目录
- 一、场景
- 二、SpringBoot默认静态资源访问方式
- 三、上传的文件应该存储在哪?怎么访问?
- 1.文件存储在哪?
- 2.怎么访问?
- 四、测试
- 五、总结
一、场景
Java实现文件上传到服务器本地开发者_C学习,并通过url访问
有个需求,前端上传文件,需要用开关的方式同时支持上传七牛和服务器本地,方便不同的用户需求合理分配资源。本篇主要介绍文件上传到本地,然后通过url访问。
二、SpringBoot默认静态资源访问方式
首先想到的就是可以通过SpringBoot通常访问静态资源的方式,当访问:项目根路径 + / + 静态文件名时,SpringBoot会依次去类路径下的四个静态资源目录下查找(默认配置)。
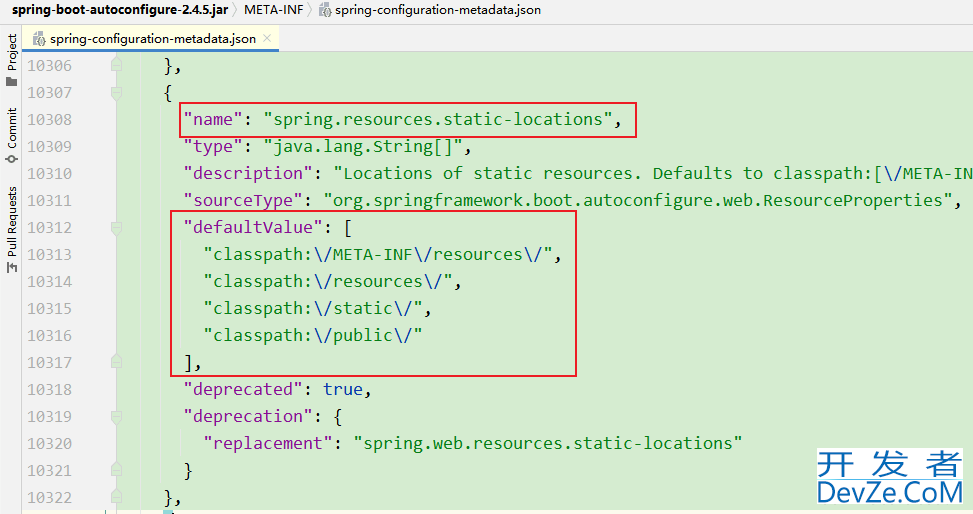
在资源文件resources目录下建立如下四个目录:
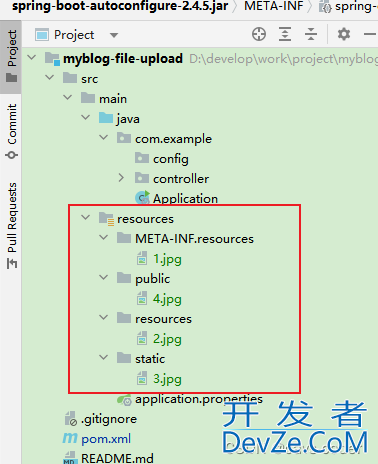
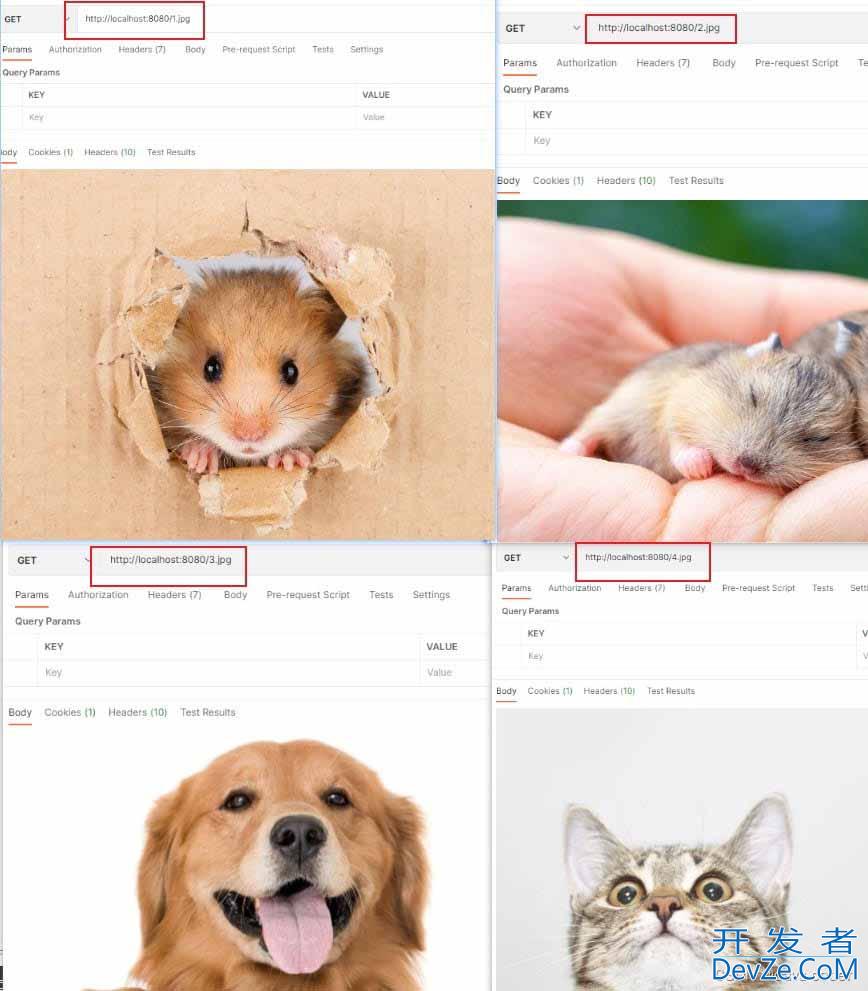
重启Spring boot,访问
http://localhost:8080/1.jpg
http://localhost:8080/2.jpghttp://localhost:8080/3.jpghttp://localhost:8080/4.jpg
结果:
三、上传的文件应该存储在哪?怎么访问?
1.文件存储在哪?
前文所说外部用户可通过url访问服务器资源文件resources目录下的静态资源,但若是将上传的文件都保存在resources相关目录下,将会导致后续打包过大,程序和代码不分离,无法查看等问题。
解决方案:文件上传到服务器某个目录,然后SpringBoot配置虚拟路径,映射到此目录。
2.怎么访问?
通过WebMvcConfigurer 的addResourceHandlers将匹配上虚拟路径的url映射到文件上传到服务器的目录,这样就可以通过url来获取服务器上的静态资源了。
示例代码
代码仓库github路径
目标:Windows本地测试,将文件上传到 D:\develop\work\project\myblog\myblog-file-upload\fileStorage 目录下,然后通过http://localhost:8080/files/文件名 访问。
配置类
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
FileServiceImpl fileService;
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//将匹配上/files/**虚拟路径的url映射到文件上传到服务器的目录,获取静态资源
registry.addResourceHandler("/" + fileService.pathPattern + "/**").addResourceLocations("file:" + fCkMpAwqZjfileService.filePath);
WebMvcConfigurer.super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
}
Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileController {
@Autowired
private FileServiceImpl fileService;
@PostMapping("/upload")
public FileUploadResponse upload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
return fileService.upload(file);
}
}
上传文件目录创建好后,主要通过 file.transferTo(new File(absolutePath)) 完成。
Service
@Slf4j
@Service
public class FileServiceImpl {
//拦截的url,虚拟路径
public String pathPattern = "files";
//自己设置的目录
private static final String fileDir = "fileStorage";
//上传文件存放目录 = 工作目录绝对路径 + 自己设置的目录,也可以直接自己指定服务器目录
//windows本地测试
//绝对路径: D:\develop\work\project\myblog\myblog-file-upload\fileStorage\2023020210103456www.devze.com80.jpg
//System.getProperty("user.dir") D:\develop\work\project\myblog\myblog-file-upload
//fileDir fileStorage
//fileName 202302021010345680.jpg
public String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + fileDir + File.separator;
private static final AtomicInteger SUFFIX = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Value(value = "${file.upload.suffix:jpg,jpeg,png,bmp,xls,xlsx,pdf}")
private String fileUploadSuffix;
public FileUploadResponse upload(MultipartFile file) {
FileUploadResponse result = new FileUploadResponse();
if (file.isEmpty()) {
log.error("the file to be uploaded is empty");
return result;
}
List<String> suffixList = Lists.newArrayList(fileUploadSuffix.split(","));
try {
//校验文件后缀
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
String suffix = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
if (!suffixList.contains(suffix)) {
log.error("unsupported file format");
return result;
}
//首次需生成目录
File folder = new File(filePath);
if (!folder.exists()) {
folder.mkdirs();
}
String fileName = timeFormat(Systandroidem.currentTimeMillis()) + SUFFIX.getAndIncrement() + "." + suffix;
String absolutePath = filePath + fileName;
log.info("absolutePath is {}", absolutePath);
file.transferTo(new File(absolutePath));
String separator = "/";
String path = separator + pathPattern + separator + fileName;
result.setPath(path);
result.setFileName(fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("the file upload error occurred. e ", e);
}
return result;
}
public static String timeFormat(Long time) {
if (Objects.isNull(time)) {
return null;
}
DateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS");
return s编程客栈df.format(time);
}
}
四、测试
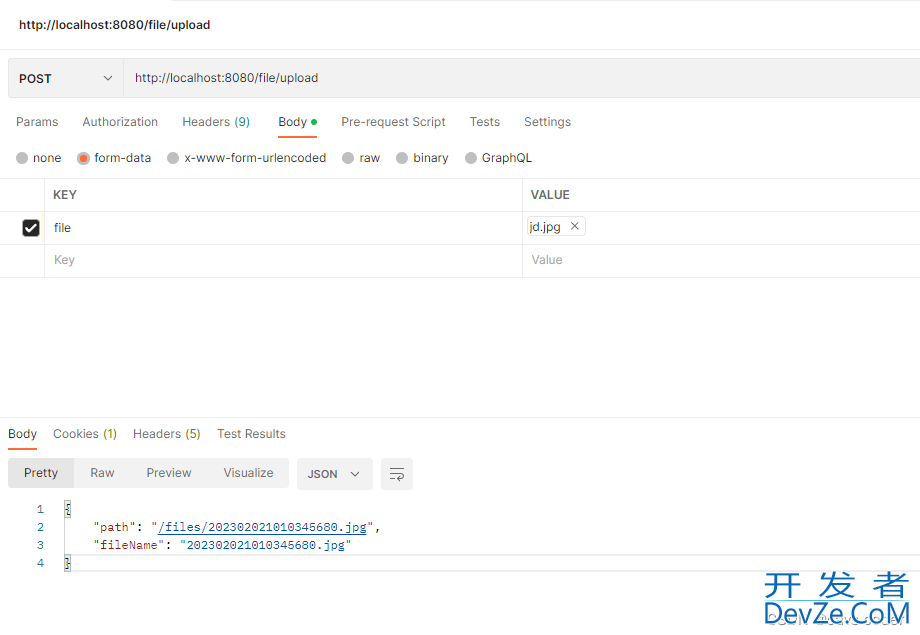
查看文件夹,已上传成功
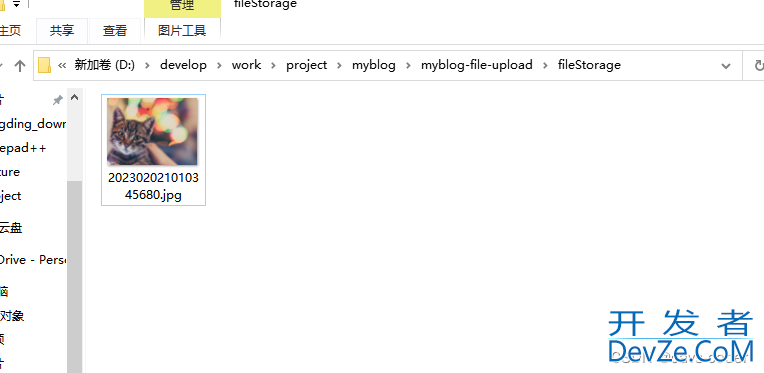
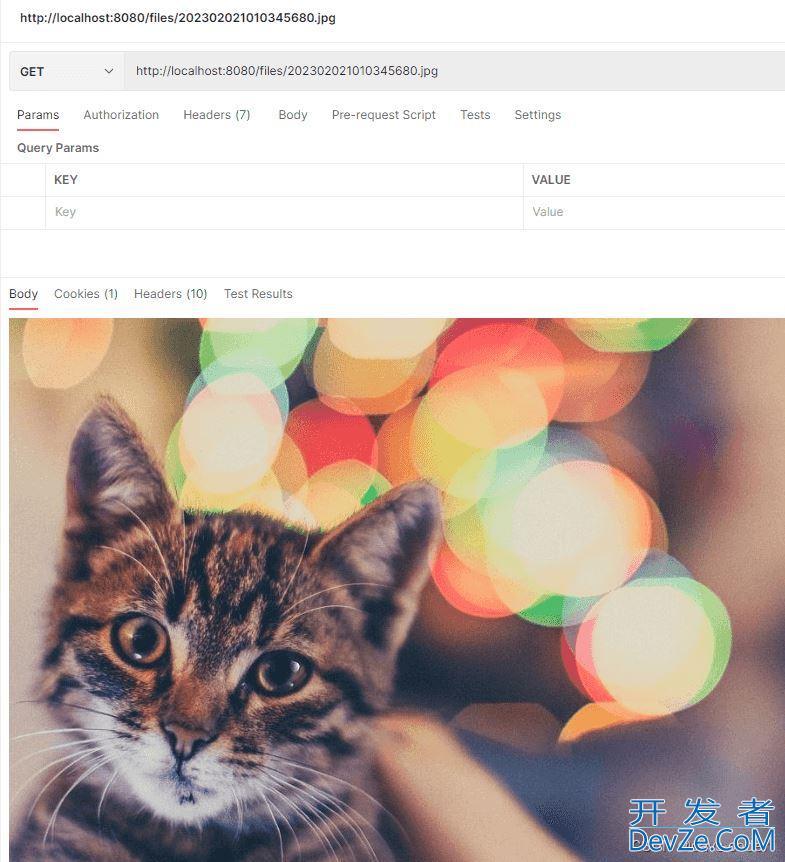
将上传接口返回的path拼接上域名或者ip端口、访问 http://localhost:8080/files/202302021010345680.jpg,得到:
五编程、总结
其实这和最初的SpringBoot获取静态资源的方式又有点不一样,针对url做拦截,实际上resources目录下并没有files这个文件夹,它只是一个虚拟路径,通过映射转发到文件夹上传目录,在该目录下通过文件名去定位。
另外,如果有用nginx,也可以在其配置中设置转发。
到此这篇关于Java实现文件上传到服务器本地并通过url访问的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java文件上传到服务器本地并访问内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论