return loadedUser;
}
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException var4) {
this.mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw var4;
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var5) {
throw var5;
} catch (Exception var6) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(var6.getMessage(), var6);
}
}
三. JWT
1. 什么是JWT?
JWT主要用于用户登陆鉴权, 在之前可能会使用session和token认证, 下面简述三者session和JWT的区别
Session
用户向服务器发送一个请求时, 服务器并不知道该请求是谁发的, 所以在用户发送登录请求时, 服务器会将用户提交的用户名和密码等信息保存在session会话中(一段内存空间)。同时服务器保存的用户信息会生成一个sessionid(相当于用户信息是一个value值, 而sessionid是value值的key)返回给客户端, 客户端将sessionid保存到cookie中, 等到下一次请求客户端会将cookie一同请求给服务器做认证
如果用户过多, 必然会耗费大量内存, 在cookie中存放sessionid会存在暴露用户信息的风险
Token
token是一串随机的字符串也叫令牌, 其原理和session类似, 当用户登录时, 提交的用户名和密码等信息请求给服务端, 服务端会根据用户名或者其他信息生成一个token而不是sessionid, 这和sessionid唯一区别就是, token不再存储用户信息, 客户端下一次请求会携带token, 此时服务器根据此次token进行认证。
token认证时也会到数据库中查询, 会造成数据库压力过大。
JWT
JWT将登录时所有信息都存在自己身上, 并且以json格式存储, JWT不依赖Redis或者数据库, JWT安全性不太好, 所以不能存储敏感信息
2. SpringSecurity集成JWT
(1) 认证配置
a) 配置SpringSecurity
首先配置一个SpringSecurity的配置类, http://www.devze.com因为是基于JWT进行认证, 所以需要在配置中禁用session机制, 并不是禁用整个系统的session功能
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserServiceImpl userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private LoginFilter loginFilter;
@Autowired
private AuthFilter authFilter;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 禁用session机制
http.csrf().disable()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
http.authorizeRequests()
// 指定某些接口不需要通过验证即可访问。像登陆、注册接口肯定是不需要认证的
.antMatchers("/sec/jslogin").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
// 自定义权限配置
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(O o) {
o.setAccessDecisionM编程客栈anager(customUrlDecisionManager);
o.setSecurityMetadataSource(customFilter);
return o;
}
})
.and()
// 禁用缓存
.headers()
.cacheControl();
http.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthencationTokenFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// 添加自定义未授权和未登陆结果返回
http.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedHandler(restfulAccessDeniedHandler)
.authenticationEntryPoint(restAuthoricationEntryPoint);
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// 指定UserDetailService和加密器
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Bean
@Override
protected AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManager();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
b) 实现登录接口
先按照正常流程, 实现一个登录的接口然后在业务层中实现
@PostMapping("/login")
public Res login(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest request) {
return userService.login(user, request);
}
在业务层中, 首先对密码和用户名进行检验, 然后更新security登录用户对象, 在此之前我们先来认识几个在SpringSecurity中重要的变量
Authentication: 存储了认证信息, 代表登录用户SecurityContext: 上下文对象, 用来获取Authentication(用户信息)SecurityContextHolder: 上下文管理对象, 用来在程序任何地方获取SecurityContextUserDetails: 存储了用户的基本信息, 以及用户权限、是否被禁用等
在Authentication中的认证信息有
Principal: 用户信息Credentials: 用户凭证, 一般是密码Authorities: 用户权限
@Override
public Res login(User user, HttpServletRequest request) {
String username = user.getUsername();
String password = user.getPassword();
// 登陆 检测
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if(null == userDetails || !passwordEncoder.matches(password, userDetails.getPassword())) {
return Res.error("用户名或密码不正确!");
}
// 更新security登录用户对象
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails,
null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
// 创建一个token
String token = jwtTokenUtil.generateToken(userDetails);
Map<String, String> tokenMap = new HashMap<>();
tokenMap.put("token", token);
tokenMap.put("tokenHead", tokenHead);
return Res.success("登陆成功", tokenMap);
}
下面这行代码主要是在数据库或者缓存中查询用户提交的用户名以及用户的权限信息, 将这些信息保存在userDetails中
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 实现了Authentication, 也就是说此时将userDetails中的信息以及权限信息存放在Authentication中
创建Token需要JWT的工具类, 在网上开发者_Python培训随便找个都可以, 大致都一样, 这个只需要知道就行了
c) 过滤请求
在原生SpringSecurity中默认的拦截在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter这个类中,该类主要拦截表单提交的用户名和密码, 显然在前后端分离项目中不适用, 而且我们用到了JWT的验证方式, 前端每次请求都需要带上token, 所以我们需要在后端对每个请求进行提前过滤拦截
public class JwtAuthencationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Value("${jwt.tokenHeader}")
private String tokenHeader;
@Value("${jwt.tokenHead}")
private String tokenHead;
@Autowired
private JwtTokenUtil jwtTokenUtil;
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 请求头中获取token信息
String authheader = request.getHeader(tokenHeader);
// 存在token
if(null != authheader && authheader.startsWith(tokenHead)) {
// 去除字段名称, 获取真正token
String authToken = authheader.substring(tokenHead.length());
// 利用token获取用户名
String username = jwtTokenUtil.getUserNameFromToken(authToken);
// token存在用户但未登陆
// SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() 获取上下文对象中认证信息
if(null != username && null == SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()) {
// 自定义数据源获取用户信息
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
// 验证token是否有效 验证token用户名和存储的用户名是否一致以及是否在有效期内, 重新设置用户对象
if(jwtTokenUtil.validateToken(authToken, userDetails)) {
// 重新将用户信息封装到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
// 将信息存入上下文对象
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
该过滤器主要做的是:
- 提取前端发送的请求头信息, 根据JWT的工具类获取用户名
- 如果请求头具有有效的字符串(也就是拥有用户信息)并且上下文对象存在用户信息(数据库或者缓存中查的用户信息)则直接到下一个过滤器, 否则请求头中有信息而当前上下文对象没有存储用户信息则将请求头中的用户在数据层验证之后重新放入上下文对象中(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)。
- 如果当前用户没有登录或者没有token信息(可能是token过期), 而当前请求的地址符合权限中包含的地址(也就是数据库中存在的), 则会进入权限验证(下面会讲)
当然以上的逻辑可以自己自定义, 不管以上什么情况都会进入权限验证
要让这个过滤器加入到SpringSecurity的过滤器链中, 就需要在SecurityConfig类的configure方法添加下面一条语句, addFilterBefore()将jwtAuthencationTokenFilter(), 放在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter之前
http.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthencationTokenFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
(2) 权限配置
在一个项目中, 不同的用户需要具有不同的权限, 我们怎么对用户进行区分呢?
a) RBAC权限表
将用户、角色和权限绑定,这样可以知道某个用户具有哪些角色, 而某个角色对应有哪些权限(能干什么,不能干什么),这样就知道哪些用户拥有的角色和权限信息。
基于以上的想法, 我们需要三张实体表, 还需要两张多对多的关系表, 这样就构成了RBAC的五张表
b) 授权流程
在SpringSecurity中授权的过滤器是FilterSecurityInterceptor
默认的流程
- 调用
SecurityMetadataSource获取当前请求的鉴权规则 - 接着调用
AccessDecisionManager来校验当前用户的是否拥有当前权限 - 如果有权限就放行, 否则抛出异常, 该异常则会被
AccessDeniedHandler处理
c) 自定义SecurityMetadataSource
@Component
public class CustomUrlDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager {
@Override
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object o, Collection<ConfigAttribute> collection) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException {
if(Collections.isEmpty(collection)) {
return;
}
for (ConfigAttribute configAttribute : collection) {
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
if("ROLE_ANONYMOUS".equals(authority.getAuthority())) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("尚未登录, 请登录");
}
if(Objects.equals(authority.getAuthority(), configAttribute.getAttribute())) {
return;
}
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("权限不足, 请联系管理员!");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute configAttribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource继承SecurityMetadataSource
在getAttributes方法中, o参数封装了request的相关信息, 可以从中获取请求的方法和URL等信息
然后menus得到的是当前数据层中所有的权限路径, 接着循环所有的路径信息与当前请求的方法和URL进行验证, 如果在数据层中没有当前请求则返回null, 否则将该权限的在数据层中的信息返回
c) 自定义AccessDecisionManager
如果在SecurityMetadataSource中有权限信息, 则会进入该方法
@Component
public class CustomUrlDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager {
@Override
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object o, Collection<ConfigAttribute> collection) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException {
if(Collections.isEmpty(collection)) {
return;
}
for (ConfigAttribute configAttribute : collection) {
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
if("ROLE_ANONYMOUS".equals(authority.getAuthority())) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("尚未登录, 请登录");
}
if(Objects.equals(authority.getAuthority(), configAttribute.getAttribute())) {
return;
}
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("权限不足, 请联系管理员!");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute configAttribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
首先来看几个变量
- ConfigAttribute: 这个是鉴权的规则, 根据自己项目设定, 我们这里填入的是当前请求和数据层中相匹配的权限信息id
- GrantedAuthority: 当前认证用户所拥有的权限信息
在上述的decide方法中, 主要验证了用户所拥有的权限和当前请求的权限信息是否一致
如果不一致, 则抛出异常, 被AccessDeniedHandler处理
d) 自定义AccessDeniedHandler
自定义返回json格式数据
@Component
public class RestfulAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setCharacte编程rEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("application/json");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Res bean = Res.error("权限不足, 请联系管理员!");
bean.setCode(403);
out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(bean));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
e) 在SpringSecurity中的配置
在configure方法中, 进行了动态权限配置
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(O o) {
o.setAccessDecisionManager(customUrlDecisionManager);
o.setSecurityMetadataSource(customFilter);
return o;
}
})
插入: 还有一个认证异常处理
- 用户首次登录且验证成功, 此时正常用户权限授权
- 请求数据时, 非首次登录, 如果没有携带token(token过期), 又或者没有登录访问内部路径时, 说明没有认证权限不能访问, 抛出未登录异常
- 请求数据时, 有token信息, 而上下文对象中没有用户信息, 则会重新将用户信息放入上下文对象中, 接着进入权限验证, 如果用户拥有该权限则放行, 如果没有该权限则抛出权限不足异常
在configure中配置未登录和未授权异常处理
http.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedHandler(restfulAccessDeniedHandler)
.authenticationEntryPoint(restAuthoricationEntryPoint);
四. 总结
其实以上配置还有很多漏洞, 比如token的过期时间, 当用户上一秒还在请求数据, 下一秒token过期, 则会造成用户需要重新登录, 显然不合适
这是项目的地址 github下载
到此这篇关于Spring Security+JWT简述的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Security JWT简述内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论