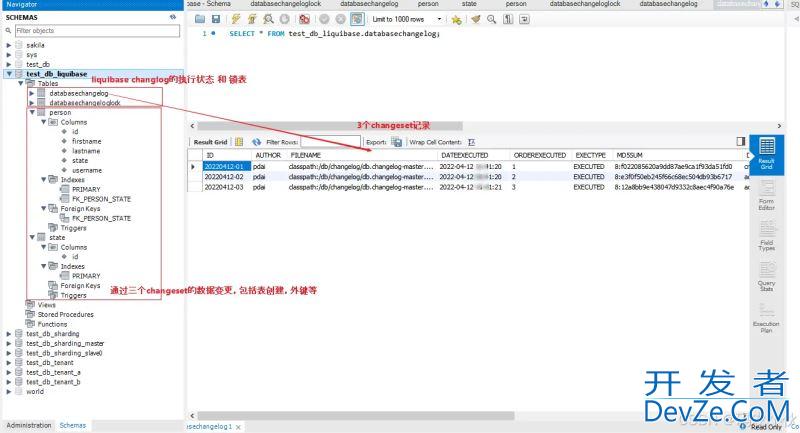
目录
- 前言
- Random的使用
- 实现原理
- ThreadLocalRandom的使用
- 实现原理
- 性能对比
- 总结
前言
大家项目中如果有生成随机数的需求,我想大多都会选择使用Random来实现,它内部使用了CAS来实现。 实际上,JDK1.7之后,提供了另外一个生成随机数的类ThreadLocalRandom,那么他们二者之间的性能是怎么样的呢?
Random的使用
Random类是JDKjs提供的生成随机数的类, 这个类不是随机的,而是伪随机的。什么是伪随机呢? 伪随机是指生成的随机数是有一定规律的,这个规律出现的周期因伪随机算法的优劣而异。 一般来说,周期比较长,但可以预见。 我们可以通过以下代码简单地使用 Random:
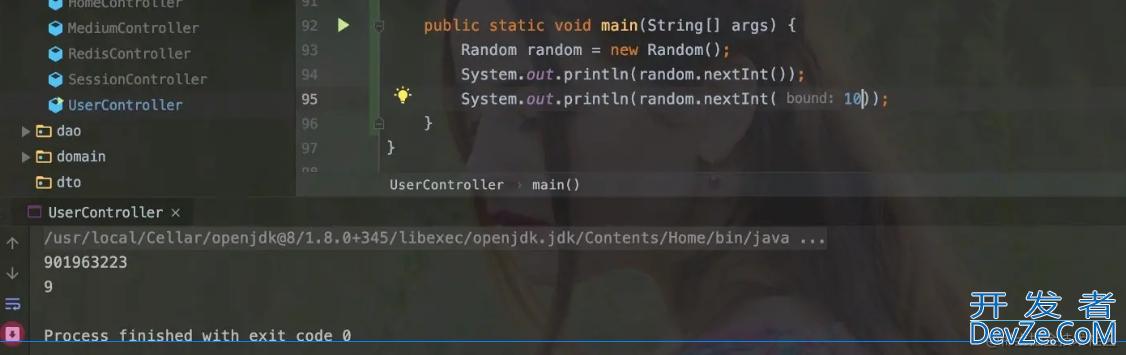
Random中有很多方法。 这里我们就分析比较常见的nextInt()和nextInt(int bound)方法。
nextInt()会计算int范围内的随机数,nextInt(int bound)会计算[0,bound) 之间的随机数,左闭右开。
实现原理
Random类的构造函数如下图所示:
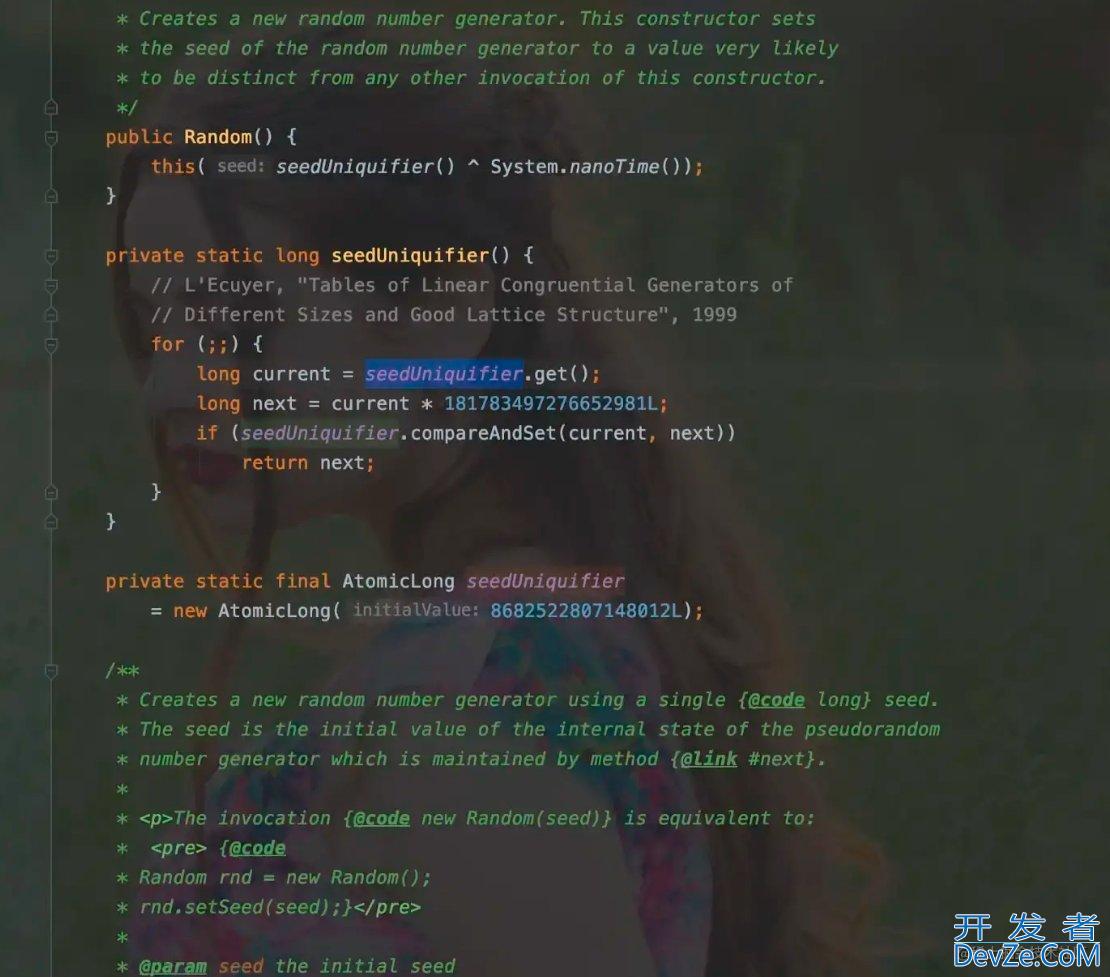
可以看到在构造方法中,根据当前时间seed生成了一个AtomicLong类型的seed。
public int nextInt() {
return next(32);
}
这里面直接调用了next()方法,传入了32,这里的32是指Int的位数。
protected int next(int bits) {
long oldseed, nextseed;
AtomicLong seed = this.seed;
do {
oldseed = seed.get();
nextseed = (oldseed * multiplier + addend) & mask;
} while (!seed.compareAndSet(oldseed, nextseed));
return (intphp)(nextseed >>> (48 - bits));
}
这里会根据seed的当前值,通过一定的规则(伪随机)计算出下一个seed,然后进行CAS。 如果CAS失败,继续循环上述操作。 最后根据我们需要的位数返回。
小结:
可以看出在next(int bits)方法中,对AtomicLong进行了CAS操作,如果失败则循环重试。 很多人一看到CAS,因为不需要加锁,第一时间就想到了高性能、高并发。 但是在这里,却成为了我们多线程并发性能的瓶颈。 可以想象,当我们有多个线程执行CAS时,只有一个线程一定会失败,其他的会继续循环执行CAS操作。 当并发线程较多时,性能就会下降。
ThreadLocalRandom的使用
JDK1.7之后,提供了一个新类ThreadLocalRandom来替代Random。
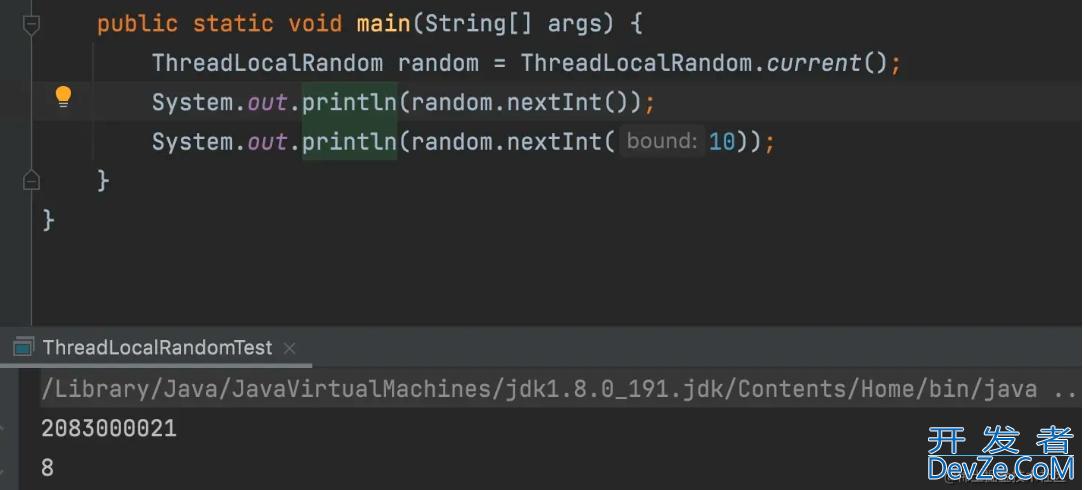
实现原理
我们先来看下current(http://www.devze.com)方法。
public static ThreadLocalRandom current() {
if (UNSAFE.getInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE) == 0)
localInit();
return instance;
}
static final void localInit() {
int p = probeGenerator.addAndGet(PROBE_INCREMENT);
int probe = (p == 0) ? 1 : p; // skip 0
long seed = mix64(seeder.getAndAdd(SEEDER_INCREMENT));
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
UNSAFE.putLong(t, SEED, seed);
UNSAFE.putInt(t, PROBE, probe);
}
如果没有初始化,先进行初始化,这里我们的seed不再是全局变量了。 我们的线程中有三个变量:
/** The current seed for a ThreadLocalRandom */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
long threadLocalRandomSeed;
/** Probe hash value; nonzero if threadLocalRandomSeed initialized */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
int threadLocalRandomProbe;
/** Secondary seed isolated from public ThreadLocalRandom sequence */
@sun.misc.Contended("tlr")
int threadLocalRandomSecondarySeed;
threadLocalRandomSeed:这是我们用来控制随机数的种子。threadLocalRandomProbe:这个就是ThreadLocalRandom,用来控制初始化。threadLocalRandomSecondarySeed:这是二级种子。
关键代码如下:
UNSAFE.putLong(t = Thread.currentThread(), SEED,r=UNSAFE.getLong(t, SEED) + GAMMA);
可以看出,由于每个线程都维护自己的seed,所以此时不需要CAS,直接进行put。 这里通过线程间的隔离来减少并发冲突,所以ThreadLocalRandom的性能非常高。
性能对比
通过基准工具JMH测试:
@BenchmarkMode({Mode.AverageTime})
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)
@Warmup(iterations=3, time = 5, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
@Measurement(iterations=3,time = 5)
@Threads(4)
@Fork(1)
@State(Scoandroidpe.Benchmark)
public class Myclass {
Random random = new Random();
ThreadLocalRandom threadLocalRandom = ThreadLocalRandom.current开发者_JAVA();
@Benchmark
public int measureRandom(){
return random.nextInt();
}
@Benchmark
public int threadLocalmeasureRandom(){
return threadLocalRandom.nextInt();
}
}
运行结果如下图所示,最左边是并发线程的数量:

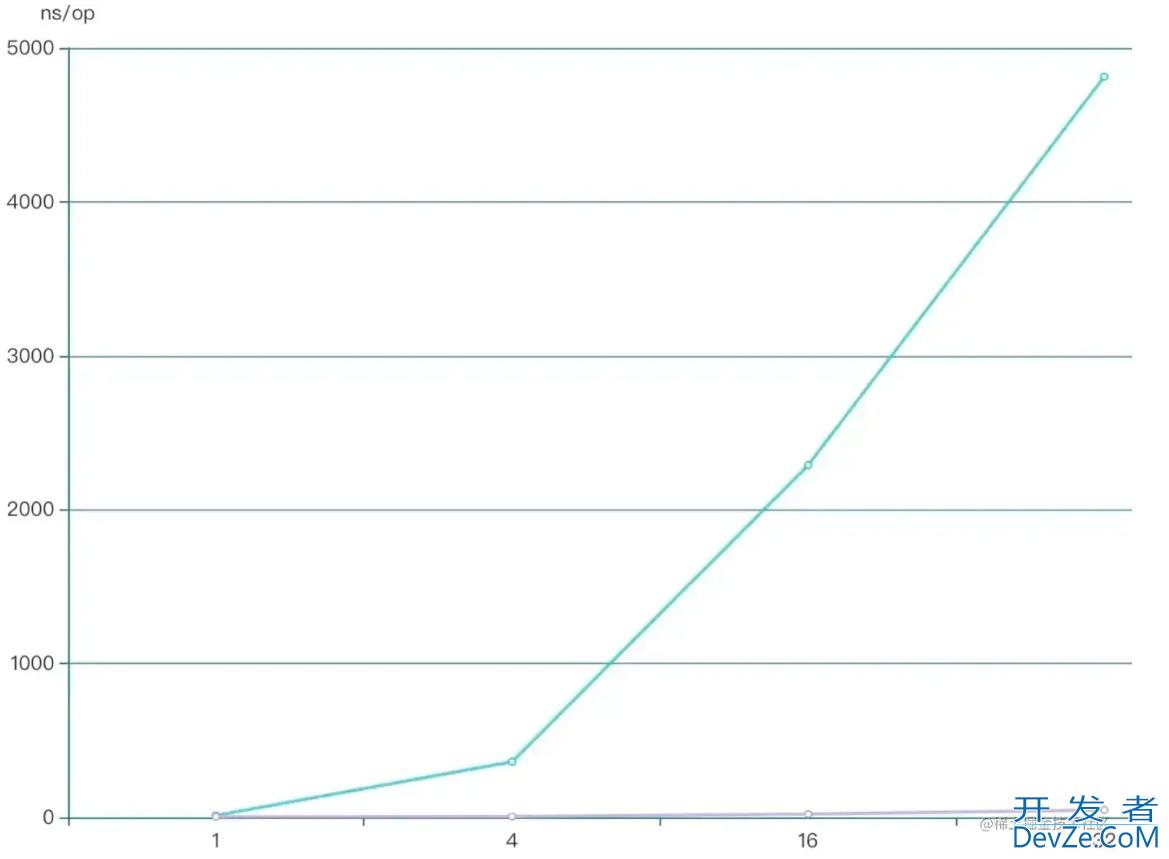
显而易见,无论线程数量是多少,ThreadLocalRandom性能是远高于Random。
总结
本文讲解了JDK中提供的两种生成随机数的方式,一个是JDK 1.0引入的Random类,另外一个是JDK1.7引入的ThreadLocalRandom类,由于底层的实现机制不同,ThreadLocalRandom的性能是远高于Random,建议后面大家在技术选型的时候优先使用ThreadLocalRandom。
到此这篇关于Java生成随机数之Random与ThreadLocalRandom性能比较详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java Random ThreadLocalRandom内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论