目录
- 事件背景
- 现象获取
- 架构图
- 问题定位
- 原理分析
- 处理方法
- 最终效果
事件背景
现网上运行着一个自己开发的 metrics exporter,它是专门来捕获后端资源的运行状态,并生成对应的 prometheus metrics 供监控报警系统使用。当然这个 exporter 只是负责远程监控资源,并不能实际控制后端的资源,也不能实时动态获得被监控的资源的变动事件。当我们的运维小伙伴手动错误删除后端被监控的资源,导致业务流量异常。此时也没有报警出来,而这个报警却是依赖这个 metrics exporter 所采集的数据,导致了一次小型事件。因为这个事件,才有今天写文章的动力,同时也分享下解决这个问题的方法。
现象获取
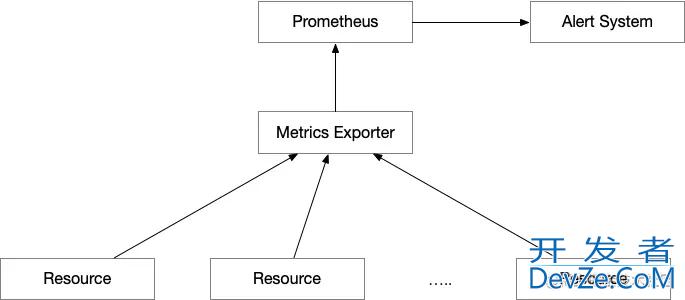
架构图
问题定位
通过跟小伙伴们一起复盘,以及追查可能出现问题的位置后,大家都觉得没有任何问题。在运维删除对应的监控资源后,同时没有关闭报警规则的情况下,应该有大量的任何异常报警产生。但实际情况,没有任何报警发出来。
当大家一筹莫展的时候,我突然说了一句,会不会是数据采集出现了问题?大家眼前一亮,赶紧拿出 metrics exporter 的代码检查。通过反复检查,也没有发现可疑的地方,于是大家又开始了思考。这时我打开了 metrics exporter 调试模式,打上断点,然后请运维小伙伴删除一个测试资源,观察监控数据的变化。果不其然,资源删除了,对应监控的 metrics 条目的值没有变化(也就是说,还是上次资源的状态)。
这下破案了,搞了半天是因为 metrics 条目内容没有跟随资源的删除而被自动的删除。导致了报警系统一直认为被删除的资源还在运行,而且状态正常。
原理分析
既然知道了原因,再回过头看 metrics exporter 的代码,代码中有 prometheus.MustRegister、prometheus.Unregister 和相关的 MphpetricsVec 值变更的实现和调用。就是没有判断监控资源在下线或者删除的情况下,如何删除和清理创建出来的 MetricsVec。
在我的印象中 MetricsVec 会根据 labels 会自动创建相关的条目,从来没有手动的添加和创建。根据这个逻辑我也认为,MetricsVec 中如果 labels 对应的值不更新或者处于不活跃的状态,应该自动删除才是。
最后还是把 golang 的 github.com/prometheus/client_golang 这个库想太完美了。没有花时间对 github.com/prometheus/client_golang 内部结构、原理、处理机制充分理解,才导致这个事件的发生。
github.com/prometheus/client_golang 中的 metrics 主要是 4 个种类,这个可以 baidu 上搜索,很多介绍,我这里不详细展开。这些种类的 metrics 又可以分为:一次性使用和多次使用。
- 一次性使用:当请求到达了 http 服务器,被 promhttp 中的 handler 处理后,返回数据给请求方。随后 metrics 数据就失效了,不保存。下次再有请求到 http 接口查询 metrics,数据重新计算生成,返回给请求方。
- 多次性使用:当请求到达了 http 服务器,被 promhttp 中的 handler 处理后,返回数据给请求方。随后 metrics 保存,并不会删除,需要手动清理和删除。 下次再有请求到 http 接口查询 metrics,直接返回之前存储过的数据给请求方。
注意这两者的区别,他们有不同的应用场景。
- 一次性使用:一次请求一次新数据,数据与数据间隔时间由数据读取者决定。 如果有多个数据读取者,每一个读取者读取到的数据可能不会相同。每一个请求计算一次,如果采集请求量比较大,或者内部计算压力比较大,都会导致负载压力很高。 计算和输出是同步逻辑。 例如:k8s 上的很多 exporter 是这样的方式。
- 多次性使用:每次请求都是从 map 中获得,数据与数据间隔时间由数据写入者决定。如果有多个数据读取者,每一个读取者采集的数据相同(读取的过程中没有更新数据写入)。每一个请求获得都是相同的计算结果,1 次计算多数读取。计算和输出是异步逻辑。例如:http server 上 http 请求状态统计,延迟统计,转发字节汇总,并发量等等。
这次项目中写的 metrics exporter 本应该是采用 “一次性使用” 这样的模型来开发,但是内部结构模型采用了 “多次性使用” 模型,因为指标数据写入者和数据读取者之间没有必然联系,不属于一个会话系统,所以之间是异步结构。具体我们看下图:
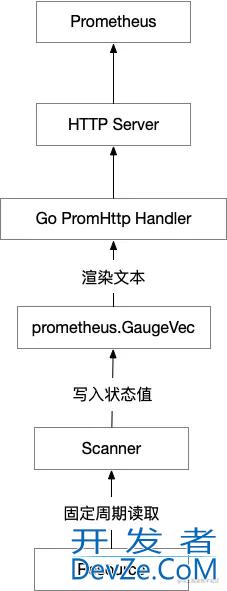
从图中有 2 个身份说明下:
- 数据读取者:主要是 Prometheus 系统的采集器,根据配置的规则周期性的来 metrics 接口读取数据。
- 数据写入者:开发的 scanner ,通过接口去读远程资源状态信息和相关数据,通过计算得到最后的结果,写入指定的 metrics 条目内。
在此次项目中 metrics 条目是用 prometheus.GaugeVec 作为采集数据计算后结果的存储类型。
说了这么多,想要分析真正的原因,就必须深入 github.com/prometheus/client_golang 代码中 GaugeVec 这个具体代码实现。
// GaugeVec is a Collector that bundles a set of Gauges that all share the same
// Desc, but have different values for their variable labels. This is used if
// you want to count the same thing partitioned by various dimensions
// (e.g. number of operations queued, partitioned by user and operation
// type). Create instances with NewGaugeVec.
type GaugeVec struct {
*MetricVec
}
type MetricVec struct {
*metricMap
curry []curriedLabelValue
// hashAdd and hashAddByte can be replaced for testing collision handling.
hashAdd func(h uint64, s string) uint64
hashAddByte func(h uint64, b byte) uint64
}
// metricMap is a helper for metricVec and shared between differently curried
// metricVecs.
type metricMap struct {
mtx sync.RWMutex // Protects metrics.
metrics map[uint64][]metricWithLabelValues // 真正的数据存储位置
desc *Desc
newMetric func(labelValues ...string) Metric
}
通过上面的代码,一条 metric 条目是保存在 metricMap.metrics 下。 我们继续往下看:
读取数据
// Collect implements Collector.
func (m *metricMap) Collect(ch chan<- Metric) {
m.mtx.RLock()
defer m.mtx.RUnlock()
// 遍历 map
for _, metrics := range m.metrics {
for _, metric := range metrics {
ch <- metric.metric // 读取数据到通道
}
}
}
写入数据
// To create Gauge instances, use NewGauge.
type Gauge interface {
Metric
Collector
// Set sets the Gauge to an arbitrary value.
Set(float64)
// Inc increments 开发者_Go学习the Gauge by 1. Use Add to increment it by arbitrary
// values.
Inc()
// Dec decrements the Gauge by 1. Use Sub to decrement it by arbitrary
// values.
Dec()
// Add adds the given value to the Gauge. (The value can be negative,
// resulting in a decrease of the Gauge.)
Add(float64)
// Sub subtracts the given value from the Gauge. (The value can be
// negative, resulting in an increase of the Gauge.)
Sub(float64)
// SetToCurrentTime sets the Gauge to the current Unix time in seconds.
SetToCurrentTime()
}
func NewGauge(opts GaugeOpts) Gauge {
desc := NewDesc(
BuildFQName(opts.Namespace, opts.Subsystem, opts.Name),
opts.Help,
nil,
opts.ConstLabels,
)
result := &gauge{de编程客栈sc: desc, labelPairs: desc.constLabelPairs}
result.init(result) // Init self-collection.
return result
}
type gauge struct {
// valBits contains the bits of the represented float64 value. It has
// to go first in the struct to guarantee alignment for atomic
// operations. http://golang.org/pkg/sync/atomic/#pkg-note-BUG
valBits uint64
selfCollector
desc *Desc
labelPairs []*dto.LabelPair
}
func (g *gauge) Set(val float64) {
atomic.StoreUint64(&g.valBits, math.Float64bits(val)) // 写入数据到变量
}
看到上面的代码,有的小伙伴就会说读取和写入的位置不一样啊,没有找到真正的位置。不要着急,后面还有。
// getOrCreateMetricWithLabelValues retrieves the metric by hash and label value
// or creates it and returns the new one.
//
// This function holds the mutex.
func (m *metricMap) getOrCreateMetricWithLabelValues(hash uint64, lvs []string, curry []curriedLabelValue,) Metric { // 返回了一个接口
m.mtx.RLock()
metric, ok := m.getMetricWithHashAndLabelValues(hash, lvs, curry)
m.mtx.RUnlock()
if ok {
return metric
}
m.mtx.Lock()
defer m.mtx.Unlock()
metric, ok = m.getMetricWithHashAndLabelValues(hash, lvs, curry)
if !ok {
inlinedLVs := inlineLabelValues(lvs, curry)
metric = m.newMetric(inlinedLVs...)
m.metrics[hash] = append(m.metrics[hash], metricWithLabelValues{values: inlinedLVs, metric: metric}) // 这里写入 metricMap.metrics
}
return metric
}
// A Me编程客栈tric models a single sample value with its meta data being exported to
// Prometheus. Implementations of Metric in this package are Gauge, Counter,
// Histogram, Summary, and Untyped.
type Metric interface { // 哦哦哦哦,是接口啊。Gauge 实现这个接口
// Desc returns the descriptor for the Metric. This method idempotently
// returns the same descriptor throughout the lifetime of the
// Metric. The returned descriptor is immutable by contract. A Metric
// unable to describe itself must return an invalid descriptor (created
// with NewInvalidDesc).
Desc() *Desc
// Write encodes the Metric into a "Metric" Protocol Buffer data
// transmission object.
//
// Metric implementations must observe concurrency safety as reads of
// this metric may occur at any time, and any blocking occurs at the
// expense of total performanPOvAVce of rendering all registered
// metrics. Ideally, Metric implementations should support concurrent
// readers.
//
// While populating dto.Metric, it is the responsibility of the
// implementation to ensure validity of the Metric protobuf (like valid
// UTF-8 strings or syntactically valid metric and label names). It is
// recommended to sort labels lexicographically. Callers of Write should
// still make sure of sorting if they depend on it.
Write(*dto.Metric) error
// TODO(beorn7): The original rationale of passing in a pre-allocated
// dto.Metric protobuf to save allocations has disappeared. The
// signature of this method should be changed to "Write() (*dto.Metric,
// error)".
}
看到这里就知道了写入、存储、读取已经连接到了一起。 同时如果没有显式的调用方法删除 metricMap.metrics 的内容,那么记录的 metrics 条目的python值就会一直存在,而原生代码中只是创建和变更内部值。正是因为这个逻辑才导致上面说的事情。
处理方法
既然找到原因,也找到对应的代码以及对应的内部逻辑,就清楚了 prometheus.GaugeVec 这个变量真正的使用方法。到此解决方案也就有了,找到合适的位置添加代码,显式调用 DeleteLabelValues 这个方法来删除无效 metrics 条目。
为了最后实现整体效果,我总结下有几个关键词:“异步”、“多次性使用”、“自动回收”。
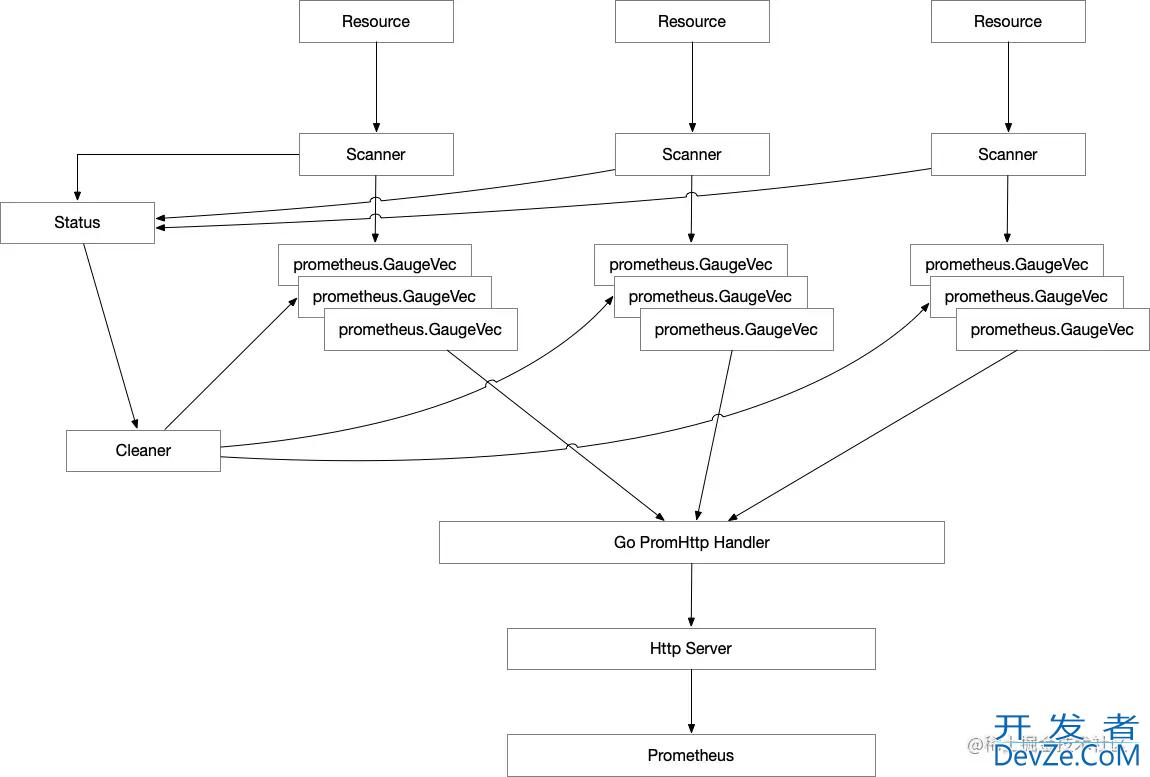
最后的改造思路:
- 创建一个 scanner 扫描结果存储的状态机 (status)
- 每次 scanner 扫描结果会向这个状态机做更新动作,并记录对应的更新时间
- 启动一个 goroutine (cleaner) 定期扫描状态机,然后遍历分析记录数据的更新时间。如果遍历到对应数据的更新时间跟现在的时间差值超过一个固定的阈值,就主动删除状态机中对应的信息,同时删除对应的 metrics 条目
通过这个动作就可以实现自动回收和清理无效的 metrics 条目,最后验证下来确实有效。
最终效果
通过测试代码来验证这个方案的效果,具体如下演示:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus/promhttp"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"sync"
"time"
)
type metricsMetaData struct {
UpdatedAt int64
Labels []string
}
func main() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
var status sync.Map
vec := prometheus.NewGaugeVec(
prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Namespace: "app",
Name: "running_status",
}, []string{"id"},
)
prometheus.MustRegister(vec)
defer prometheus.Unregister(vec)
// 写入数据
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
labels := strconv.Itoa(i)
vec.WithLabelValues(labels).Set(1) // 写入 metric 条目
status.Store(labels, metricsMetaData{UpdatedAt: time.Now().Unix(), Labels: []string{labels}}) // 写入状态
}
// 创建退出 ctx
stopCtx, stopCancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
// 启动清理器
go func(ctx *context.Context, g *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer g.Done()
ticker := time.NewTicker(time.Second * 2)
for {
select {
case <-ticker.C:
now := time.Now().Unix()
status.Range(func(key, value interface{}) bool {
if now-value.(metricsMetaData).UpdatedAt > 5 {
vec.DeleteLabelValues(value.(metricsMetaData).Labels...) // 删除 metrics 条目
status.Delete(key) // 删除 map 中的记录
}
return true
})
break
case <-(*ctx).Done():
return
}
}
}(&stopCtx, &wg)
wg.Add(1)
// 创建 http
http.Handle("/metrics", promhttp.Handler())
srv := http.Server{Addr: "0.0.0.0:8080"}
// 启动 http server
go func(srv *http.Server, g *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer g.Done()
_ = srv.ListenAndServe()
}(&srv, &wg)
wg.Add(1)
// 退出
time.Sleep(time.Second * 10)
stopCancel()
_ = srv.Shutdown(context.Background())
wg.Wait()
}
结果动画:

以上就是Go prometheus metrics条目自动回收与清理方法的详细内容,更多关于Go prometheus metrics回收清理的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论