目录
- 前言
- 什么是MQTT协议
- MQTT协议的模型
- 开发MQTT通信
- 1. 处理客户端和服务端
- (1)服务端开发
- (2)客户端开发
- 2. 客户端开发
- Paho的mqtt的BUG
- 总结
前言
为什么要讲MQTT协议?因为现在越来越多的领域会使用到这个协议,无论是做M2M,还是做Iot,或是想实现推送功能,MQTT都是一个不错的选择。
什么是MQTT协议
MQTT协议又称为消息队列要测传输协议,他是一种基于发布/订阅范式的消息协议,并且它是一种基于TCP/IP协议族的应用层协议。
可以看出的它的特点:轻量、简单、基于发布/订阅范式、基于TCP/IP、是一种应用层协议。
如果还是不明白,我们可以简单拿它和我们常用的http协议做个比较。
| HTTP协议 | MQTT协议 |
|---|---|
| 基于TCP或UDP | 基于TCP |
| 基于 请求/响应 模型 | 基于 发布/订阅 模型 |
| http1.x是传数据包 | 传输二进制数据 |
MQTT协议的模型
我们得知道它是一个怎样的模型才好去了解它的一个工作方式。比如说HTTP协议简单分为两个角色,一个Client代表客户端,一个Server代表服务端。
而MQTT简单来看分为3个角色,publisher表示发布者,subscriber表示订阅者,它们两个都是Client,所以任何一个Client客户端既能充当publisher,也能充当subscriber。还有一个角色是broker表示代理,它是Server服务端。可以看出MQTT也是基于C/S的通信架构,只不过分为3种角色。
如果理解了这个模型之后,你就会有个疑问,发布和订阅什么呢?这就需要引入一个新的东西叫主题topic(如果不理解主题这个概念的话也没关系,后面用代码就很容易理解主题是什么)
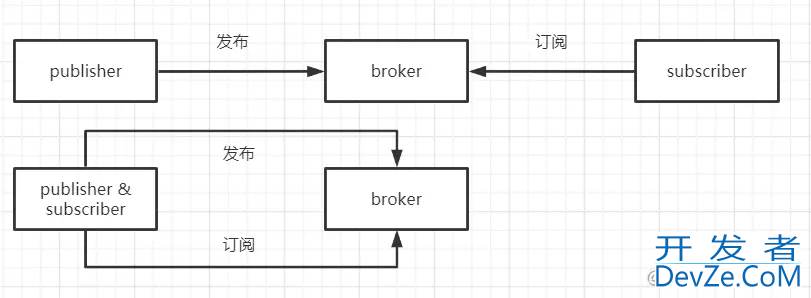
所以它的工作流程就是:
- subscriber订阅者连接broker代理,并订阅主题topic
- publisher发布者连接broker代理(当然如何订阅者和发布者是同一个Client的话就不需要重复连接),并发布消息到相应开发者_JAVA入门的主题
- broker代理会把消息发给对应订阅的主题的subscriber订阅者
开发MQTT通信
1. 处理客户端和服务端
前面我们说了MQTT是继续C/S的结构,那我们就需要有一个客户端和一个服务端。
(1)服务端开发
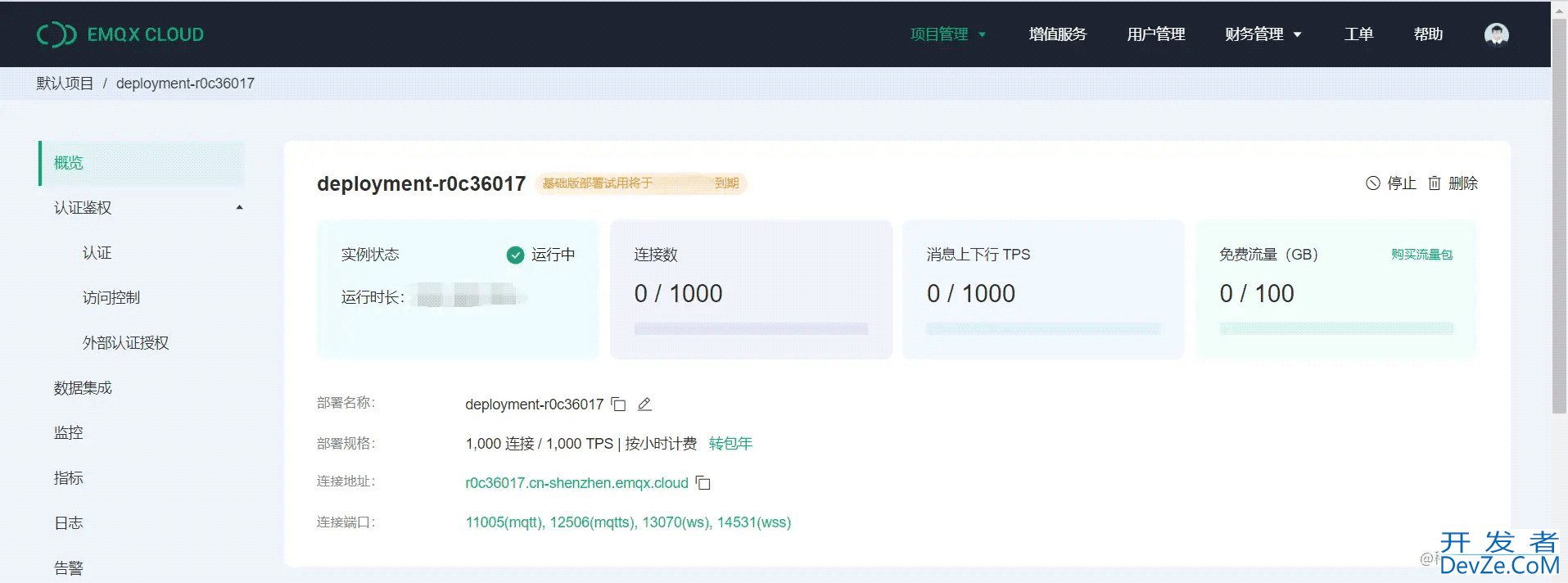
很不幸我是开发前MCvbp端的,后台的开发我并不熟悉,所以这里的演示中我选择用云服务EMQX,想尝试的朋友可以上这个网页去部署自己的云服务,流程很简单 cloud.emqx.com/ ,免费试用14天。
(2)客户端开发
因为我是做android开发的,所以这里我用Android来举例子。正常来说可以在TCP的基础上开发,自己去封装,但我这只是浅谈,所以我用第三javascript方框架进行演示,用Paho的mqtt
2. 客户端开发
先导入Paho的mqtt
dependencies {
......
implementation 'org.eclipse.paho:org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3:1.1.0'
implementation 'org.eclipse.paho:org.eclipse.paho.android.service:1.1.1'
}
在manifest中注册Paho的MqttService
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.MyApplication">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="org.eclipse.paho.android.service.MqttService"/>
<service android:name=".MqttActionService"/>
</application>
我这边为了用一个项目来演示Mqtt通信,所有把MainActivity当成publisher发布者,把MqttActionService当成subscriber订阅者。
所以整体的流程是这样的,我们先开启MqttActionService,然后在MqttActionService中进行连接和订阅。再在MainActivity进行连接和发送消息。
先把Mqtt的Client给封装起来(我这里防止有些朋友看不懂Kotlin,我就用了Java,后面不重要的地方我直接用Kotlin,一般也比较容易看懂)。
public class MyMqttClient {
private MqttAndroidClient mClient;
private MqttConnectOptions mOptions;
private OnMqttConnectListener mOnMqttConnectListener;
private final String mClientId;
private 编程客栈MqttCallbackExtended mExtended = new MqttCallbackExtended() {
@Override
public void connectComplete(boolean reconnect, String serverURI) {
if (mOnMqttConnectListener != null){
mOnMqttConnectListener.onConnectComplete(serverURI);
}
}
@Override
public void connectionLost(Throwable cause) {
if (mOnMqttConnectListener != null){
mOnMqttConnectListener.onConnectFailure(cause);
}
}
@Override
public void messageArrived(String topic, MqttMessage message) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void deliveryComplete(IMqttDeliveryToken token) {
}
};
private IMqttActionListener mConnectAction = new IMqttActionListener() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(IMqttToken asyncActionToken) {
}
@Override
public void onFailure(IMqttToken asyncActionToken, Throwable exception) {
if (mOnMqttConnectListener != null){
mOnMqttConnectListener.onConnectFailure(exception);
}
exception.printStackTrace();
}
};
private IMqttMessageListener messageListener = new IMqttMessageListener() {
@Override
public void messageArrived(String topic, MqttMessage message) throws Exception {
if (mOnMqttConnectListener != null){
mOnMqttConnectListener.onMessageArrived(topic, message);
}
}
};
public MyMqttClient(Context context){
this(context, null);
}
public MyMqttClient(Context context, String clientId){
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(clientId)) {
this.mClientId = clientId;
}else {
this.mClientId = MqttConfig.clientId;
}
init(context);
}
public void init(Context context){
mClient = new MqttAndroidClient(context, MqttConfig.mqttUrl, mClientId);
mClient.setCallback(mExtended);
mOptions = new MqttConnectOptions();
mOptions.setConnectionTimeout(4000);
mOptions.setKeepAliveInterval(30);
mOptions.setUserName(MqttConfig.username);
mOptions.setPassword(MqttConfig.password.toCharArray());
}
public void setOnMqttConnectListener(OnMqttConnectListener onMqttConnectListener) {
this.mOnMqttConnectListener = onMqttConnectListener;
}
/**
* 连接
*/
public void connect(){
try {
if (!mClient.isConnected()){
mClient.connect(mOptions, null, mConnectAction);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 订阅
*/
public void subscribeToTopic(String mTopic){
thiphps.subscribeToTopic(mTopic, 0);
}
public void subscribeToTopic(String mTopic, int qos){
try {
mClient.subscribe(mTopic, qos, null,null, messageListener);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 发送消息
*/
public void sendMessage(String mTopic, byte[] data){
try {
MqttMessage message = new MqttMessage();
message.setPayload(data);
mClient.publish(mTopic, message);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void onDestroy(){
try {
mClient.disconnect();
mExtended = null;
mConnectAction = null;
messageListener = null;
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 提供给外层的回调,更方便进行使用
*/
public interface OnMqttConnectListener{
void onConnectComplete(String serverURI);
void onConnectFailure(Throwable e);
void onMessageArrived(String topic, MqttMessage message);
}
}
当中有些配置我直接抽出来
public interface MqttConfig {
String mqttUrl = "tcp://r0c36017.cn-shenzhen.emqx.cloud:11005";
String clientId = "deployment-r0c36017";
String username = "yeshuaishizhenshuai";
String password = "123456";
String oneTopic = "kylin/topic/one";
}
可以讲一下这些参数:
(1) mqttUrl: 连接代理的连接,可以看到我上面云服务那张截图里面的“连接地址”和“连接端口” (2) clientId: 客户端ID,无论是subscriber还是publisher都属于客户端,这个在上面说过,所以都有一个对应的ID标识他们是属于哪个客户端。我下面的Demo中MqttActionService用的ClienId是deployment-r0c36017,MainActivity用的ClienId是deployment-r0c36018,不同的,所以是两个客户端。 (3) username和password: 这两个参数都是一个标识,会和后台编程记录,如果你没有的话,那你就连不上代理,也就是连不上服务端。 (4) oneTopic: 就是主题,你订阅和发送消息都要对应是哪个主题。
然后subscriber连接并订阅主题
class MqttActionService : Service() {
private var mqttClient : MyMqttClient ?= null
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
mqttClient = MyMqttClient(this)
mqttClient?.setOnMqttConnectListener(object : MyMqttClient.OnMqttConnectListener{
override fun onConnectComplete(serverURI: String?) {
mqttClient?.subscribeToTopic(MqttConfig.oneTopic)
}
override fun onConnectFailure(e: Throwable?) {
}
override fun onMessageArrived(topic: String?, message: MqttMessage?) {
val h = Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())
h.post {
Toast.makeText(this@MqttActionService.applicationContext, message.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
})
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent?, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
val handler = Handler()
handler.postDelayed({ mqttClient?.connect() }, 1000)
return START_STICKY
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder? {
return null
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
mqttClient?.onDestroy()
}
}
然后publisher连接并发送消息
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var clinet : MyMqttClient ?= null
private var isConnect = false
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
init()
val btn : Button = findViewById(R.id.btn_connect)
val send : Button = findViewById(R.id.btn_send)
val open : Button = findViewById(R.id.open)
open.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent()
intent.setClass(this, MqttActionService::class.java)
startService(intent)
}
btn.setOnClickListener {
clinet?.connect()
}
send.setOnClickListener {
clinet?.sendMessage(MqttConfig.oneTopic, "你干嘛啊~哎呦~".toByteArray())
}
}
private fun init(){
clinet = MyMqttClient(this, "deployment-r0c36018")
clinet?.setOnMqttConnectListener(object : MyMqttClient.OnMqttConnectListener{
override fun onConnectComplete(serverURI: String?) {
isConnect = true
}
override fun onConnectFailure(e: Throwable?) {
e?.printStackTrace()
isConnect = false
}
override fun onMessageArrived(topic: String?, message: MqttMessage?) {
}
})
}
}
我这定了3个按钮,第一个按钮open会跳转Service然后subscriber连接并订阅主题,第二个按钮btn会连接代理,第三个按钮send发送消息。看MqttActionService的代码可以看出,我这里发送消息后,会弹出Toast。
Paho的mqtt的BUG
这库我也是第一次用,我们那用的都是自己撸的(这边肯定没法放上来),然后我用的时候发现一个问题。我想给Service去开一条进程去处理订阅的操作的,这样能更真实的去模拟,结果就在连接时出问题了
经检查,连接的context的进程要和org.eclipse.paho.android.service.MqttService的进程一致。我去看他源码是怎么回事。
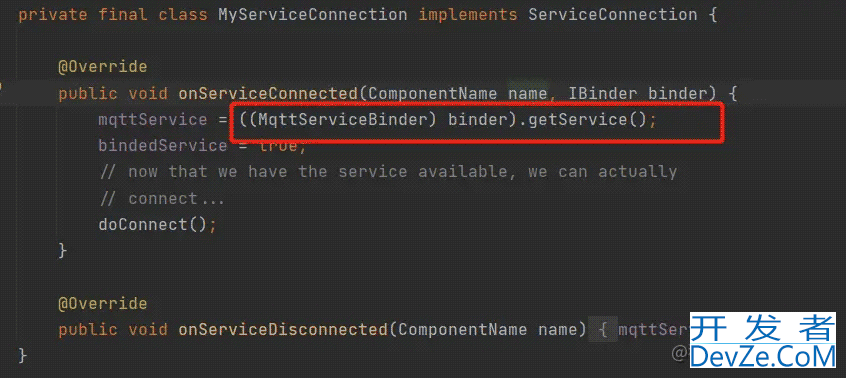
发现它内部的Binder竟然做了强转,这里因为不是代理而会出现报错。如果使用这个库的话就小心点你要做的夸进程的操作。
总结
今天只是浅谈一些MQTT的一些原理和流程,其实还有更深的功能,比如Qos啊这些还没说,我觉得一次说太多可能会让第一次接触的人混乱。先简单的了解MQTT是什么,主要使用的场景,内部的原理大致是怎样的。当了解这些之后再去深入的看,会能够更好的去理解。
以上就是Android开发MQTT协议的模型及通信浅析的详细内容,更多关于Android MQTT协议模型通信的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!









 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论