目录
- 复合查询
- 导入数据库
- 表的基础查询
- 多表查询
- 自连接
- 子查询
- 单行子查询
- 多行子查询
- 多列子查询
- from中使用子查询
- 合并查询
- union
- union all
复合查询
本篇开始将介绍在mysql中进行复合查询的操作。平时在开发过程中只对一张表进行查询的操作是远远不够的,更多的都是多张表一起查询,所以本篇将介绍多张表中的复合查询,主要介绍多表查询、自连接以及子查询。
导入数据库
本篇中使用的数据库如下,若想要与本篇进行相同的操作,可以先导入与本篇相同的数据库,按步骤:
- 在某目录下创建sql文件:soctt_data.sql
- 将如下内容复制到soctt_data.sql文件中
- 然后登陆进mysql,执行命令:source 某目录/scott_data.sql
mysql> source /home/jzhong/mysql/scott_data.sql Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | scott | | sys | | testdb | +--------------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) -- 切换使用数据库 mysql> use scott Database changed mysql> show tables; +-----------------+ | Tables_in_scott | +-----------------+ | dept | | emp | | salgrade | +-----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
soctt_data.sql:
DROP database IF EXISTS `scott`; CREATE database IF NOT EXISTS `scott` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; USE `scott`; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `dept`; CREATE TABLE `dept` ( `deptno` int(2) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '部门编号', `dname` varchar(14) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门名称', `loc` varchar(13) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门所在地点' ); DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `emp`; CREATE TABLE `emp` ( `empno` int(6) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '雇员编号', `ename` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULandroidL COMMENT '雇员姓名', `job` varchar(9) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员职位', `mgr` int(4) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员领导编号', `hiredate` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇佣时间', `sal` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '工资月薪', `comm` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '奖金', `deptno` int(2) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门编号' ); DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salgrade`; CREATE TABLE `salgrade` ( `grade` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '等级', `losal` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '此等级最低工资', `hisal` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '此等级最高工资' ); insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc) values (10, 'ACCOUNTING', 'NEW YORK'); insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc) values (20, 'RESEARCH', 'DALLAS'); insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc) values (30, 'SALES', 'CHICAGO'); insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc) values (40, 'OPERATIONS', 'BOSTON'); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7369, 'SMITH', 'CLERK', 7902, '1980-12-17', 800, null, 20); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7499, 'ALLEN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-02-20', 1600, 300, 30); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7521, 'WARD', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-02-22', 1250, 500, 30); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7566, 'JONES', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-04-02', 2975, null, 20); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7654, 'MARTIN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-09-28', 1250, 1400, 30); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7698, 'BLAKE', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-05-01', 2850, null, 30); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7782, 'CLARK', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-06-09', 2450, null, 10); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7788, 'SCOTT', 'ANALYST', 7566, '1987-04-19', 3000, null, 20); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7839, 'KING', 'PRESIDENT', null, '1981-11-17', 5000, null, 10); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7844, 'TURNER', 'SALESMAN', 7698,'1981-09-08', 1500, 0, 30); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7876, 'ADAMS', 'CLERK', 7788, '1987-05-23', 1100, null, 20); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7900, 'JAMES', 'CLERK', 7698, '1981-12-03', 950, null, 30); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7902, 'FORD', 'ANALYST', 7566, '1981-12-03', 3000, null, 20); insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno) values (7934, 'MILLER', 'CLERK', 7782, '1982-01-23', 1300, null, 10); insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (1, 700, 1200); insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (2, 1201, 1400); insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (3, 1401, 2000); insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (4, 2001, 3000); insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (5, 3001, 9999);
表的基础查询
先对以上数据库进行一些基本查询,如下:
查询工资高于500或者岗位为MANAGER的雇员,同时还需要满足他们的姓名首字母为大写的J,如下:
-- 使用模糊匹配 mysql> select * from emp where (sal > 500 or job = 'MANAGER') and ename like 'J%'; -- 使用编程字符串函数进行匹配 mysql> mysql> select * from emp where (sal > 500 or job = 'MANAGER') and substring(ename, 1, 1) = 'J';
按照部门号升序而雇员的工资降序排序:
mysql> select * from emp order by deptno asc, sal desc;
使用年薪进行降序排序,如下:
mysql> select ename, sal * 12 + ifnull(comm, 0) 年薪 from emp order by 年薪 desc;
显示工资最高的员工的名字和工作岗位:
mysql> select ename, job from emp where
-> sal = (select max(sal) from emp);
显示工资高于平均工资的员工信息:
mysql> select * from emp where sal > (select avg(sal) from emp);
显示每个部门的平均工资和最高工资:
mysql> select deptno, format(max(sal), 2), format(avg(sal), 2) from emp group by deptno;
显示平均工资低于2000的部门号和他的平均工资:
mysql> select deptno, avg(sal) from emp group by deptno having avg(sal) < 2000;
显示每种岗位雇员的总数以及平均工资:
mysql> select deptno, avg(sal), count(*) from emp group by deptno;
多表查询
实际的开发场景中数据往往来自不同的表,所以需要多表查询,多表查询的核心思想:先选定来源的数据有哪些表,然后对表格进行笛卡尔积连接(从第一张表中取出一条记录,和第二个表中所有记录进行组合,接着从第一张表中取出第二条数据,以此类推不加过滤),形成一张表格,然后在这一张表格中进行查询,如下为emp和dept两个表的笛卡尔积:
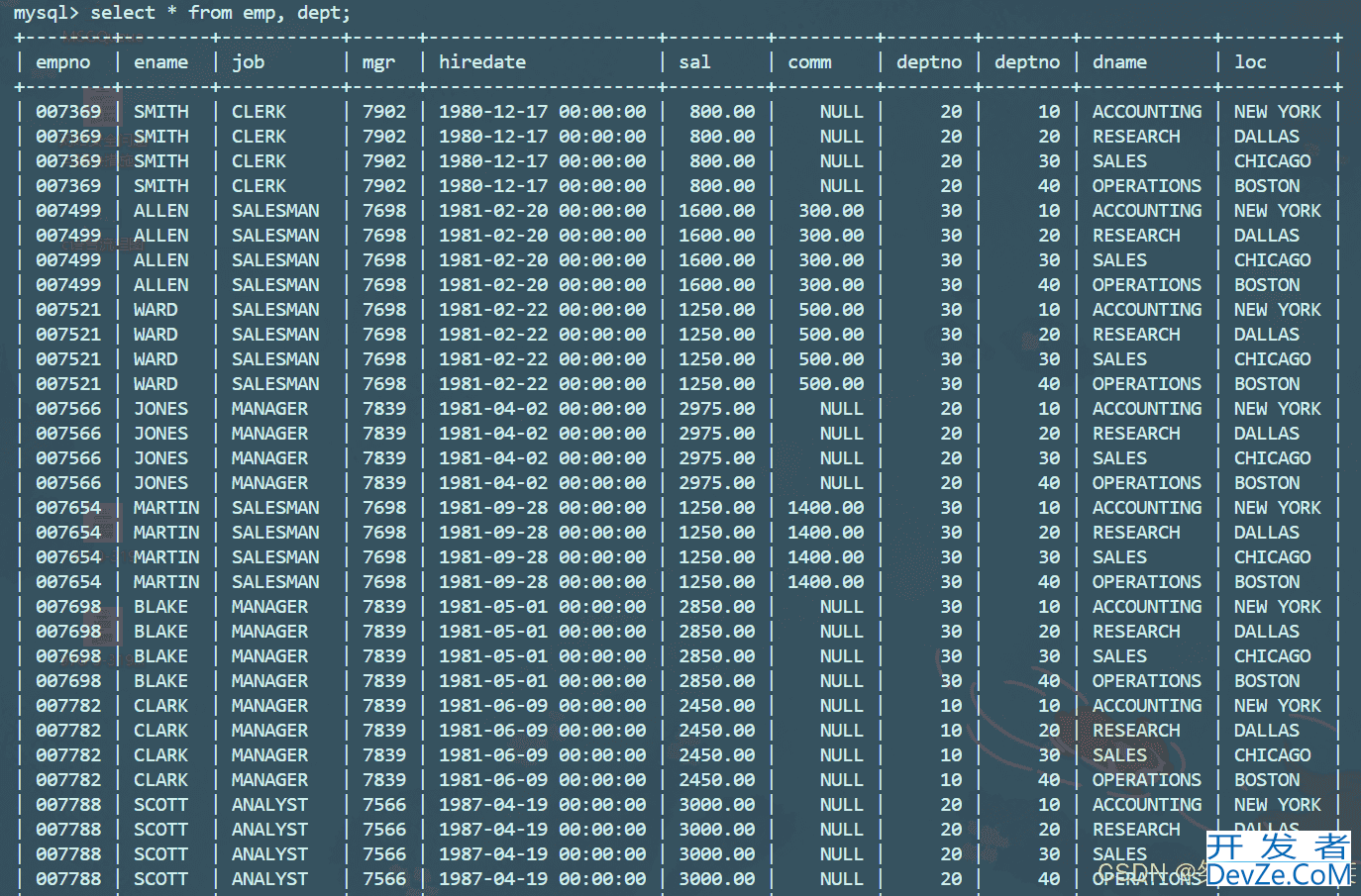
进行多表查询其实就是将多表进行笛卡尔积连接,然后进行在单表中查询,所以多表查询的本质也是单表查询,只不过通常笛卡尔积连接形成的单表是中间生成的表。对于以上生成的连接表数据太过冗余,我们通常需要找的是两个表中有关联的数据,比如emp和dept中的deptno就存在相同的字段,所以可以将以上表格给过滤,如下:
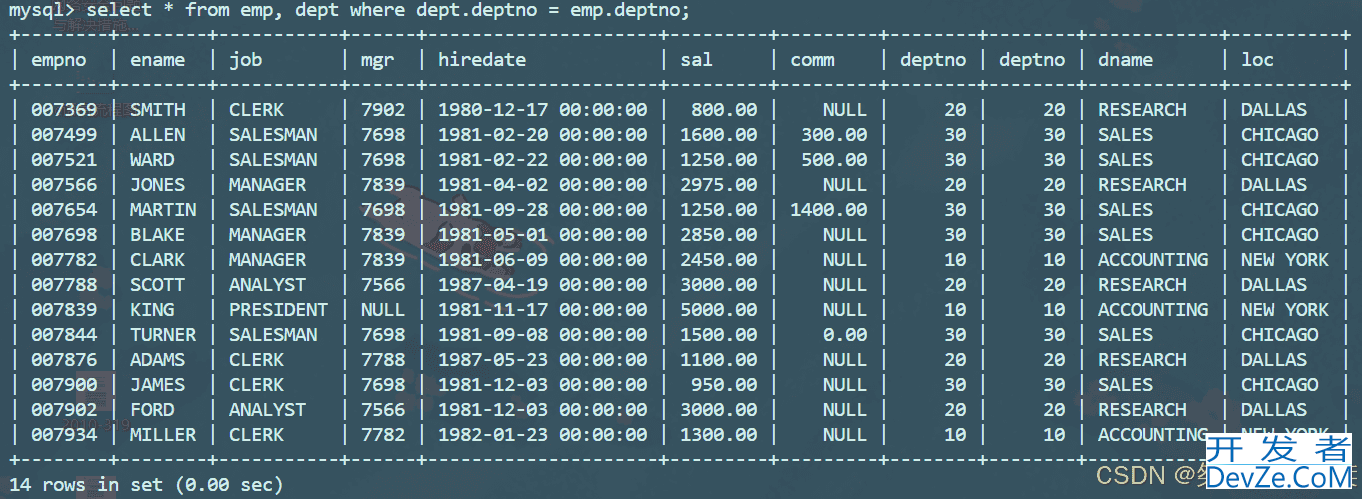
假若我们需要查询显示部门号为10的部门名,员工名和工资,如下:
-- 先将表格使用笛卡尔积连接起来,然后筛选出有效数据,接着筛选部门号为10的数据 mysql> select emp.deptno, dept.loc, emp.ename, emp.sal from emp, dept where dept.deptno = emp.deptno and dept.deptno = 10;
显示各个员工的姓名,工资,以及工资级别:
mysql> select ename, sal, grade from salgrade, emp where sal between losal and hisal;
自连接
自连接同样也是多表查询中较为特殊的一种,因为需要使用笛卡尔积连接起来的是两个相同的表。
查询员工FORD的上级领导的编号和姓名,如下:
-- 多表查询思路 select t2.ename, t2.empno from emp as t1, emp as t2 where t1.ename = 'FORD' and t2.empno = t1.mgr; -- 子查询思路 mysql> select ename, empno from emp where empno in (select mgr from emp where ename = 'FORD');
子查询
子查询值得是嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询
单行子查询
单行子查询就是返回一行记录的子查询。
查询与SMITH同一部门的员工,如下:
mysql> select * from emp where deptno = (select deptno from emp where ename = 'SMITH');
多行子查询
多行子查询就是返回多行记录的子查询。
in关键字:查询和10号部门的工作岗位相同的雇员的名字,岗位,工资,部门号,但是不包含10号自己的,如下:
mysql> select ename, job, sal, deptno from emp
-> where job in (select job from emp where deptno = 10) and deptno!=10;
all关键字:查询工资比部门30的所有员工的工资的工资搞的员工的姓名,工资和部门号,如下:
mysql> select ename, sal, deptno from emp where sal > all(select sal from emp where deptno = 30); -- 使用max聚合函数 mysql> select ename, sal, deptno from emp where sal > (select max(sal) from emp where deptno = 30);
any关键字:查询工资比部门30的任意员工的工资高(高于最低工资)的员工的姓名、工资和部门号(包含自己的部门),如下:
mysql> select ename, sal, deptno from emp where sal > any(select sal from emp where deptno = 30);
多列子查询
上文中的单列子查询和多列子查询都是返回的单列多行数据,针对的是多列,而多列子查询则是指返回多个列数据的子查询语句,如下:
查询和SMITH的部门和岗位完全相同的所有雇员,不包含SMITH本人。
mysql> select ename from emp where ename != 'SMITH' and (deptno, job) = (select deptno, job from emp where ename = 'SMITH');
from中使用子查询
通常我们在from子句的后面都是直接跟的表名,但是即使是select出来的子句也生成了一个暂时的表,我们只需要将这个暂时的表给加个别名就可以使用了,如下:
查询每个高于自己部门平均工资的员工的姓名、部门、工资、平均工资,如下:
mysql> select ename, deptno, sal, myavg from emp, (select avg(sal) as myavg, deptno as dt from emp group by deptno) as tmp where emp.deptno = tmp.dt and emp.sal > tmp.myavg;
查找每个部门工资最高的人的姓名、工资、部门、最高工资,如下:
mysql> select ename, sal, deptno, mymax from emp, (select max(sal) mymax, deptno dt from emp group by deptno) as tmp where emp.deptno = tmp.dt and emp.sal = tmp.mymax;
显示每个部门的信息(部门名、编号、地址)和人员数量,如下:
-- 子查询 mysql> select dept.deptno, dept.dname, dept.loc, mycnt from dept, (select count(*) mycnt, deptno dt from emp group by deptno) as tmp where tmp.dt = dept.deptno; -- 多表 mysql> select dept.dname, dept.deptno, dept.loc, count(*) from emp, dept where emp.deptno = dept.deptno group by dept.deptno, dept.dname, dept编程客栈.loc;
合并查询
为了合并多个select的执行结果,可以使用集合操作符union,union all。
union
改操作符用于取得两个结果集的并集,当使用该操作符时,会自动去掉结果集中的重复行。
查询工资大于2500或者职位为MANAGER的人找出来。
mysql> select * from emp where sal > 2500 union select * from emp where job = 'MANAGER';
union all
该操作用于取得两个结果的并集,当使用该操作时,不会去掉结果中的重复行,如下:
将工资大于2500或职位是MANAGER的人找出来,如下:
mysql> select * from emp where sal > 2500 union all select * from emp where job = 'MANAGER';
到此这篇关于MySql中表的复合查询实现示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MySql表复合查询内容请搜索编程客栈(www.devze.com)以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以javascript后多多支持编程客栈(wjsww.cppcns.com)!




 加载中,请稍侯......
加载中,请稍侯......
精彩评论