目录
- Pytorch四维Tensor转图片并保存
- 1.维度顺序转换
- 2.转为numpy数组
- 3.根据第一维度BATch_size逐个读取中间结果,并存储到磁盘中
- Pytorch中Tensor介绍
- torch.Tensor或torch.tensor注意事项
- 创建tensor的四种主要方法
- 总结
Pytorch四维Tensor转图片并保存
最近在复现一篇论文代码的过程中,想要输出中间图片的结果图,通过debug发现在pytorch网络中是用Tensor存储的四维张量。
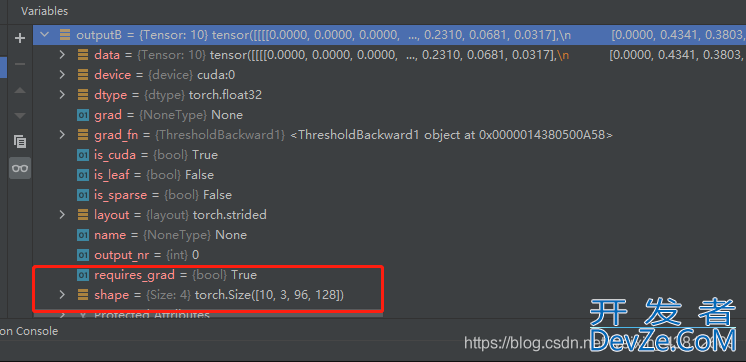
1.维度顺序转换
第一维代表的是batch_size,然后是通道数和图像尺寸,首先要进行维度顺序的转换
通过permute函数实现
outputRs = outputR.permute(0,2,3,1)
shape转为96 * 128 * 3

2.转为numpy数组
#由于代码中的中间结果是带有梯度的要进行detach()操作 k = outputRs.cpu().detach().numpy()
3.根据第一维度batch_size逐个读取中间结果,并存储到磁盘中
Image需导入from PIL import Image
for i in range(10):
res = k[i] #得到batch中其中一步的图片
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(res)).convert('RGB')
#image.show()
#通过时间命名存储结果
timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%M-%S")
savepath = timestamp + '_r.jpg'
image.save(savepath)
Pytorch中Tensor介绍
PyTorch中的张量(Tensor)如同数组和矩阵一样,是一种特殊的数据结构。在PyTorch中,神经网络的输入、输出以及网络的参数等数据,都是使用张量来进行描述。
torch包中定义了10种具有CPU和GPU变体的tensor类型。
torch.Tensor或torch.tensor是一种包含单一数据类型元素的多维矩阵。
torch.Tensor或torch.tensor注意事项
(1). torch.Tensor是默认tensor类型torch.FloatTensor的别名。
(2). torch.tensor总是拷贝数据。
(3).每一个tensor都有一个关联的torch.Storage,它保存着它的数据。
(4).改变tensor的方法是使用下划线后缀标记,如torch.FloatTensor.abs_()就地(in-place)计算绝对值并返回修改后的tensor,而torch.FloatTensor.abs()在新tensor中计算结果。
(5).有几百种tensor相关的运算操作,包括各种数学运算、线性代数、随机采样等。
创建tensor的四种主要方法
(1).要使用预先存在的数据创建tensor,使用torch.tensor()。
(2).要创建具有特定大小的tensor,使用torch.*,如torch.rand()。
(3).要创建与另一个tensor具有相同大小(和相似类型)的tensor,使用torch.*_like,如torch.rand_like()。
(4).要创建与另一个tensor类型相似但大小不同的tensor,使用tensor.new_*,如tensor.new_ones()。
以上内容及以下测试代码主要参考:
1. torch.Tensor — PyTorch 1.10.0 documentation
2. https://pytorch.apachecn.org/#/docs/1.7/03
tensor具体用法见以下test_tensor.py测试代码:
import torch
import numpy as np
var = 2
# reference: https://pytorch.apachecn.org/#/docs/1.7/03
if var == 1: # 张量初始化
# 1.直接生成张量, 注意: torch.tensor与torch.Tensor的区别: torch.Tensor是torch.FloatTensor的别名;而torch.tensor则根据输入数据推断数据类型
data = [[1, 2], [3, 4]]
x_data = torch.tensor(data); print(f"x_dpythonata: {x_data}, type: {x_data.type()}") # type: torch.LongTensor
y_data = torch.Tensor(data); print(f"y_data: {y_data}, type: {y_data.type()}") # type: torch.FloatTensor
z_data = torch.IntTensor(data); print(f"z_data: {z_data}, type: {z_data.type()}") # type: torch.IntTensor
# 2.通过Numpy数组来生成张量,反过来也可以由张量生成Numpy数组
np_array = np.array(data)
x_np = torch.from_numpy(np_array); print("x_np:\n", x_np)
y_np = torch.编程客栈tensor(np_array); print("y_np:\n", y_np) # torch.tensor总是拷贝数据
z_np = torch.as_tensor(np_array); print("z_np:\n", z_np) # 使用torch.as_tensor可避免拷贝数据
# 3.通过已有的张量来生成新的张量: 新的张量将继承已有张量的属性(结构、类型),也可以重新指定新的数据类型
x_ones = torch.ones_like(x_data); print(f"x_ones: {x_ones}, type: {x_ones.type()}") # 保留x_data的属性
x_rand = torch.rand_like(x_data, dtype=torch.float); print(f"x_rand: {x_rand}, type: {x_rand.type()}") # 重写x_data的数据类型: long -> float
tensor = torch.tensor((), dtype=torch.int32); print(f"shape of tensor: {tensor.shape}, type: {tensor.type()}")
new_tensor = tensor.new_ones((2, 3)); print(f"shape of new_tensor: {new_tensor.shape}, type: {new_tensor.type()}")
# 4.通过指定数据维度来生成张量
shape = (2, 3) # shape是元组类型,用来描述张量的维数
rand_tensor = torch.rand(shape); print(f"rand_tensor: {rand_tensor}, type: {rand_tensor.type()}")
ones_tensor = torch.ones(shape, dtype=torch.int); print(f"ones_tensor: {ones_tensor}, type: {ones_tensor.type()}")
zeros_tensor = torch.zeros(shape, device=torch.device("cpu")); print("zeros_tensor:", zeros_tensor)
# 5.可以使用requires_grad=True创建张量,以便torch.autograd记录对它们的操作以进行自动微分
x = torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
out = x.pow(2).supythonm(); print(fjs"out: {out}")
# out.backward(); print(f"x: {x}\nx.grad: {x.grad}")
elif var == 2: # 张量属性: 从张量属性我们可以得到张量的维数、数据类型以及它们所存储的设备(CPU或GPU)
thttp://www.devze.comensor = torch.rand(3, 4)
print(f"shape of tensor: {tensor.shape}")
print(f"datatype of tensor: {tensor.dtype}") # torch.float32
print(f"device tensor is stored on: {tensor.device}") # cpu或cuda
print(f"tensor layout: {tensor.layout}") # tensor如何在内存中存储
print(f"tensor dim: {tensor.ndim}") # tensor维度
elif var == 3: # 张量运算: 有超过100种张量相关的运算操作,例如转置、索引、切片、数学运算、线性代数、随机采样等
# 所有这些运算都可以在GPU上运行(相对于CPU来说可以达到更高的运算速度)
tensor = torch.rand((4, 4), dtype=torch.float); print(f"src: {tensor}")
# 判断当前环境GPU是否可用,然后将tensor导入GPU内运行
if torch.cuda.is_available():
tensor = tensor.to("cuda")
# 1.张量的索引和切片
tensor[:, 1] = 0; print(f"index: {tensor}") # 将第1列(从0开始)的数据全部赋值为0
# 2.张量的拼接: 可以通过torch.cat方法将一组张量按照指定的维度进行拼接,也可以参考torch.stack方法,但与torch.cat稍微有点不同
cat = torch.cat([tensor, tensor], dim=1); print(f"cat:\n {cat}")
# 3.张量的乘积和矩阵乘法
print(f"tensor.mul(tensor):\n {tensor.mul(tensor)}"开发者_Go培训) # 逐个元素相乘结果
print(f"tensor * tensor:\n {tensor * tensor}") # 等价写法
print(f"tensor.matmul(tensor.T):\n {tensor.matmul(tensor.T)}") # 张量与张量的矩阵乘法
print(f"tensor @ tensor.T:\n {tensor @ tensor.T}") # 等价写法
# 4.自动赋值运算: 通常在方法后有"_"作为后缀,例如:x.copy_(y), x.t_()操作会改变x的取值(in-place)
print(f"tensor:\n {tensor}")
print(f"tensor:\n {tensor.add_(5)}")
elif var == 4: # Tensor与Numpy的转化: 张量和Numpy array数组在CPU上可以共用一块内存区域,改变其中一个另一个也会随之改变
# 1.由张量变换为Numpy array数组
t = torch.ones(5); print(f"t: {t}")
n = t.numpy(); print(f"n: {n}")
t.add_(1) # 修改张量的值,则Numpy array数组值也会随之改变
print(f"t: {t}")
print(f"n: {n}")
# 2.由Numpy array数组转为张量
n = np.ones(5); print(f"n: {n}")
t = torch.from_numpy(n); print(f"t: {t}")
np.add(n, 1, out=n) # 修改Numpy array数组的值,则张量值也会随之改变
print(f"n: {n}")
print(f"t: {t}")
print("test finish")
github:GitHub - fengbingchun/PyTorch_Test: PyTorch's usage
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论