目录
- 简介
- 服务端配置
- 客户端配置
- 最后
简介
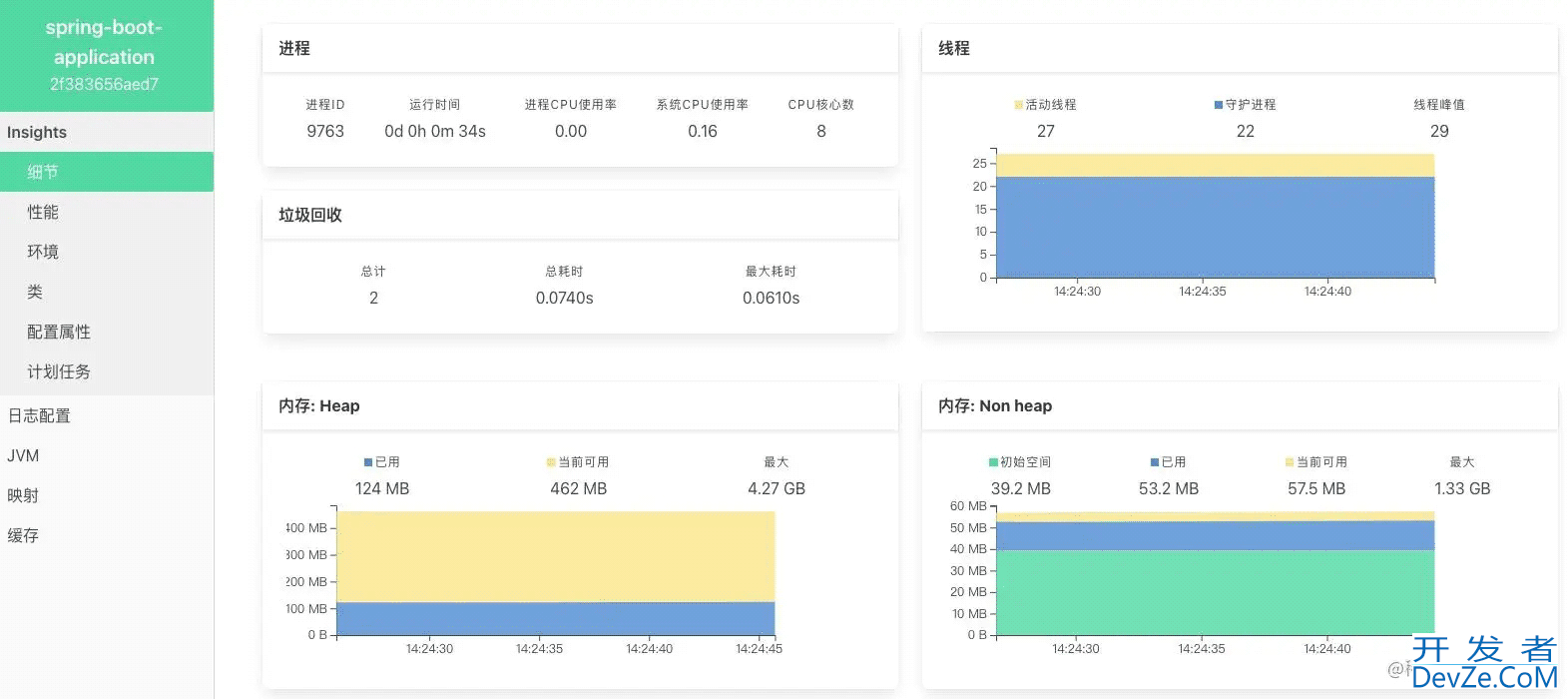
Springboot Admin是一个管理和监控Springboot项目的组件,分为服务端和客户端,两端通过http进行通信。由于其轻量级的特性,所以特别适合中小项目使用。
其效果图如下:
服务端配置
1,引入Springboot admin和Spring Security依赖。
<depe编程ndency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</arti开发者_Python学习factId>
</dependency>
2,配置相关属性。
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /server
spring:
security:
user:
#admin Server端登录时用的账户密码
name: server123
password: 123456
boot:
admin:
instance-auth:
#启用header验证
enabled: true
#Server访问client接口时会使用下面的配置生成authorization
default-user-name: "name_shishan"
default-password: "pwd_shishan"
3,配置@EnableAdminServer注解
@SpringBootApplication
@Configuration
@EnableAdminServer
public claswww.devze.coms ServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
经过以上3步,服务端就可以启动了。
访问 http://localhost:8080/server/,就可以看到以下登录界面。
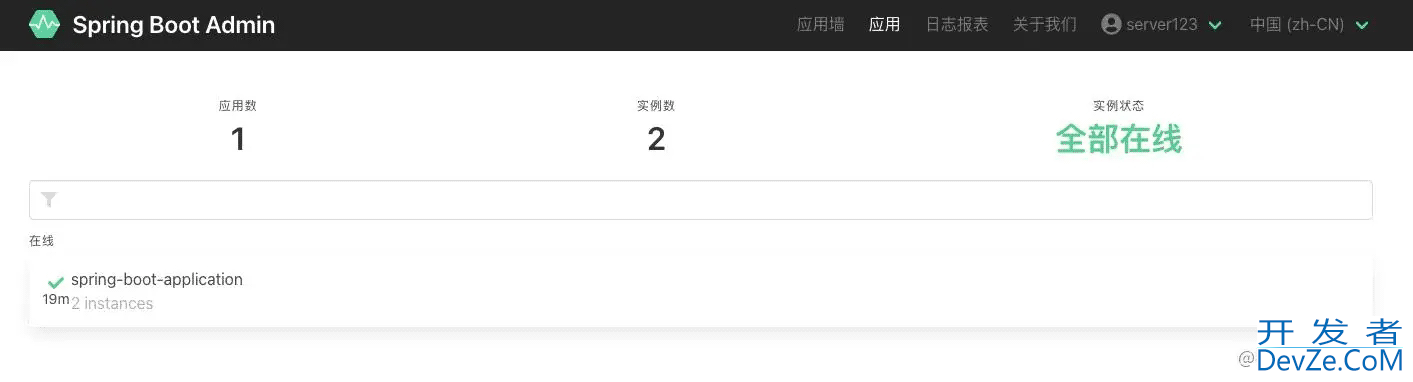
使用在yml文件中配置的账户密码就可以登录了。
客户端配置
1,在我们要监控的客户端中加入以下依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<js/dependency>
2,暴露监控接口以及配置Server地址。
客户端在启动后会向配置的Server发起注册申请,此时为了安全性还需要Server端的账户密码进行校验。
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
#admin注册地址
url: http://localhost:8080/server
#配置admin的账户
username: server123
password: 123456
admin:
header:
auth:
name: "name_shishan"
password: "pwd_shishan"
#暴露出端口
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
3,对暴露的接口进行权限校验。
由于我们将监控接口进行了暴露,所以必须对相关的接口进行权限校验,否则就有可能泄露相关信息。
对接口进行权限过滤有很多种选择,比如设置IP访问的白名单,只允许admin Server所在的服务器访问,也可以配置相关的token等等。
下面我们以一个简单的接口过滤器实现对/actuator/**相关接口的权限校验。
@Component
public class PathFilter implements Filter {
@Value("${admin.header.auth.name}")
private String username;
@Value("${admin.header.auth.password}")
private String password;
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
if (antPathMatcher.match("/actuator/**", request.getServletPath())) {
String authorization = request.getHeader("authorization");
if (StringUtils.hasText(authorization)) {
String token = Base64Utils.encodeToString((username + ":" + password).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
if (authorization.equals("Basic " + token)) {
//token匹配才放行
filterChain.doFilter(request, servletResponse);
return;
}
}
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTFandroid-8");
resandroidponse.setStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value());
response.getWriter().print("权限不足");
return;
}
//其他接口直接放行
filterChain.doFilter(request, servletResponse);
}
}
在这个filter中,对actuator相关的接口进行了header参数的校验,只有通过校验才可以访问暴露出的actuator接口。
当然,如果我们使用了SpringSecurity或者SaToken这样的第三方权限框架,也可以去重写相关的配置完成权限的判断,原理都是一样的。
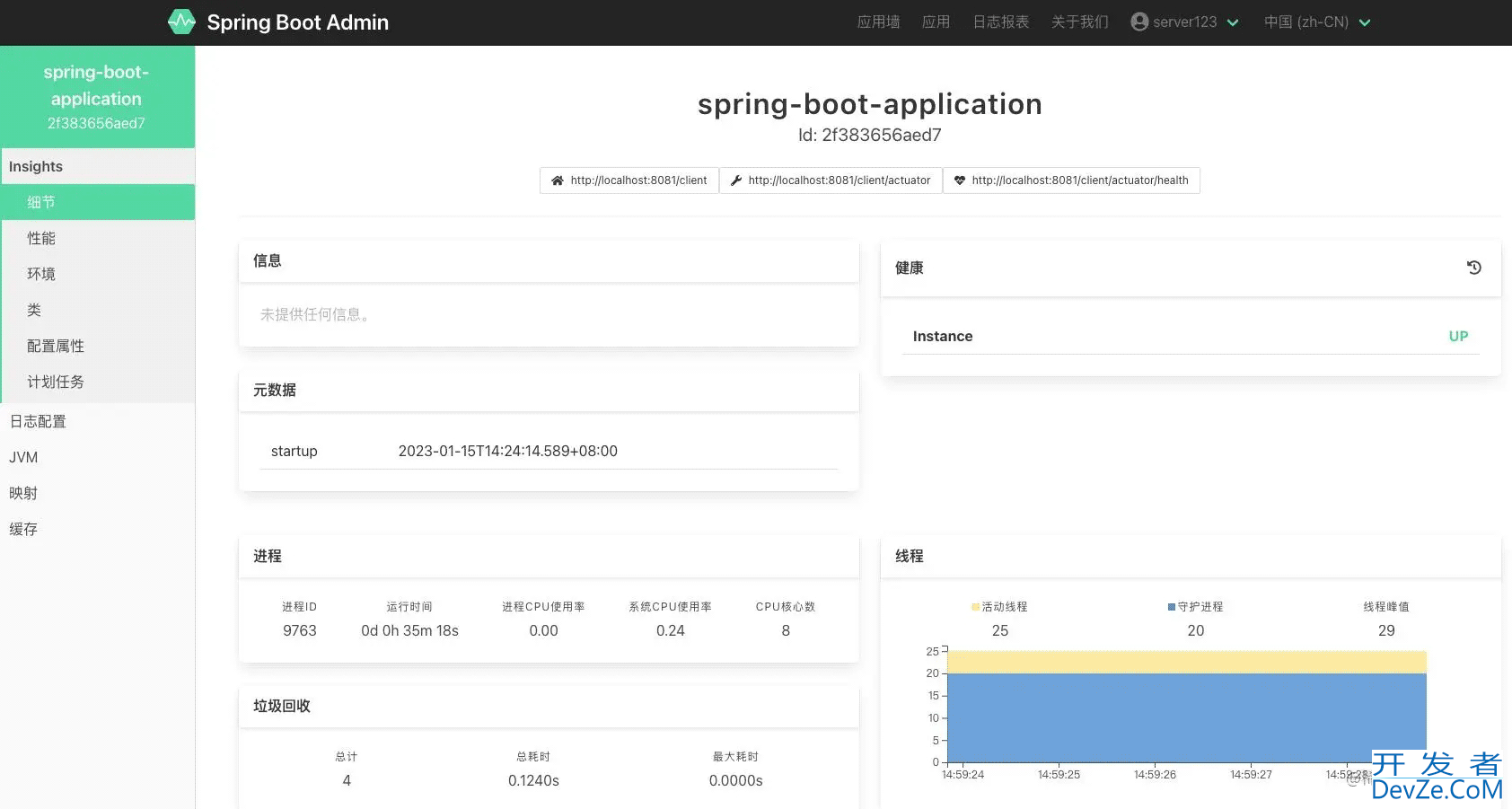
下面我们看一下最终的监控效果:
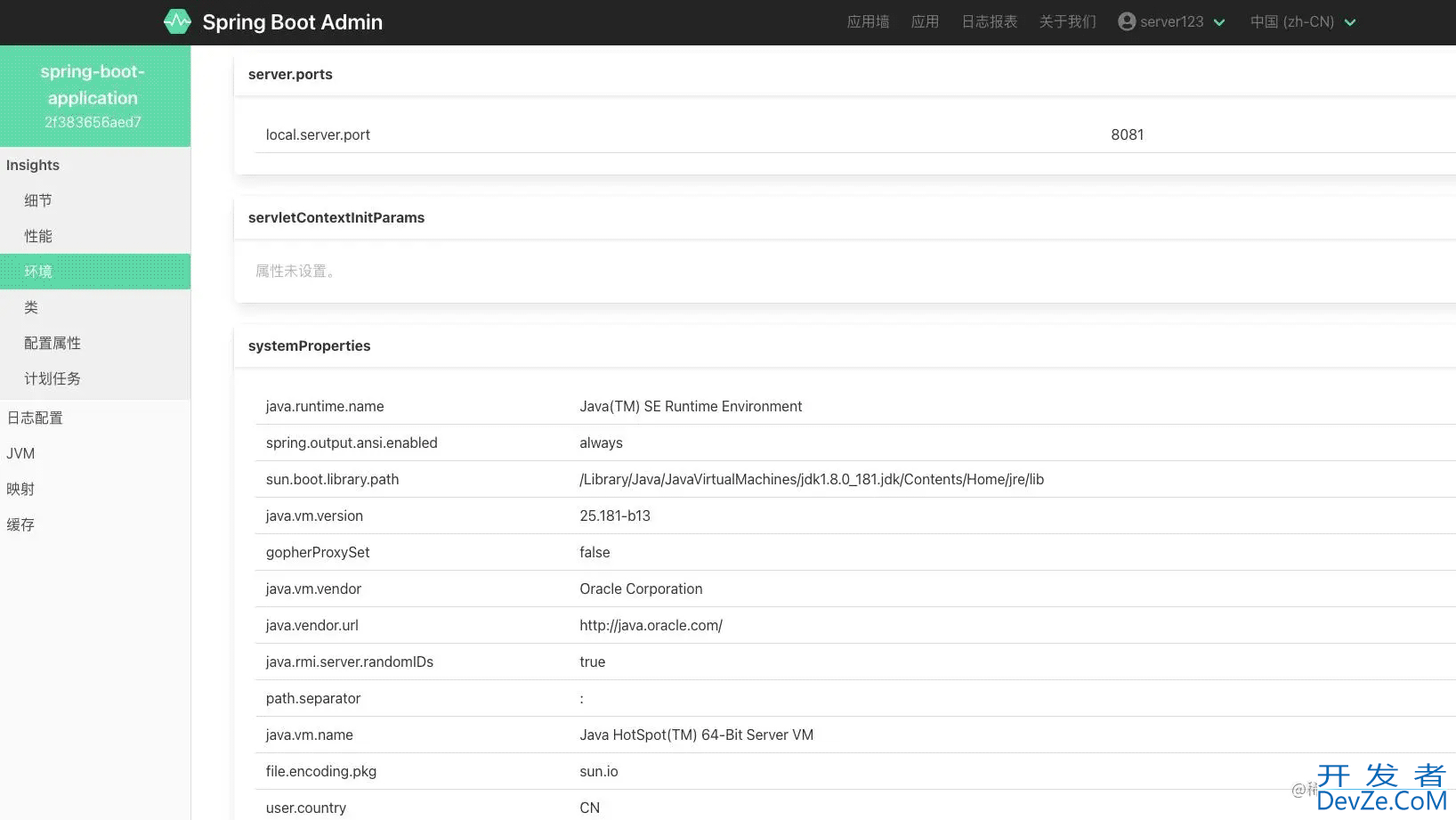
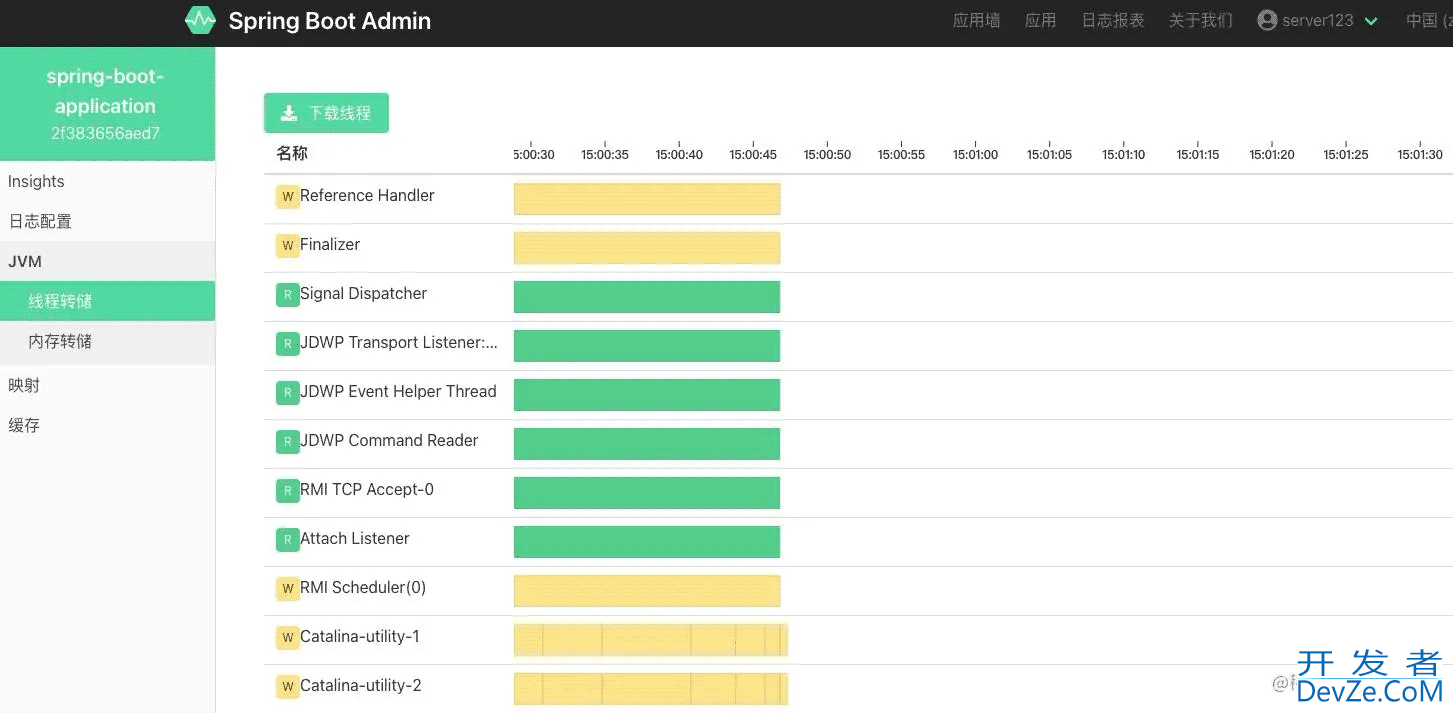
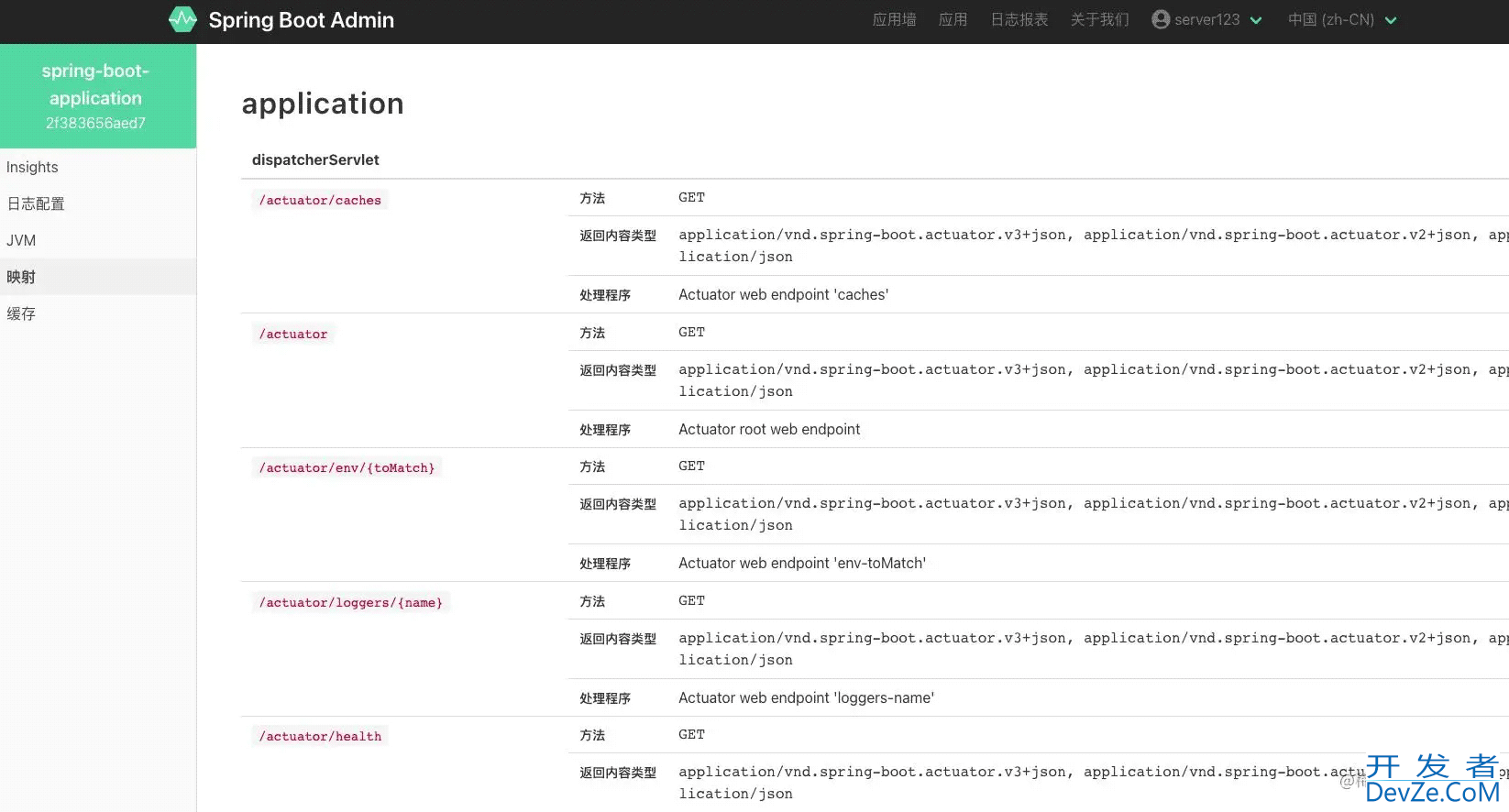
最后
除了通过普通http请求方式获取监控信息以外,Springboot admin还支持通过注册中心的方式获取相关信息,在其官方文档大家也可以看到相关的配置。
官方文档:codecentric.github.io/spring-boot…
以上就是Springboot轻量级的监控组件SpringbootAdmin的详细内容,更多关于Springboot监控组件的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论